Glyphosate-resistant transgenic soybean as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of genetically modified soybeans and soybeans, which is applied in the field of plant genetic engineering technology or breeding, and can solve the problems of not being able to prevent and control large areas in time, time-consuming and labor-intensive, and limiting the use of herbicides, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Embodiment 1, genetic transformation of transgenic soybean
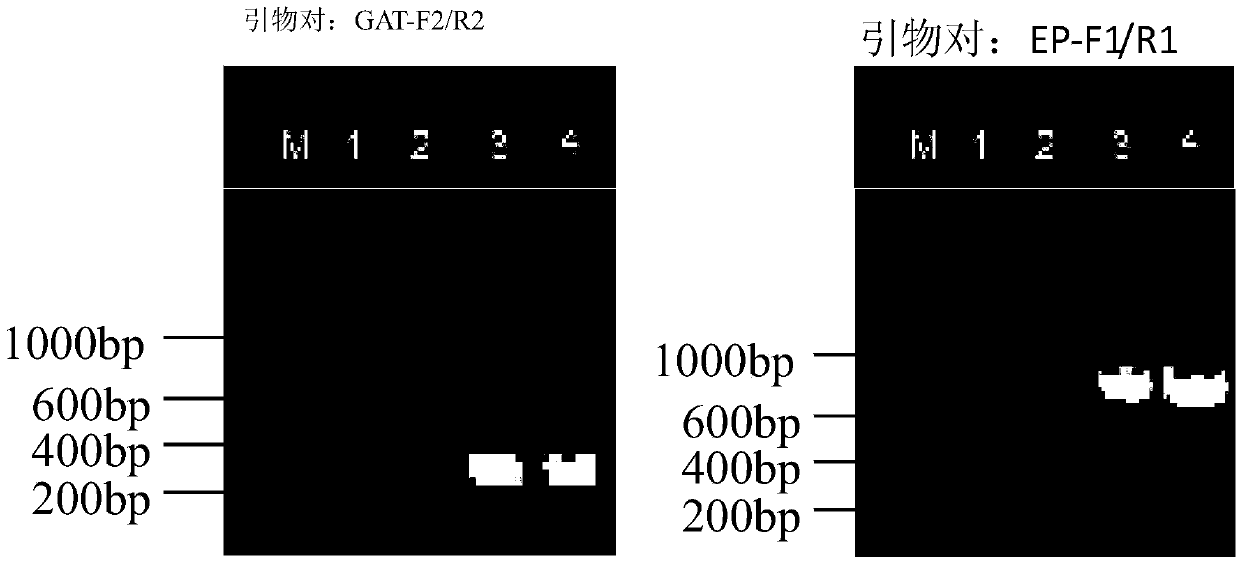
[0072] 1. Obtaining the recombinant vector
[0073] (1) According to the optimized synthetic sequence of A.thaliana-rbcS plus G2-EPSPS (G2-aroA) gene, the PCR primers were redesigned. The rbcS-G2-EPSPS(aroA) fragment (nucleotides 8204-9784 from the 5' end of Sequence 1) was added and connected to the T-A vector to obtain the plasmid prbcS-G2-EPSPS(aroA), which was digested and sequenced for verification.
[0074] (2) pBI121 (Wang Huaxin, Cao Jiashu, Xiang Xun et al. Construction of pBI121 expression vector and rapid identification of transformed plants. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2008, 34(2): 137-142; public available Obtained from the Institute of Crop Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) and pCAMBIA2300 (Gong Yuanyong, Feng Yongkun, Ni Wanchao, etc. Construction and verification of plant expression vector pCAMBIA2300-35S-GUS-CaMVterm. China Biotechnology Jo...
