An electro-hydraulic valve-controlled displacement module and its application method
An electro-hydraulic valve, displacement technology, applied in the hydraulic field, can solve problems such as low precision, complex structure, difficult maintenance, etc., and achieve the effect of meeting highly accurate work requirements, accurate flow adjustment, and low change accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
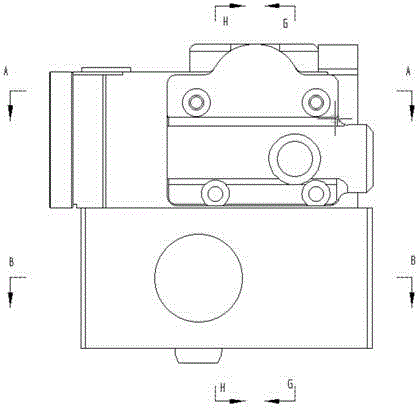
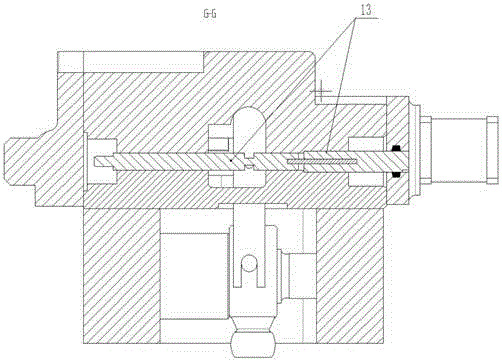
[0033] Such as Figure 2 to Figure 10b As shown, an electro-hydraulic valve-controlled displacement module includes a housing 4. End caps I5 and II6 are installed on both sides of the housing 4 respectively. The housing 4 is assembled into a sealed structure and installed on one side of the housing 4. A stepping motor 1, the stepping motor 1 is a Haydn 3500 series linear stepping motor, and a transmission rod 17, a feedback connecting rod 11, a three-position three-way valve, a linear variable differential transformer 13, a differential The dynamic cylinder 10 and the differential cylinder liner 9. In this embodiment, the linear variable differential transformer adopts the 0500MHR-018 sensor of Antai Electronics, and the bottom of the shell 4 is provided with a base 8 connected with the shell. The cylinder and the differential cylinder liner 9 are placed in the base 8; the output shaft of the stepping motor 1 penetrates into the housing 4 and is threadedly connected with one e...
Embodiment 2
[0041] An electro-hydraulic valve-controlled displacement module, the structure of which is as described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that the output shaft of the stepper motor 1 is connected to one end of the transmission rod 17 through a coupling.
Embodiment 3
[0043] A method for using an electro-hydraulic valve-controlled displacement module, comprising the following steps,
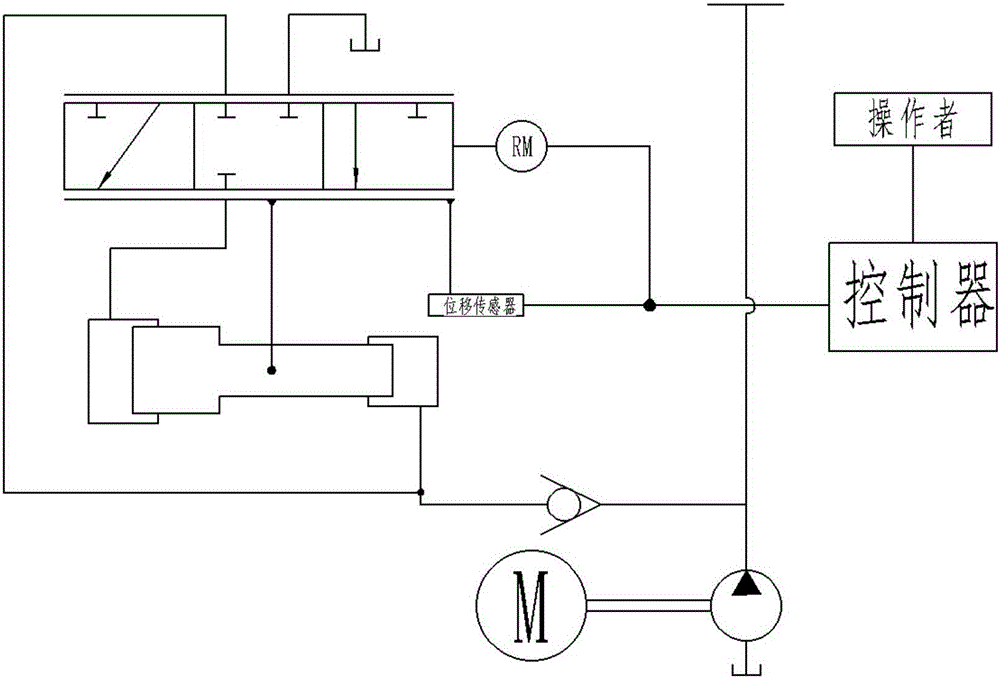
[0044] When the operator wants to change the working status, he starts the stepper motor 1, and the output shaft of the stepper motor 1 drives the transmission rod 17 to move. The rotation of the transmission rod 17 is limited, so that the transmission rod 17 can smoothly and accurately transmit the displacement of the stepper motor 1, and the movement of the stepper motor 1 leads to the movement of the feedback link 11 through the transmission rod 17. At this time, the feedback link 11 The lower fulcrum (the cylindrical pin 12 connected with the almost cylinder liner) does not move, and the feedback connecting rod 11 uses this as the fulcrum to form a lever, and then the spool 2 of the three-position three-way valve connected to the upper end of the feedback connecting rod 11 moves to control The operation of the three-position three-way valve makes the diffe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com