Powder metallurgy brake pad friction material and preparation method thereof
A technology for brake pads and friction materials, applied in the field of powder metallurgy materials, can solve the problems of high density and hardness of friction materials, various alloy components, poor stability of friction coefficient, etc. , a good match
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
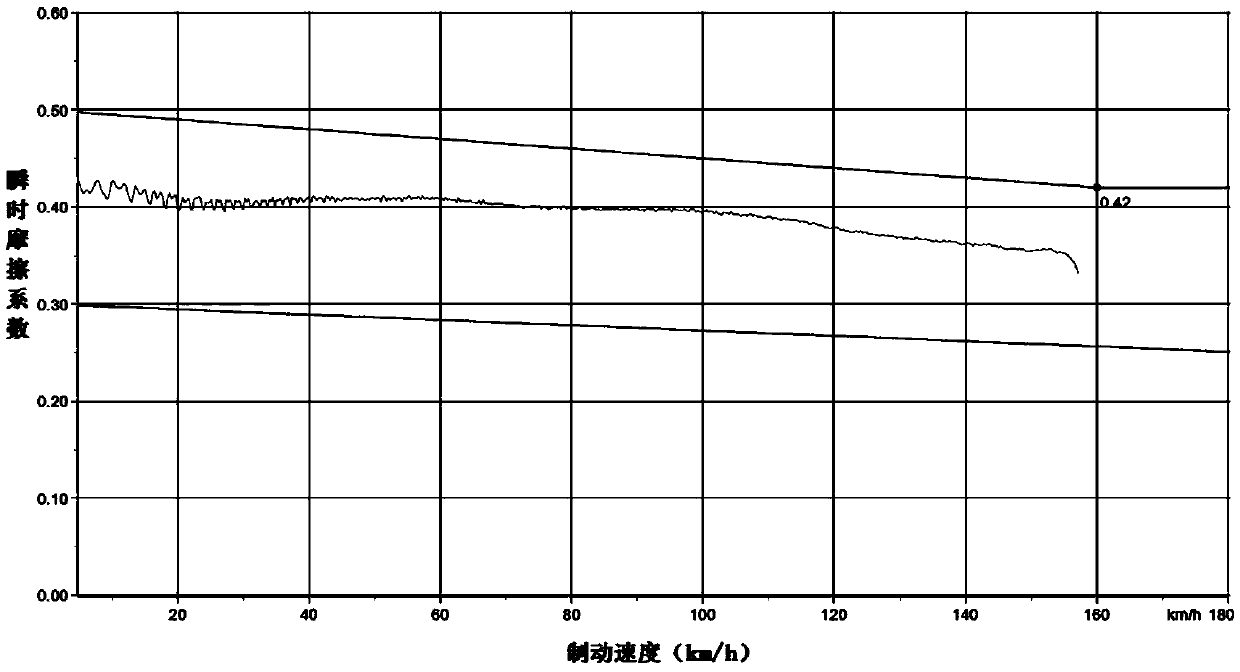
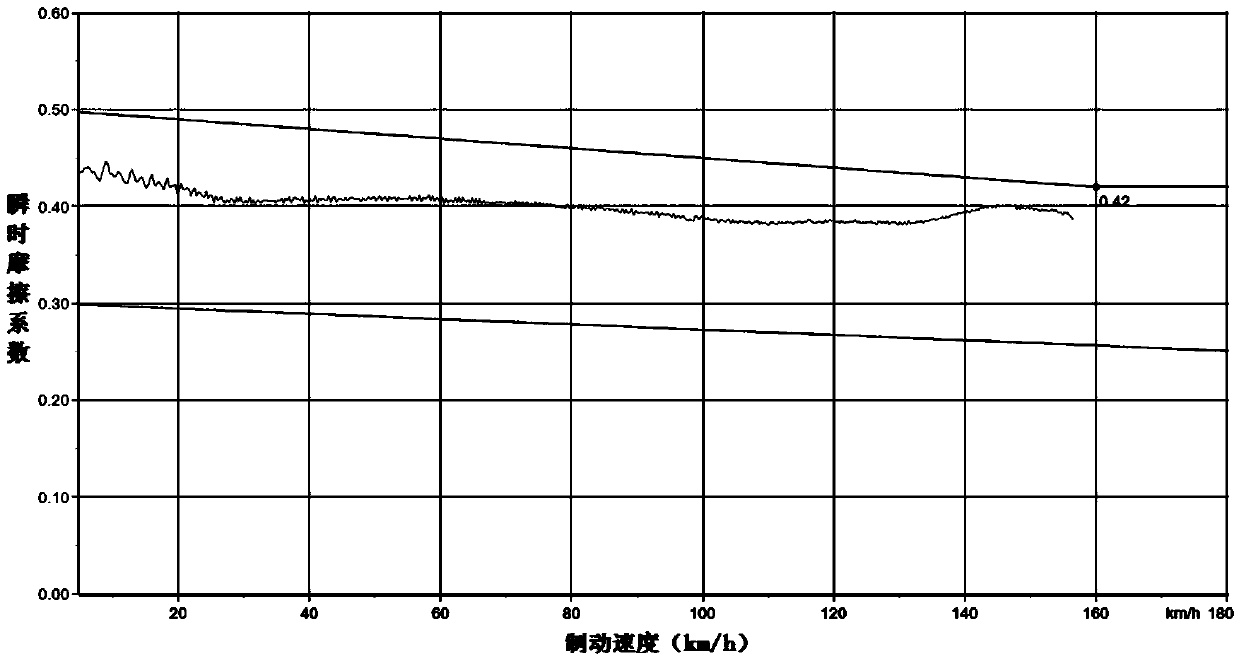
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The preparation method of the powder metallurgy brake pad friction material of this embodiment includes the following specific steps:
[0037] A. Use an electronic scale to weigh the raw materials. The composition and mass percentage of raw materials are: copper powder: 56%, ferrochrome powder: 29%, flake graphite: 10%, silicon carbide: 5%. The composition and mass percentage of ferrochrome powder are: chromium: 40%, carbon: 3%, silicon: 1.5%, and the balance is iron.
[0038] B. Fully mix the raw materials with a coulter-type high-speed mixer. In order to improve the mixing uniformity of the materials and prevent the segregation of the raw materials, 0.5% kerosene is added to the raw materials as a binder when mixing. The mixing time was 30 minutes.
[0039] C. Use a special press for powder metallurgy to press the raw materials into shape. The pressing pressure is 16 MPa.