Embodiment 2
[0094] Embodiment 2, glyphosate resistance analysis of transgenic soybean
[0095] To the T obtained in Example 1 0 Glyphosate resistance analysis of successive generations of transgenic soybean GE-J16 found that it was more resistant to glyphosate than the non-transgenic wild-type control Jack, as follows:
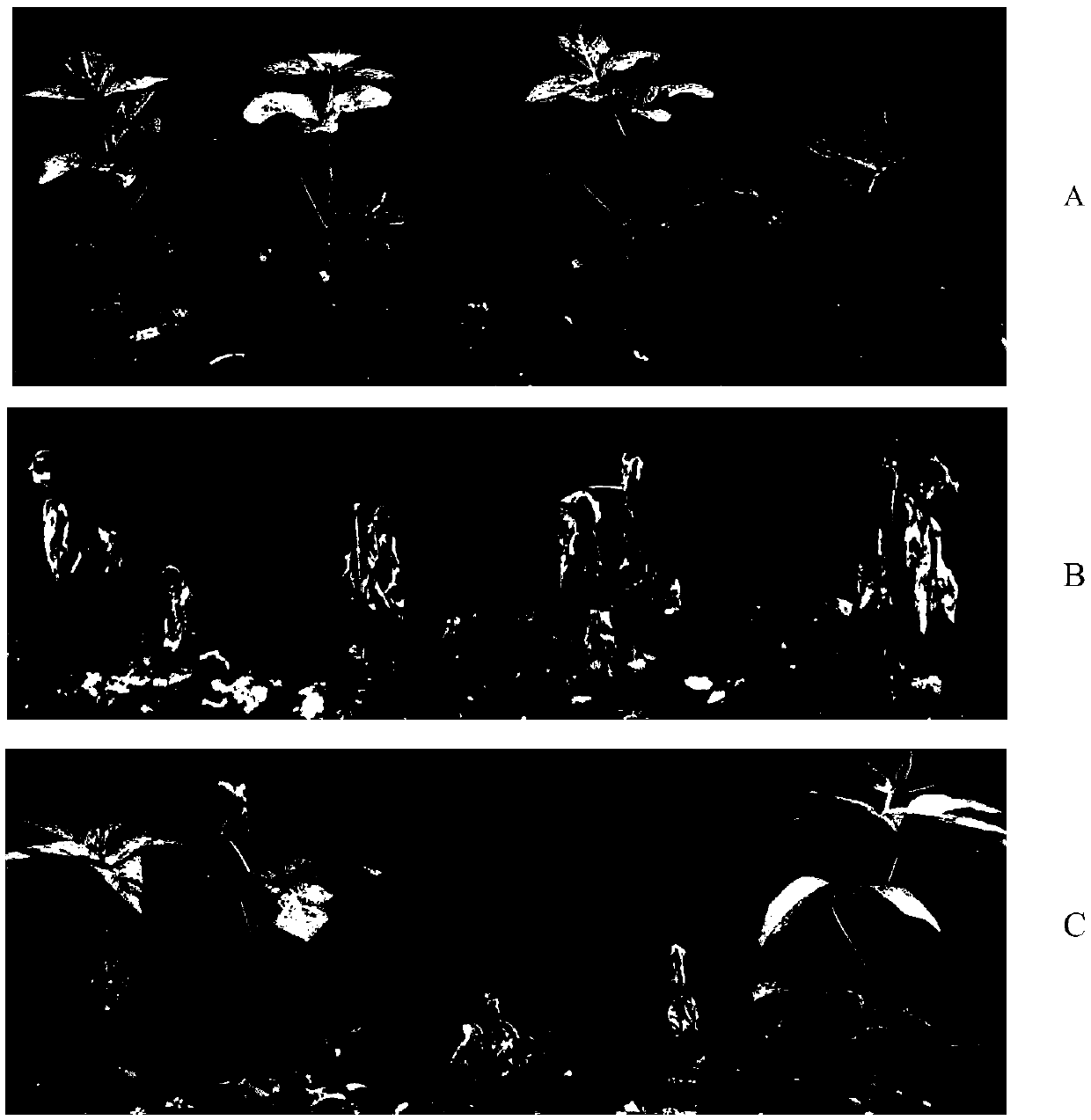
[0096] collect T 0 Genetically modified soybean GE-J16 seeds were sown to obtain T 1 The transgenic soybean GE-J16 was sprayed with 3L / ha (200ml / mu) glyphosate isopropylamine salt (Roundup) solution during the first to third compound leaf stages, and the phytotoxicity was investigated after 2 weeks.
[0097] The phenotype of non-resistant plants is dehydration and chlorosis of leaves, curling and shriveling of leaves, and necrosis of top meristem until the whole plant dies; the phenotype of resistant plants is vigorous growth, leaves do not chlorosis, curl or shrink .
