Planting method of torreya grandis
A planting method and technology of Torreya, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, seed and rhizome treatment, horticulture, etc., can solve the problems such as the infestation of Torreya seedlings by diseases and insect pests, poor ventilation effect, etc., and achieve the improvement of grafting survival rate, simple operation, and survival. high rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] In order to have a further understanding and understanding of the structural features of the present invention and the achieved effects, the preferred embodiments and accompanying drawings are used for a detailed description, as follows:
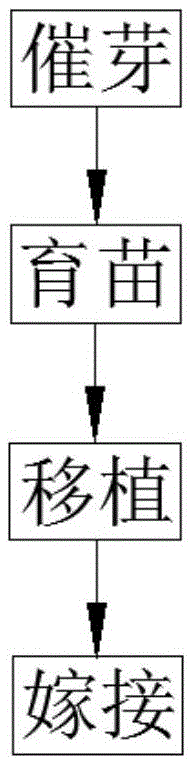
[0042] Such as figure 1As shown, the Chinese torreya tree planting method provided by the invention comprises four steps of germination, seedling raising, transplantation, and grafting. Each step is described in detail below.
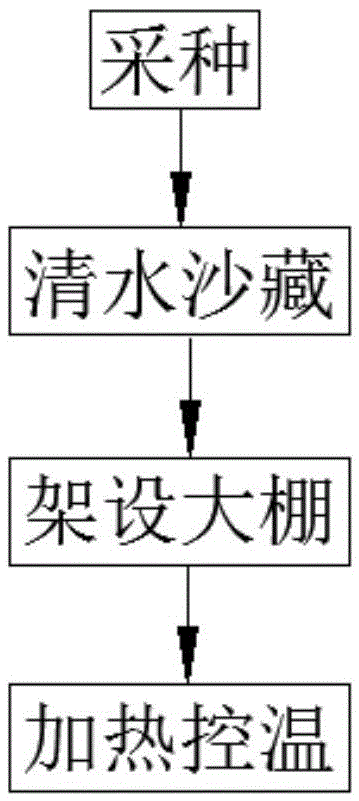
[0043] Such as figure 2 Shown, the germination method of Torreya torreya, comprises the following steps:
[0044] Step 1. Seed collection
[0045] Seeds are collected in October, and the fake skin on the surface of the species is removed. It is best to choose the torreya species that fall naturally. The removal of the fake leather is generally done manually, so as not to damage the torreya species by peeling off the fake leather by the machine.
[0046] Step 2. Sand storage in clear water
[0047] Such a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com