[0040] D. Use a bell-type pressurized sintering furnace that can raise the temperature ste...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The preparation method of the powder metallurgy brake pad friction material of this embodiment includes the following specific steps:
[0044] A. Use an electronic scale to weigh the raw materials. The components and mass percentages of the raw materials are: copper powder: 47%, ferrochrome powder: 33%, flake graphite: 15%, silicon carbide: 5%. The composition and mass percentage of ferrochromium powder are: chromium: 35%, carbon: 4%, silicon: 1%, and the balance is iron.
[0045] B. Fully mix the raw materials with a coulter-type high-speed mixer. The mixing time was 35 minutes.
[0046] C. Use a special press for powder metallurgy to press the raw materials into shape. The pressing pressure is 18MPa.
[0047] D. Use a bell-type pressurized sintering furnace that can raise the temperature step by step for pressure sintering, the sintering temperature is 1000°C, and the sintering time is 11h. During sintering, in order to improve the compactness and bonding strengt...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The preparation method of the powder metallurgy brake pad friction material of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1 except that:
[0051] In step A, the components and mass percentages of the raw materials are: copper powder: 50%, ferrochrome powder: 33%, flake graphite: 11%, and silicon carbide: 6%.
[0052] In step B, binder is the alcohol that accounts for 0.8% of raw material gross mass.
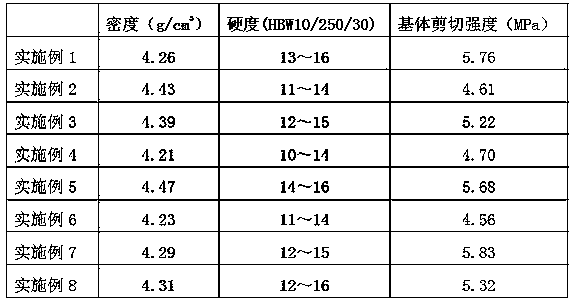
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com