PCR (polymerase chain reaction) specificity improving method
A chain reaction and high specificity technology, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA preparation, etc., can solve the problem of little difference in binding stability, weak binding force, and inability to effectively improve the specificity of PCR reactions. sexual issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
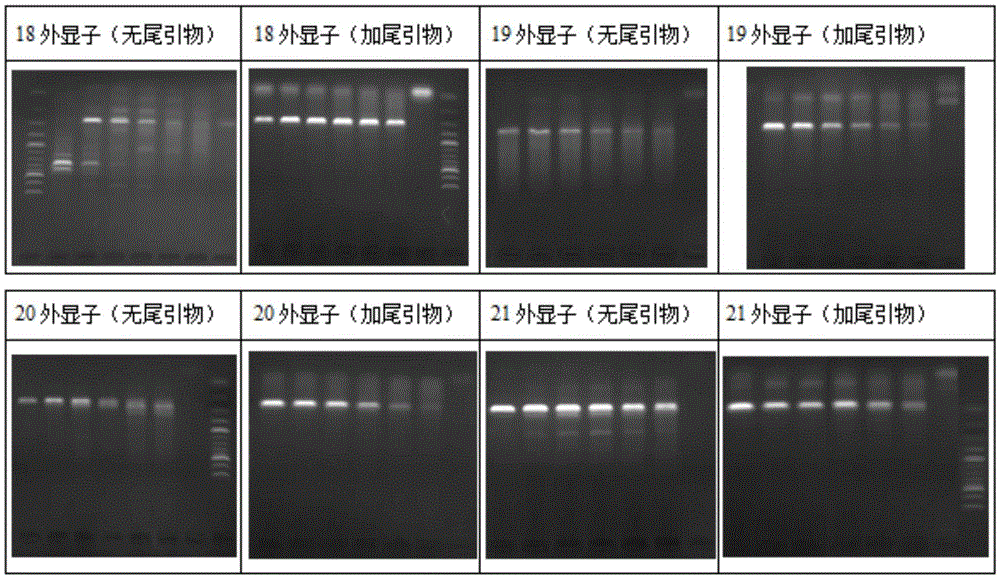
[0102] Example 1 PCR detection of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) 18, 19, 20, 21 exons——20bp tail
[0103] In this example, exons 18, 19, 20, and 21 of the EGFR gene were selected as target sequences for testing and analysis. The reaction conditions of the conventional three-step method were adopted.
[0104] 1. Design of specific primers
[0105] Design specific PCR primers for exons 18-21 of the EGFR gene, 18F / 18R (amplified fragment length 271bp), 19F / 19R (amplified fragment length 304bp), 20F / 20R (amplified fragment length 242bp), 21F / 21R (the length of the amplified fragment is 262bp), the specific primer sequence is as follows (as shown in Table 1):
[0106] 18F (shown in SEQ ID NO.1): 5'-GGCTGAGGTGACCCTT-3';
[0107] 18R (shown in SEQ ID NO.2): 5'-GAGTAAAGTAGATGATGGAAATA-3'.
[0108] 19F (shown in SEQ ID NO.3): 5'-AGCATGTGGCACCATC-3';
[0109] 19R (shown in SEQ ID NO.4): 5'-CTAGAGCTAGAAAGGGAAAG-3'.
[0110] 20F (shown in SEQ ID NO.5): 5'-CCATGCGAAGCCCACA-3'...
Embodiment 2
[0133] Example 2 PCR detection of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) 18, 19, 20, 21 exons——20bp tail
[0134] 1. Primers, tailing primers, and sample genomic DNA extraction are the same as in Example 1.
[0135] 2. Conventional three-step PCR detection
[0136] (1) PCR reaction system: 10 μL of TaqGreenmix, 1 μL of each upstream primer and downstream primer (primer concentration: 40 μmoL / L, 30 μmoL / L, 20 μmoL / L, 10 μmoL / L, 5 μmoL / L, 2.5 μmoL / L, 1.25 μmoL / L, 0.625 μmoL / L, 0.3125 μmoL / L), 6 μL of pure water, 2 μL of sample DNA, and a total volume of 20 μL.
[0137] PCR reaction conditions: 94°C for 3min; 40 cycles of 94°C for 30s, 56°C for 30s, 72°C for 45s; 72°C for 7min.
[0138] PCR product identification: PCR amplification products were identified by 2% agarose electrophoresis.
[0139] (2) The result is as follows figure 2 As shown, after the 5' end of the specific PCR detection primer was tailed, the detection specificity was significantly improved.
[0140] at...
Embodiment 3
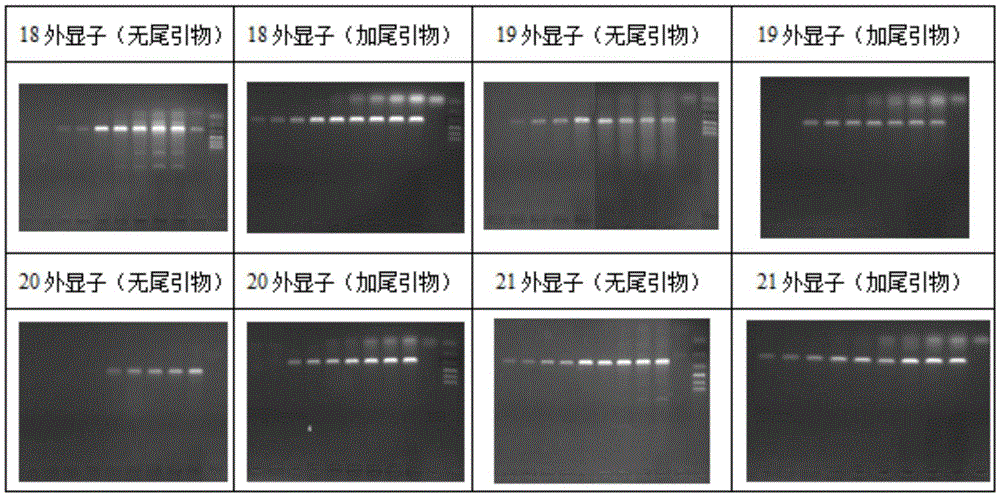
[0142] Example 3 PCR detection of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 18, 19, 20, 21——15bp tailing
[0143] 1. The specific PCR primers 18F / 18R, 19F / 19R, 20F / 20R and 21F / 21R of the 18~21 exons of the EGFR gene designed in embodiment 1, and 5' tailed specific PCR primers (tail length 20bp), respectively designed and synthesized 5' tailed specific PCR primers with a 5' tailed length of 15 bp. The specific primer sequences after tailed are as follows:
[0144] 18F-15T (shown in SEQ ID NO.17): 5'-TGTTACTCGGGATTAGGCTGAGGTGACCCTT-3';
[0145] 18R-15T (shown in SEQ ID NO.18): 5'-CACGACTGAGAGCACGAGTAAAGTAGATGATGGAAATA-3'.
[0146] 19F-15T (shown in SEQ ID NO.19): 5'-GGTCAGTCGGCATTAAGCATGTGGCACCATC-3';
[0147] 19R-15T (shown in SEQ ID NO. 20): 5'-CACGACGGTCAGCACCCTAGAGCTAGAAAGGGAAAG-3'.
[0148] 20F-15T (shown in SEQ ID NO.21): 5'-AGTCAAGCGGAATTACCATGCGAAGCCCACA-3';
[0149] 20R-15T (shown in SEQ ID NO. 22): 5'-CACCACTCTCAGCACTCCCTTCCCCTGATTACCT-3'.
[0150] 21F-15T (sho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com