Method for screening rice plant subjected to targeted gene editing
A technology targeting genes and plants, which is applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of false positives, low sensitivity, lack of single plant identification methods, etc., achieve high accuracy, simple and fast operation, and improve the efficiency of plant screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
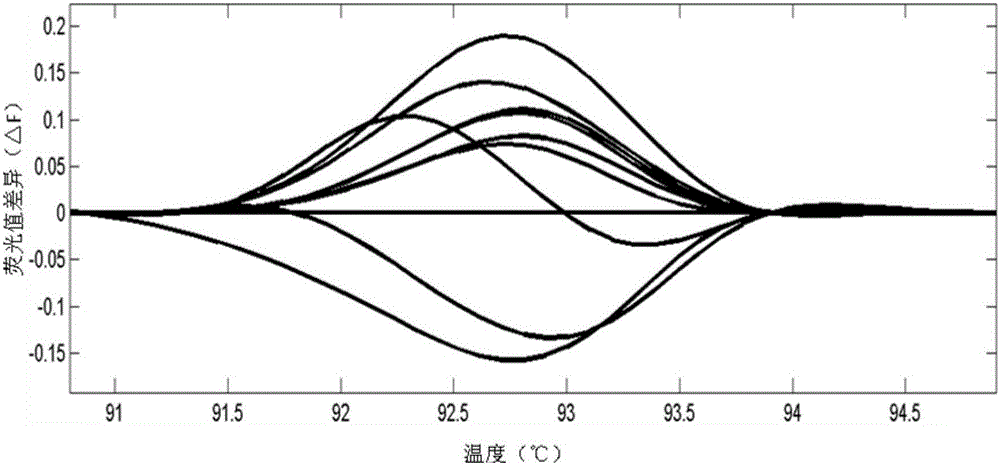
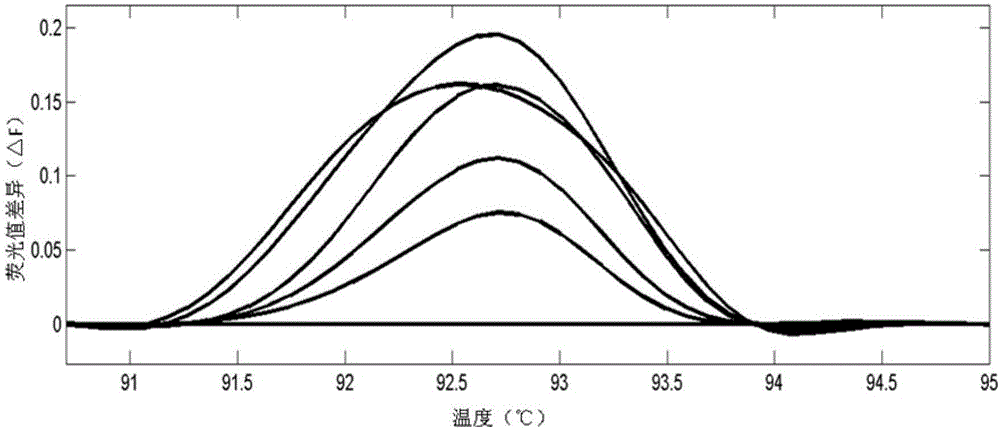
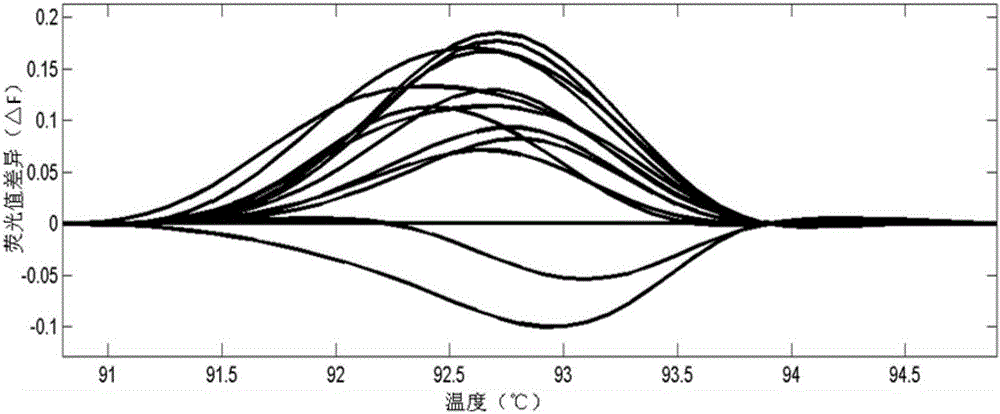
[0080] The population of CRISPR targeted editing of the rice LOC_Os03g55240 gene is the test plants, and the unedited rice plants are the control plants. The steps of detecting and screening the plants to be tested are as follows:
[0081] 1. Extraction of rice genomic DNA
[0082](1) Shred the rice leaves and put them in a 2.0mL centrifuge tube, put a steel ball at the same time, and grind them with a tissue mill;
[0083] (2) Add 800 μL CTAB extraction buffer (Tris-HCl, 100 mM, pH8.0; EDTA, 20 mM, pH8.0; NaCl, 500 mM; CTAB, 2%), 65 ° C water bath for 40 min, shake 3-4 times during the period;
[0084] (3) Add an equal volume of chloroform-isoamyl alcohol mixture (the volume ratio of chloroform to isoamyl alcohol is 24:1), mix upside down, and centrifuge at 10000r / min for 10min;
[0085] (4) Transfer the supernatant to a new 1.5mL centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of isopropanol pre-cooled at -20°C, mix gently by inversion, settling at -20°C for 30min, and centrifuge at ...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Adopt the method substantially identical with embodiment 1, detect and screen the plant to be tested, and its difference is only that the PCR amplification step is different, specifically as follows:
[0103] The PCR primer pair adopted in this embodiment is as follows:
[0104] Upstream primer B2F: 5'-TCACCGAGCACGACGTGACCTT-3'; (SEQ ID NO: 6)
[0105] Downstream primer B2R: 5'-CACGCTGAGGGAGACCTCGAACA-3'; (SEQ ID NO: 7)
[0106] Synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd.
[0107] The reaction system for PCR amplification is as follows: rTaq, 0.2 μL; 2×GCbuffer, 5 μL; 2.5mixdNTP 1.6 μL; 10 μM upstream primer B2F, 0.2 μL; 10 μM downstream primer B2R, 0.2 μL; 10×EvaGreen (fluorescent dye), 1 μL; 50ng / μL DNA, 1 μL; sterile water 1.3 μL; mineral oil 10-20 μL.
[0108] The PCR reaction program was: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 58°C for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 30 s, a total of 40 cycles; extension at 72°C f...
Embodiment 3
[0151] The above-mentioned CRISPR targeted edited population of rice large spot gene LOC_Os12g16720 was the test plants, and the unedited rice plants were the control plants. The steps of detecting and screening the plants to be tested are as follows:
[0152] 1. Extraction of rice genomic DNA
[0153] (1) Shred the rice leaves and put them in a 2.0mL centrifuge tube, put a steel ball at the same time, and grind them with a tissue mill;
[0154] (2) Add 800 μL CTAB extraction buffer (Tris-HCl, 100 mM, pH8.0; EDTA, 20 mM, pH8.0; NaCl, 500 mM; CTAB, 2%), 65 ° C water bath for 40 min, shake 3-4 times during the period;
[0155] (3) Add an equal volume of chloroform-isoamyl alcohol mixture (the volume ratio of chloroform to isoamyl alcohol is 24:1), mix upside down, and centrifuge at 10000r / min for 10min;
[0156] (4) Transfer the supernatant to a new 1.5mL centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of isopropanol pre-cooled at -20°C, mix gently by inversion, settling at -20°C for 30m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com