Compound High Voltage Semiconductor Devices
A semiconductor and device technology, applied in the field of compound high-voltage semiconductor devices, can solve the problems of increased electric field, lower device reliability, and increased manufacturing costs, and achieve the effects of increasing junction depth, improving reliability, and reducing parasitic resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
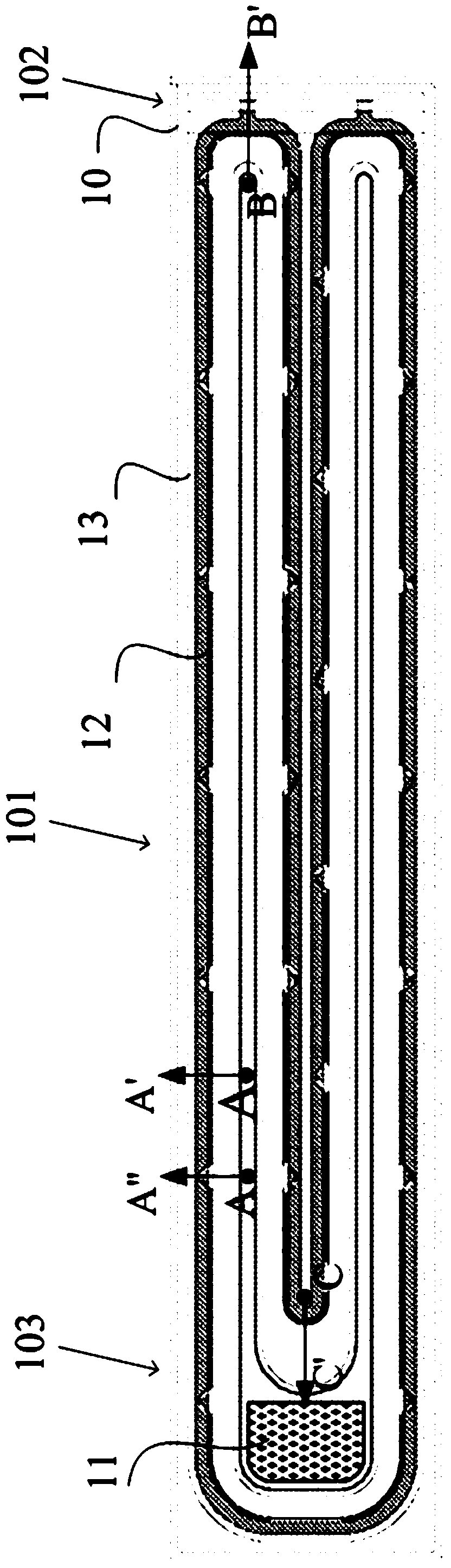
[0070] refer to figure 1 , figure 1 The layout structure of the composite high-voltage semiconductor device is shown, including a straight edge portion 101, a chamfered drain fingertip portion 102, and a chamfered source fingertip portion 103. The chamfered drain fingertip portion 102 and the source fingertip chamfered portion 103 are respectively Connect with straight side part 101. Wherein, the straight edge portion 101 is arranged along a straight line; the chamfered portion 102 of the drain fingertip and the chamfered portion 103 of the source fingertip are arranged in a curved manner, for example, the two may have appropriate chamfered shapes. Wherein, the straight side part 101 includes a plurality of straight side conductive parts and a plurality of straight side connecting parts spaced apart from each other, the area where the section line AA' is located is one of the straight side conductive parts, and the area where the section line AA" is located is A straight-edg...
