Phi-4 polypeptides and methods for their use
A PHI-4, AXMI-205 technology, applied in the field of molecular biology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0588] Example 1: Generation of the PHI-4 gene
[0589] A polynucleotide having a single codon substitution compared to the PHI-4 polypeptide of SEQ ID NO: 1 was generated. As described in the Examples below, the corresponding PHI-4 polypeptides were expressed, purified and assayed for WCRW insecticidal activity to evaluate the corresponding activity diversity. A reverse mutagenesis primer and a complementary forward mutagenesis primer were designed to produce the desired amino acid substitution at the site of interest. Typically, the mutagenic primers are between 30 and 45 bases in length and flank the site of interest by two or more bases, usually 10 to 15 bases. For saturation mutagenesis, degenerate primers covering all possible amino acid residues were used. Unless otherwise stated, mutagenesis reactions described were performed using the Agilent QuikChange TM Lightening site-directed mutagenesis kit (Agilent'sQuikChange TM LighteningSite-DirectedMutagenesiskit). A...
example 2
[0591] Example 2: Purification of MBP::PHI-4 Fusion Polypeptides
[0592] The polynucleotide encoding the PHI-4 polypeptide was used as a fusion with MBP (maltose binding protein) in an improved pMAL vector (New England BioLab) (i.e. MBP::PHI-4; SEQ ID NO:6 )Express. The pMAL vector was modified to attach a 6X histidine tag to the N-terminus of MBP. To clone the polynucleotide encoding the MBP::PHI-4 fusion protein (SEQ ID NO: 6), Sph1 and BamH1 sites were engineered into the vector at the cloning site. The polynucleotide (SEQ ID NO: 1) encoding the PHI-4 polypeptide (SEQ ID NO: 2) was amplified using a forward primer (SEQ ID NO: 32) covering the Sph1 site and a reverse primer (SEQ ID NO: 33) covering the BamH1 site. This PCR product was digested with Sph1 and BamH1 and cloned into pMAL previously cut with the same enzymes. The forward primer was designed such that the polynucleotides encoding both MBP and the PHI-4 polypeptide (SEQ ID NO: 2) within the MBP::PHI-4 gene (S...
example 3
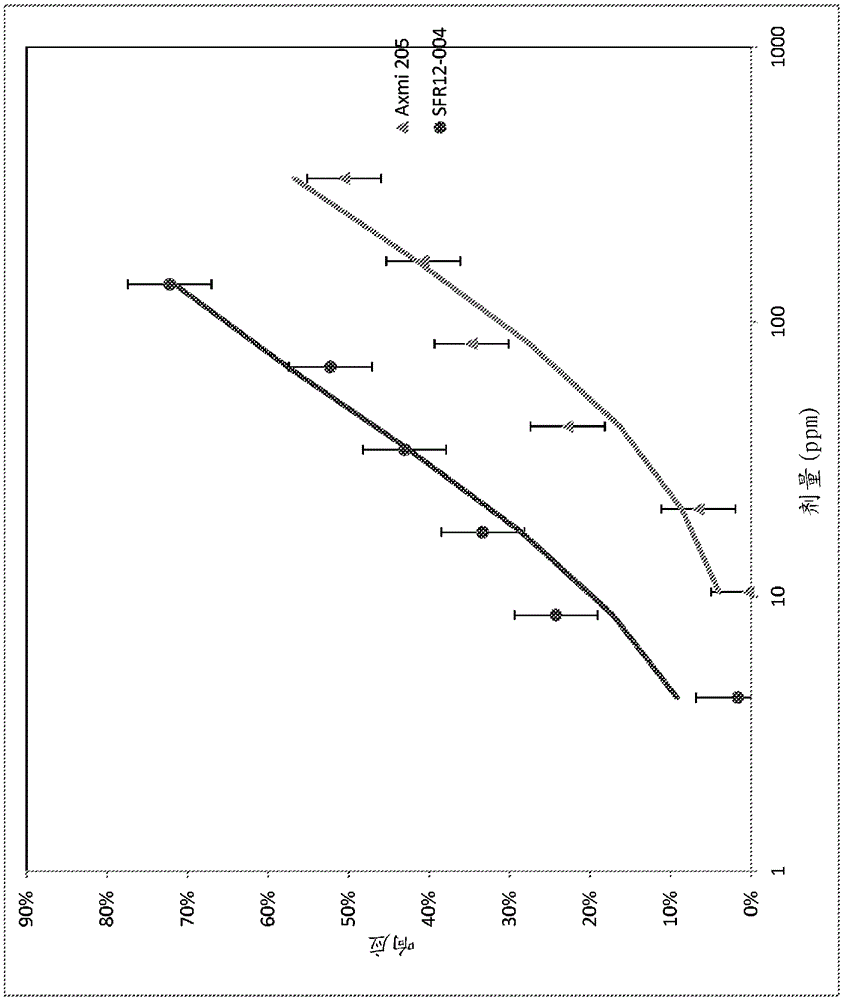
[0594] Example 3: MBP::PHI-4 polypeptide (SEQ ID NO:6) and MBP::PHI-4-SFR12-004 polypeptide (SEQ ID NO:6) NO: 31) Determination of WCRW Insecticidal Activity
[0595] Substantially as in Cong, R. et al. (Proceedings of the 4th Pacific Rim Conference on Biotechnology of Bacillus thuringiensis and its environmental impact), pp. 118-123, edited by R.J. Akhurst, C.E. Beard and P. Hughes , 2002 publication, described in Canberra, Australia (Canberra, Australia)), measure MBP::PHI-4 polypeptide (SEQIDNO:6) and MBP::PHI-4-SFR12-004 polypeptide (SEQIDNO :31; Example 8) Activity against WCRW (Western Corn Rootworm Diabroticavirgiferavirgifera). The assay was performed with artificial baits containing dilutions of these polypeptides. MBP::PHI-4-SFR12-004 polypeptide fusion (SEQ ID NO:31) and MBP::PHI-4 fusion (SEQ ID NO:6) were prepared as above, and 10 μL protein sample was mixed with 50 μL molten (40-50°C) Artificial insect bait mix prepared especially for Diabrotica sp. with lo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com