Channel type thickener
A thickener and canal-type technology, applied in the sedimentation tank and other directions, can solve the problems that restrict the application of small and medium-sized mineral processing enterprises, the concentration of tailings in the mineral processing plant is not high, and the consumption of electricity and water is large. Energy saving effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
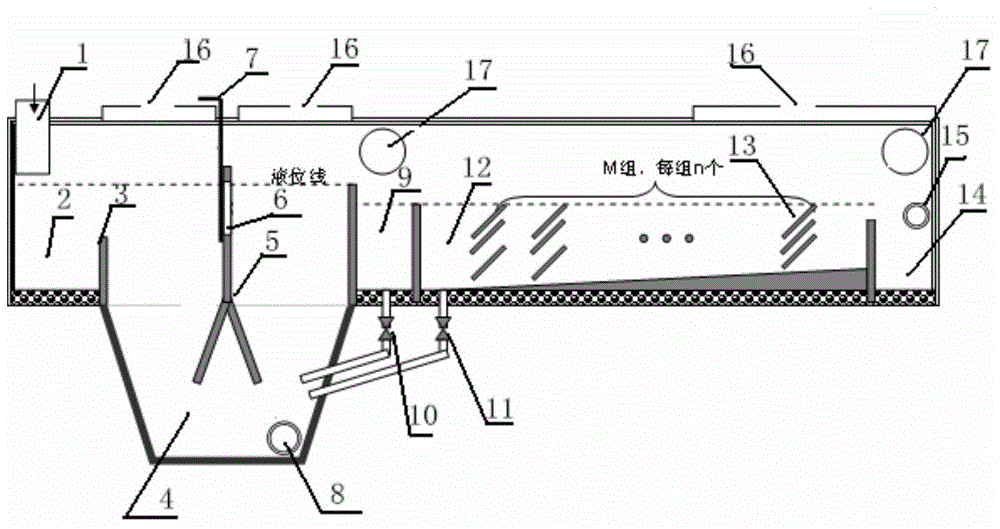
[0026] figure 1 It is an internal structure diagram of a channel thickener of the present invention, and the connection relationship and working principle between each component are as follows:
[0027] The ore pulp enters the receiving tank 2 through the feeding port 1, and crosses the partition 3, and the heavy particles in the pulp settle in the thickening tank 4. The dense pool 4 is divided into left and right parts by the gable frame 5, and the tortuosity of the water flow is increased by the gable frame 5 and the settlement height is reduced, so as to accelerate the settlement. A water-permeable window 6 is installed on the gable frame 5 to adjust the ratio of the flow rate of the upper and lower channels. The adjustment method is to adopt the gate valve 7. The settled heavy particles are discharged through the outlet 8 in the form of high-concentration slurry. The unsettled fine mud enters the buffer tank 9, where it is further settled by gravity. The settled fine s...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Dense Drain Calculation
[0031] Note: The pulp flow rate is recorded as G(m 3 / h) The settling velocity of mud in the slurry is denoted as V 1 (m / s); the horizontal running speed of the pulp is denoted as V 2 (m / s); the settlement height is recorded as H(m); the settlement time is recorded as t(s); the water level height of the dense channel is recorded as h(m), the depth channel width is recorded as b(m); the length of the dense channel is recorded as L(m); the number of each set of settling sloping plates in the channel body. Then there is the following relationship:
[0032] V 1 =0.3×10 -3 m / s (experimental data)
[0033] V 2 =G / (3600bh)
[0034] t=H / V 1 =(h / n) / V 1
[0035] L=tV 2
example
[0037] Take tailings discharge in iron concentrator as an example: Assume that the amount of tailings discharged in each iron concentrator is G=120m 3 / h, the concentration is 15%. Assuming that the canal width b=1m, the canal water level height h=1m, and the number n=10 of each set of sloping plates, it can be calculated as follows:
[0038] V 2 =G / (3600bh)=120 / (3600×1×1)=0.033333m / s
[0039] t=H / V 1 =(h / n) / V 1 =(1 / 10) / (0.33×10 -4 ) = 3030s
[0040] L=tV 2 =3030×0.033333=101m
[0041] If the HRC type high-pressure thickener is selected, the required area is at least 12m 2 , with a height of about 10m and a huge volume. If the channel-type thickener is used, although the length increases a lot, reaching 101m, but because of the linear arrangement, it will not take up too much space in the factory area, and the structure of the channel-type thickener is simple, there are basically no mechanical moving parts, and the operation and maintenance are very convenient.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com