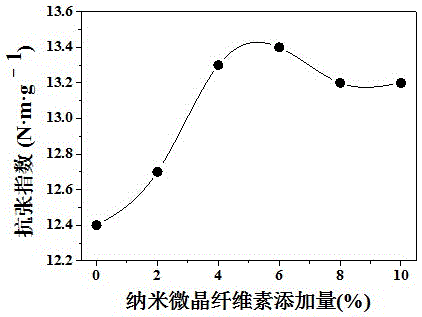
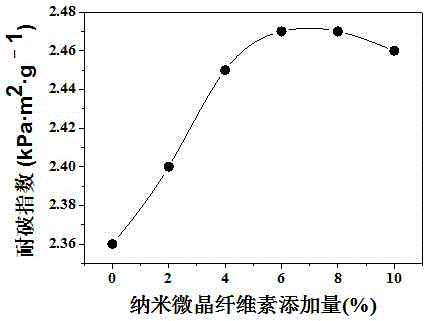
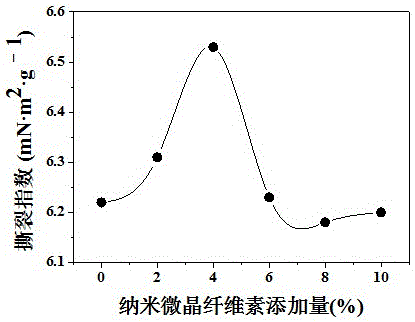
Method for improving strength of wastepaper fibers based on nanometer microcrystalline cellulose
A technology of nano crystallite and waste paper fiber, which is applied in textiles and papermaking, adding inorganic compounds, etc., to achieve the effects of high-efficiency application, easy operation and control, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] A method for improving the strength of waste paper fibers based on nanocrystalline cellulose. Take 2.0g (calculated on an absolute dry basis) of fiber slurry, add 1000ml of water, and disintegrate it in a GBJ-A fiber standard disintegrator for 1min. Add 0.3g of calcium carbonate and 1.0ml of cationic polyacrylamide solution (the amount of nano-microcrystalline cellulose added is 0), stir for 1min each time a component is added, and finally decompose in a GBJ-A fiber standard dissociation device 1min, spare. Inject 6L of water into the forming part of the ZQJ1-B-II paper extractor, pour the decomposed slurry into the former, continue to add water until the water volume is 8L, stir it up and down for 5 times with a special stirrer, and open the water release valve to release the water , so that the fibers are formed on the copper mesh. The formed wet paper was transferred between two dry cloths, a certain amount of water was removed by a pressing process, and then vacuum...
Embodiment 2
[0025] A method for improving the strength of waste paper fibers based on nanocrystalline cellulose. Take 2.0g (calculated on an absolute dry basis) of fiber slurry, add 1000ml of water, and disintegrate it in a GBJ-A fiber standard disintegrator for 1min. Add 0.3g of calcium carbonate, 1.0ml of cationic polyacrylamide solution and 1.1ml of nano-microcrystalline cellulose suspension (the amount of nano-microcrystalline cellulose is 2% of the mass of cationic polyacrylamide) Stir for 1 min, and finally disintegrate in a GBJ-A fiber standard dissociator for 1 min, and set aside. Inject 6L of water into the forming part of the ZQJ1-B-II paper extractor, pour the decomposed slurry into the former, continue to add water until the water volume is 8L, stir it up and down for 5 times with a special stirrer, and open the water release valve to release the water , so that the fibers are formed on the copper mesh. The formed wet paper was transferred between two dry cloths, a certain am...
Embodiment 3
[0027] A method for improving the strength of waste paper fibers based on nanocrystalline cellulose. Take 2.0g (calculated on an absolute dry basis) of fiber slurry, add 1000ml of water, and disintegrate it in a GBJ-A fiber standard disintegrator for 1min. Add 0.3g of calcium carbonate, 1.0ml of cationic polyacrylamide solution and 2.2ml of nano-microcrystalline cellulose suspension (the amount of nano-microcrystalline cellulose is 4% of the mass of cationic polyacrylamide) Stir for 1 min, and finally disintegrate in a GBJ-A fiber standard dissociator for 1 min, and set aside. Inject 6L of water into the forming part of the ZQJ1-B-II paper extractor, pour the decomposed slurry into the former, continue to add water until the water volume is 8L, stir it up and down for 5 times with a special stirrer, and open the water release valve to release the water , so that the fibers are formed on the copper mesh. The formed wet paper was transferred between two dry cloths, a certain am...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com