Method for Determination of Molecular Weight Distribution Curve of Hydrophobically Associating Polymers
A technology of molecular weight distribution and hydrophobic association, which is applied in the field of determination of molecular weight distribution curve of hydrophobic association polymers, can solve the problems that molecular weight distribution is not involved, and the molecular weight distribution of hydrophobic association polymers cannot be measured.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1: the selection of solvent
[0047] (1) Intrinsic viscosity test
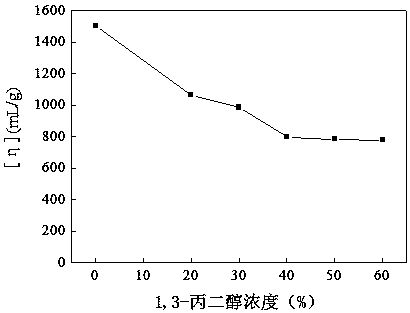
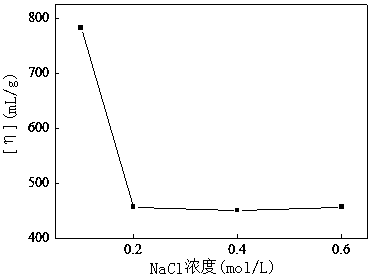
[0048] Choose 1,3 propylene glycol and NaCl mixed solvent, such as figure 1 As shown, when the NaCl concentration is 0.1mol / L, with the increase of the volume fraction of 1,3-propanediol, the intrinsic viscosity of the 1000mg / L polymer solution (HAWSP-3) first decreases and then tends to be stable. When the volume concentration of propylene glycol is 40%, the intrinsic viscosity is stable, and the association of the polymer solution has been destroyed at this time. figure 2 As shown, when the concentration of 1,3-propanediol is 50%, when the concentration of NaCl is 0.2mol / L, the intrinsic viscosity is stable, and when there is no association in HAWSP-3 solution, a small amount of salt can make the extended The molecular chain shrinks completely, eliminating the polyelectrolyte effect. Therefore, when the volume fraction of 1,3-propylene glycol in the mixed solvent is 50% and the concentr...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2: Determination of the cumulative percentage content of each fraction of hydrophobically associated polymer
[0057] Specific steps are as follows:
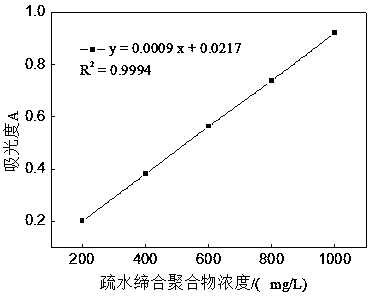
[0058] 1) The standard curve of hydrophobic association polymer absorbance-concentration: the preparation concentration is respectively the hydrophobic association polymer (HAWSP-3) solution of 200mg / L, 400mg / L, 600mg / L, 800mg / L, 1000mg / L, Among them, the volume fraction of 1,3-propanediol is 50%, and the concentration of NaCl is 0.2mol / L. Measure absorbance with UV-2601 type spectrophotometer when wavelength 220nm (1cm cuvette), obtain the standard curve equation A=0.0009c+0.0217 of hydrophobic association polymer concentration-absorbance, see image 3 .
[0059] 2) Prepare a hydrophobic association polymer target solution with a concentration of 1000 mg / L, in which the volume fraction of 1,3-propanediol is 50%, and the concentration of NaCl is 0.2 mol / L, stir with a magnetic stirrer for 4 hours, and after s...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3: Molecular Weight Determination of Fractions of Hydrophobically Associating Polymers
[0070] Calibrate the Mark-Houwink equation of hydrophobic association polymers: select the standard samples of hydrophobic association polymers (HAWSP-1, HAWSP-2), measure their molecular weight in the mixed solvent by static light scattering, and then measure the mixture of these two polymers. Intrinsic viscosity value in solvent, the test results are shown in Table 4:
[0071] Table 4: Molecular Characteristic Parameters of Standard Samples
[0072] sample
Molecular weight g / mol
Intrinsic viscosity [η] / (mL·g -1 )
HAWSP-1
3.49×10 6
1243
HAWSP-2
2.60×10 6
1046
[0073] Calibrate the Mark-Houwink equation [η]=KM of the hydrophobic association polymer under this solvent condition α For [η] = 0.182M 0.586 .
[0074] Determination of the intrinsic viscosity of each fraction of the hydrophobic association polymer (HAWSP-3), ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com