System and method for reducing boiler NOx emission by tertiary air concentrated-diluted separation
A technology of thick-thin separation and thick-thin separator, which is applied in the system field of tertiary air thick-thin separation to reduce boiler NOx emissions, can solve the problems of high carbon content in fly ash, high NOx emission of boiler tertiary air, and low burnout rate, and achieve reduction Effect of NOx emission, guarantee of burnout rate, reduction of NOx emission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
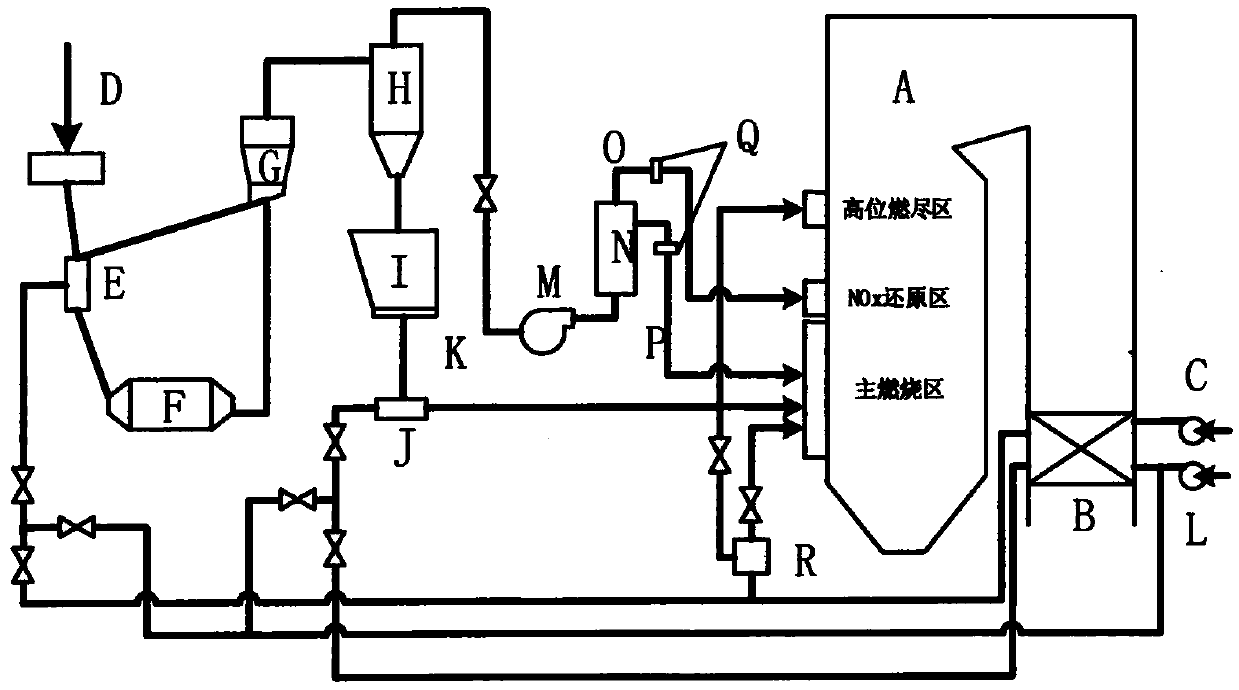
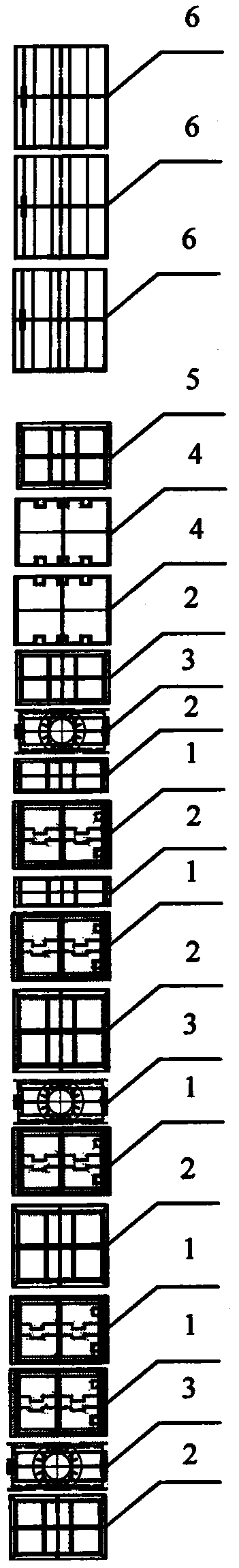
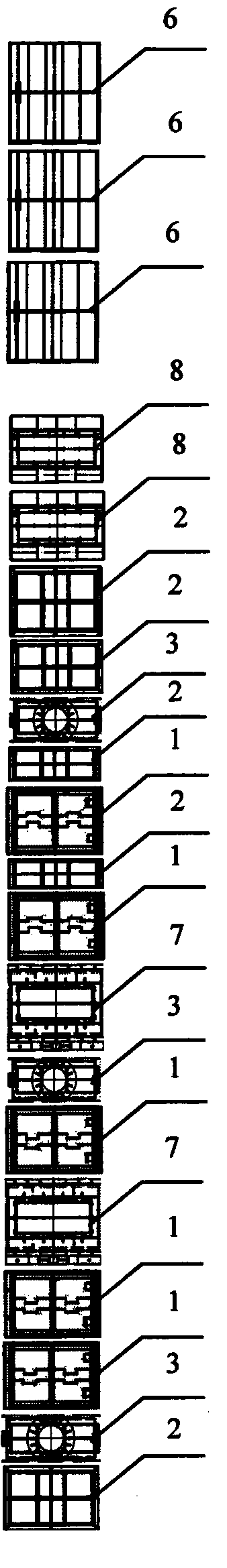
[0042] image 3 The burner arrangement provided for this embodiment. combine figure 2 , image 3 , the concentrated powder (accounting for 70% powder amount of former tertiary wind) that the tertiary air separates, sprays into the middle part of main combustion zone through two layers of tertiary air dense powder spouts 7, and arranges separately, replaces two layers of secondary air spouts 2 respectively, reduces The amount of oxygen in the main combustion zone is increased, so that the main combustion zone is in an oxygen-deficient reducing atmosphere, which is beneficial to the reduction of NOx produced by combustion. Concentrated coal powder has an average particle size of 18 μm. As a fine coal powder, it ignites quickly, gasifies quickly, and has fast response ability. It can form a large number of reducing particles in a short period of time and maintain a certain concentration. The effect of reducing NOx is remarkable. The light powder separated by the tertiary air ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Figure 4 The burner arrangement provided for this embodiment. combine figure 2 , Figure 4 , the thick powder (accounting for 70% powder amount of former tertiary wind) that the