[0098] T 1 The results of transgenic soybean GE-J16 are as follows: image 3 Shown, A: negative c...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Example 3. Analysis of exogenous DNA copy number and molecular integration stability in transgenic soybean
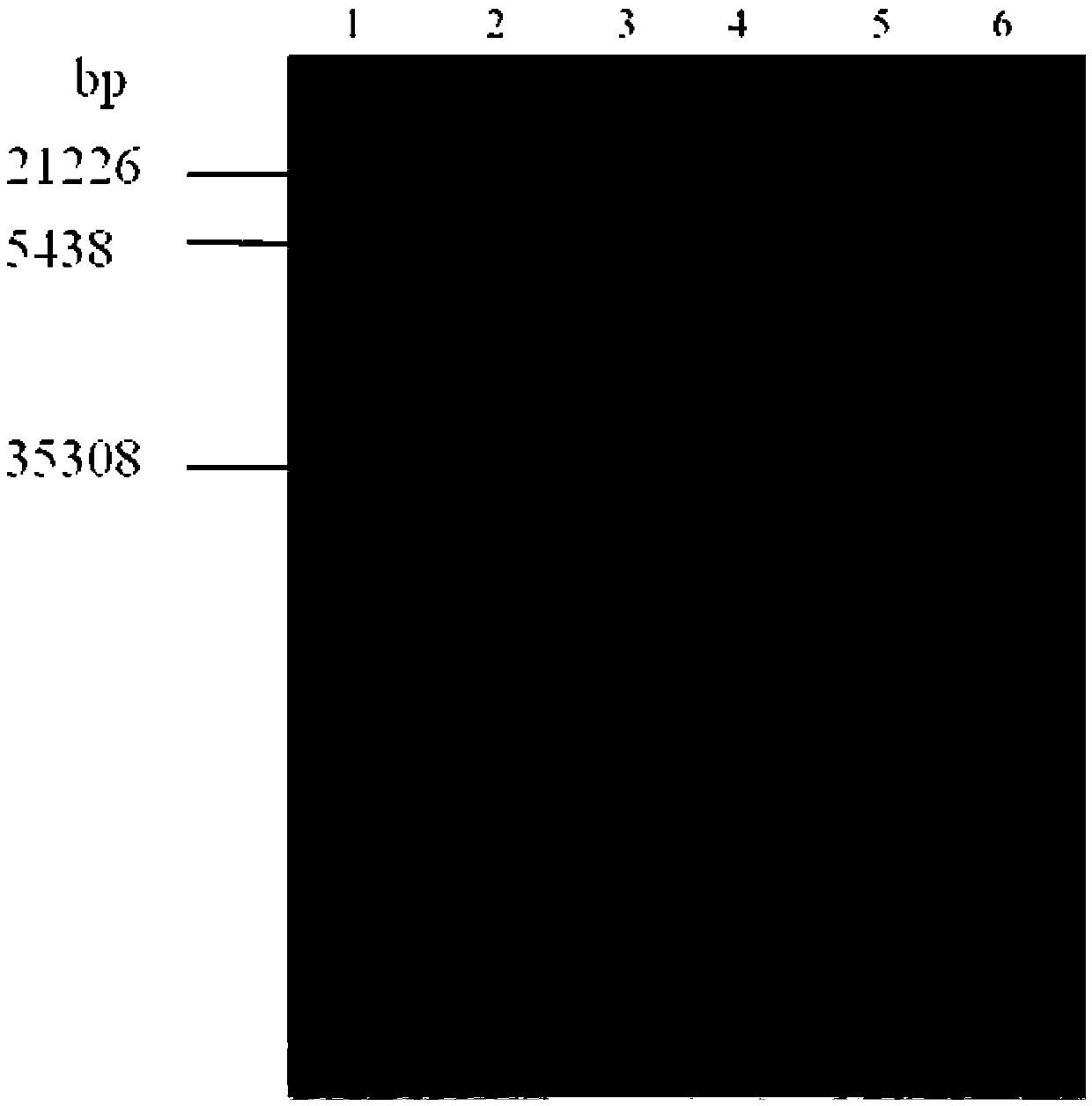
[0106] 1. Copy number of integrated exogenous T-DNA
[0107] Determination of T by Southern blotting analysis of restriction fragments extending beyond the left and right border sequences of the transformation vector used 0 Copy numbers of exogenous DNA fragments integrated in the genome of transgenic soybean GE-J16.
[0108] The probe for Southernblotting analysis is to select a 338bp carrier DNA sequence design probe (sequence 6) from the carrier T-DNA region, and prepare a high Sim-labeled probes.
[0109] Referring to the instruction manual of the digoxin hybridization kit produced by Beijing Meilaibo Medical Technology Co., Ltd., the recombinant plasmid pKT-rGE used was used as a positive control, and the genomic DNA of the non-transgenic wild-type genetically transformed recipient Jack was used as a negative control.
[0110] Extract the T obtained in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com