no. 2 example
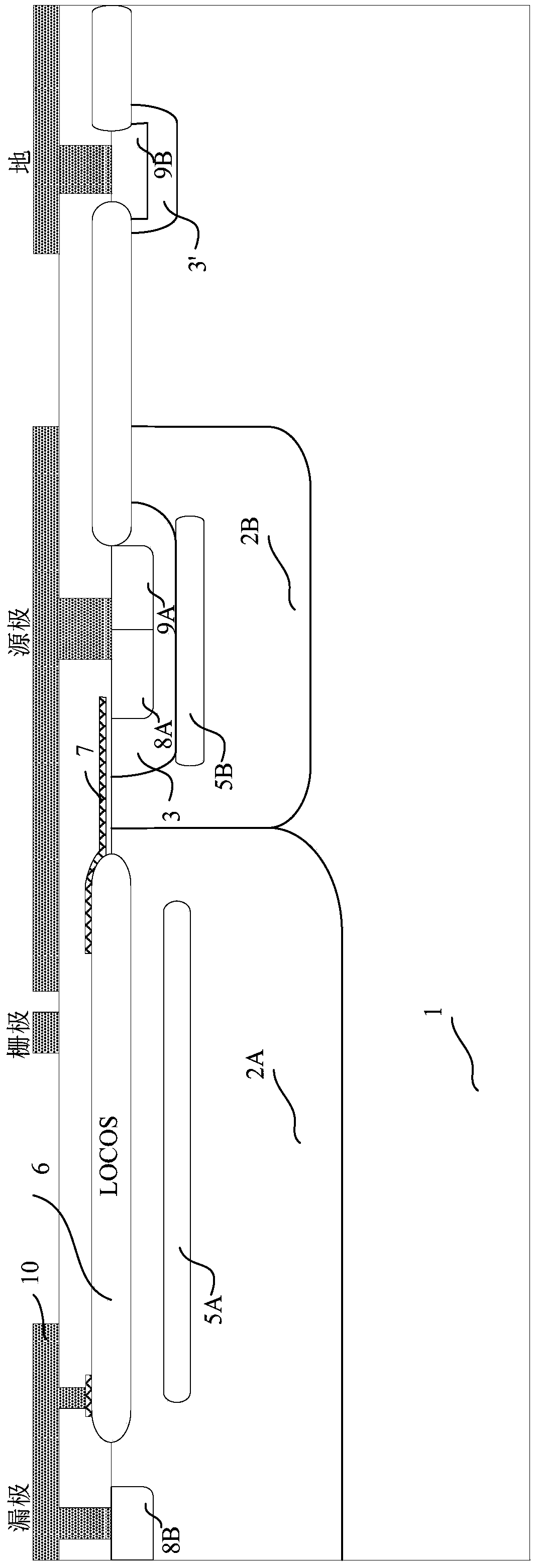
[0094] refer to Figure 7 , Figure 7 shows the cross-sectional structure of the straight-side conductive part of the compound high-voltage semiconductor device of the second embodiment, namely figure 1 The cross-sectional structure of the layout shown along the AA' direction, its structure is the same as figure 2 The structures shown are basically the same, the only difference is the doping type and figure 2 On the contrary, a P-type LDMOS structure is thus formed.
[0095] Correspondingly, the structure of the straight side connecting part is also the same as Figure 4 The same as shown, only the doping type of each doped region is reversed. For the chamfered portion of the source finger tip and the chamfered portion of the drain finger tip, the doping type of each doped region can be the same as that of the first embodiment (see Figure 5 and Figure 6 ) are the same, or vice versa.
no. 3 example
[0097] refer to Figure 8 , Figure 8 shows the cross-sectional structure of the straight-side conductive part of the composite high-voltage semiconductor device of the third embodiment, namely figure 1 The cross-sectional structure of the layout shown along the AA' direction, its structure is the same as figure 2 The structures shown are basically the same, the only difference is the doping type of the drain ohmic contact region 8B and figure 2 The illustrated embodiment is the opposite, that is, P-type doping, and the doping types of other doped regions are the same as figure 2 The illustrated embodiment is the same, resulting in a LIGBT device.
[0098] Correspondingly, the structure of the straight side connecting part is also the same as Figure 4 The same as shown, only the doping type of the drain ohmic contact region 8B is reversed. For the chamfered portion of the source finger tip and the chamfered portion of the drain finger tip, the doping type of each dope...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com