tertiary wind separates, sprays into the middle and lower part of the main combustion zone through two layers of tertiary wind thick powder nozzles 7, and one layer of tertiary wind thick powder nozzles 7 sprays into the main combustion zone at the end In the lower part, another layer of tertiary air dense powder nozzles 7 is sprayed into the middle of the main combustion zone, replacing two layers of secondary air nozzles 2, which reduces the amount of oxygen in the main combustion zone and makes the main combustion zone in an oxygen-deficient reducing atmosphere, which is conducive to combustion. NOx reduction. Concentrated coal powder has an average particle size of 18 μm. As a fine coal powder, it ignites quickly, gasifies quickly, and has fast response ability. It can form a large numb...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Figure 5 The burner arrangement provided for this embodiment. combine figure 2 , Figure 5 , the concentrated powder (accounting for 70% powder amount of the original tertiary air) separated by the tertiary air is sprayed into the middle part of the main combustion zone through two layers of tertiary air dense powder nozzles 7, and arranged adjacently, replacing the two layers of secondary air nozzles 2, reducing The amount of oxygen in the main combustion zone is increased, so that the main combustion zone is in an oxygen-deficient reducing atmosphere, which is beneficial to the reduction of NOx produced by combustion. Concentrated coal powder has an average particle size of 18 μm. As a fine coal powder, it ignites quickly, gasifies quickly, and has fast response ability. It can form a large number of reducing particles in a short period of time and maintain a certain concentration. The effect of reducing NOx is remarkable. The light powder (accounting for 30% pow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com