Device and process for utilizing waste heat of waste flue gas of hot-blast stove
A waste flue gas and hot blast stove technology, which is applied in lighting and heating equipment, furnaces, waste heat treatment, etc., can solve problems such as poor sealing, easy leakage, and equipment damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
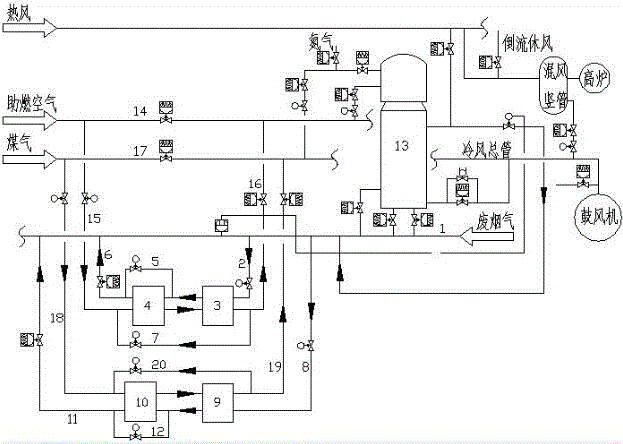
[0009] In order to enable those skilled in the art to better understand the technical solutions in the present application, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present application.
[0010] In this embodiment, the cold medium is air and gas, and the flue gas pipeline is connected with two sets of heat exchangers to preheat the air and gas at the same time. The flue gas pipe 2 in front of the heat exchanger and the pipe 8 in front of the gas heat exchanger enter the secondary air heat exchanger 3 and the secondary gas heat exchanger 9 for heat exchange, and enter the primary air heat exchanger 4 and 9 after heat exchange. The primary gas heat exchanger 10 further exchanges heat, and the waste flue gas after heat exchange passes through the rear pipe 6 of the air heat exchanger and the rear pipe 11 of the gas heat exchanger and enters the was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com