Working electrode biological reactant and electrode type test strip
A working electrode and biological reaction technology, applied in the field of electrochemical detection, can solve the problems of failing to significantly improve the anti-interference ability of the test strip, reducing the precision of the test strip, and current response signal interference.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] The structure, composition and performance test of embodiment 1 electrochemical test strip
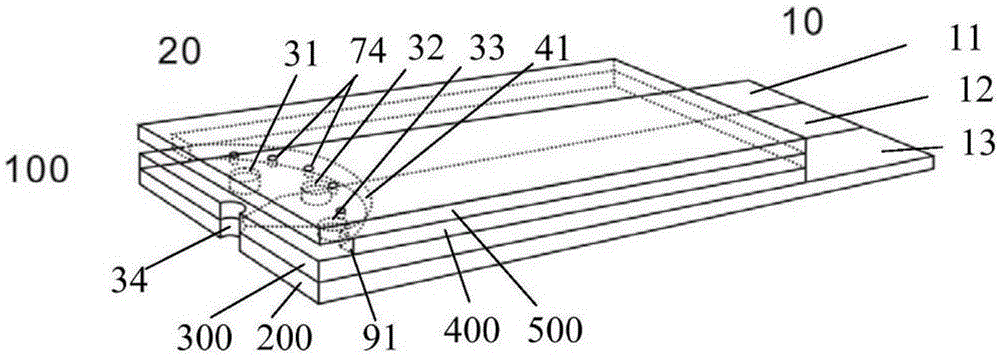
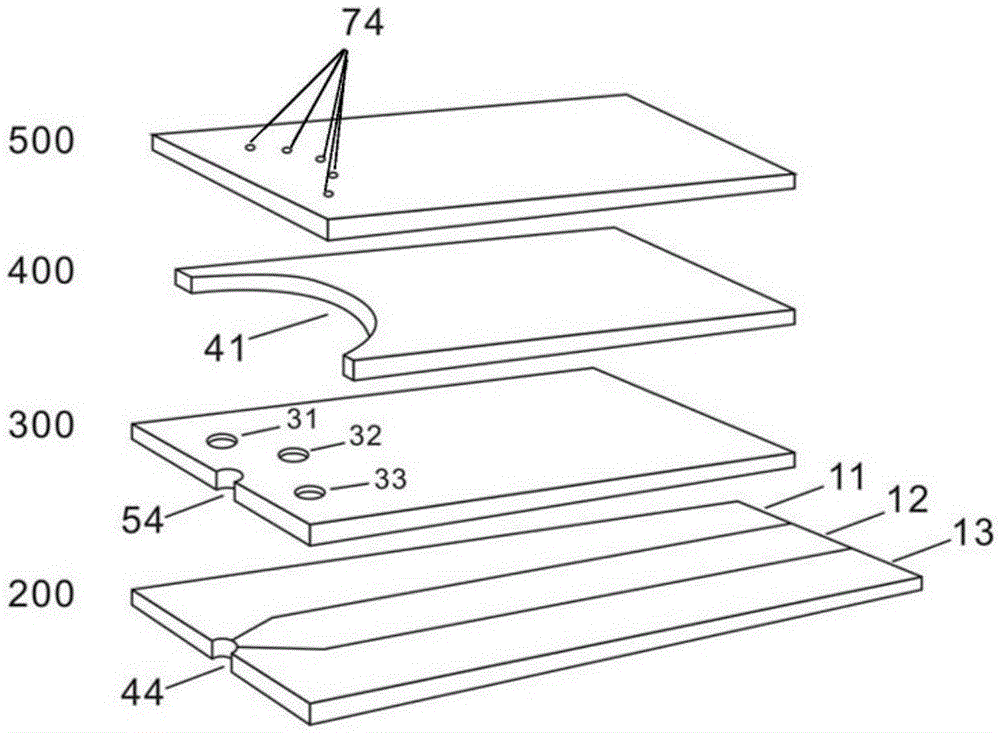
[0066] The schematic diagram of the electrode type test strip is shown in figure 1 As shown, the schematic diagram of its structural decomposition is shown in figure 2 shown.
[0067] figure 1 Schematic diagram of the structure of an electrochemical test strip used for the glucose electrochemical sensor. The test strip includes a board body 100 and electrodes located inside the board body 100 , and the two ends of the board body 100 are collecting terminals 20 and electrical contact terminals 10 respectively. Wherein, the collection end 20 is used to receive fluid samples, and the inside of the collection end 20 is provided with a liquid chamber as a liquid sample chamber. The end faces of the collecting end 20) communicate with the liquid chamber respectively, and the bottom surface of the collecting end 20 is provided with a slot 34 communicating with the liquid chamber. ...
Embodiment 2
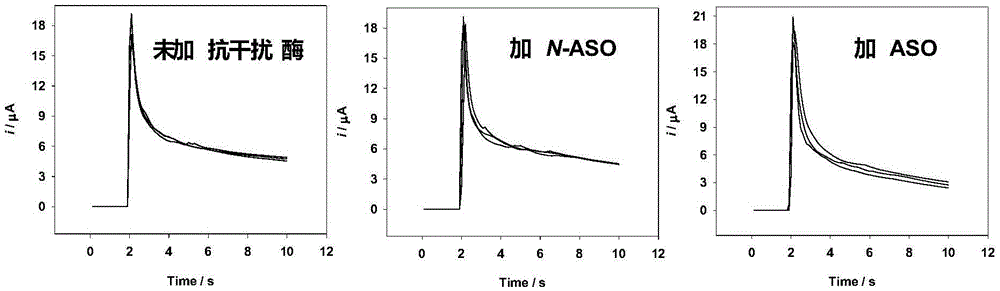
[0097] Anti-interference test of embodiment 2 glucose electrochemical sensor
[0098] This embodiment is to reduce the interference of ascorbic acid on the glucose electrochemical sensor with oxidation current as the detection signal. The structure of the electrochemical test strip used in this embodiment is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0099] (1) Single working electrode mode
[0100] When the single working electrode mode is adopted, the electrode 12 is the working electrode, and the electrodes 11 and 13 are reference electrodes. The enzyme membrane (biological reaction membrane) component on electrode 12 surface is identical with the enzyme membrane component in embodiment 1, coats A, B and C three kinds of enzyme membrane components respectively, specifically as shown in table 2 in embodiment 1 . Electrodes 11 and 13 are coated with oxidized electron mediator potassium ferricyanide, polymer adhesion promoter hydroxyethyl cellulose and filler lactose, which are th...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Embodiment 3 Anti-interference test of blood ketone electrochemical sensor
[0123] This embodiment is to reduce the interference of ascorbic acid on the blood ketone electrochemical sensor which uses the oxidation current as the detection signal. The structure of the electrochemical test strip adopted in this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1.
[0124] (1) Single working electrode mode
[0125] When the single working electrode mode is adopted, the electrode 12 is the working electrode, and the electrodes 11 and 13 are reference electrodes. The enzyme film (biological reaction film) component on the surface of the working electrode 12 is divided into the following three situations:
[0126] A: coated with β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD + ), new ascorbate oxidase (N-ASO, 216U / mg, purchased from Amano, Japan), oxidized electron mediator Azure I, macromolecule adhesion promoter hydroxyethylcellulose and filler lacto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com