Real-time scattering type terahertz quasi-time-domain near field polarization spectrograph
A terahertz, quasi-time domain technology, applied in the field of spectrum testing, can solve problems such as large volume, poor signal-to-noise ratio, and bandwidth limitations of frequency-domain continuous wave near-field systems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
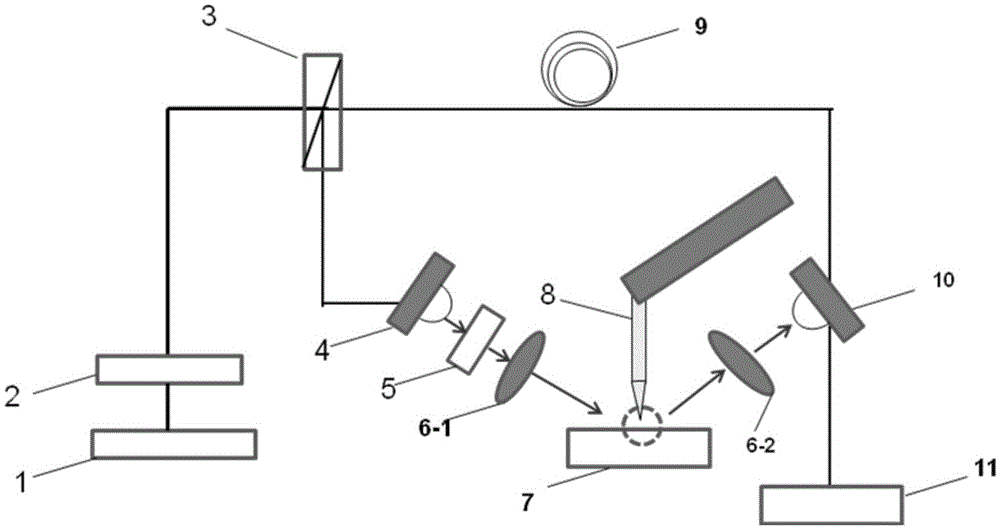
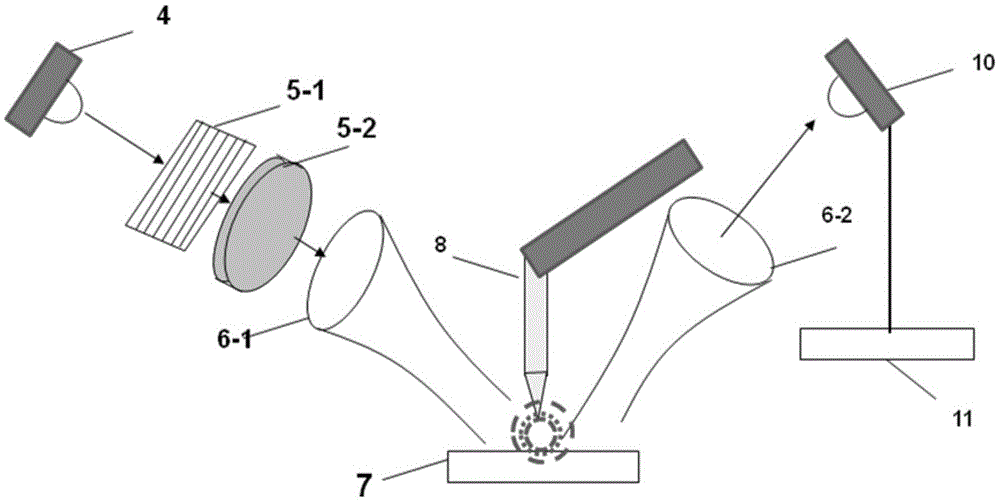
[0019] A real-time scattering terahertz quasi-time-domain near-field polarization spectrometer involved in this embodiment has a structure such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a multimode laser module 1, a fiber beam splitter 2, an erbium-doped fiber amplifier 3, a photoconductive transmitting antenna 4, a polarization module 5, a focusing lens 6-1, an atomic force microscope 8, an optical fiber extension module 9, and a photoconductive receiving antenna 10. Lock-in amplifier 11; multi-mode laser module 1 emits multi-mode laser, passes through erbium-doped fiber amplifier 2, is guided by multi-mode transmission fiber to fiber beam splitter 3, and becomes pumping and probing light, and the pumping beam excites the photoelectric The guided transmitting antenna module 4 radiates quasi-time-domain terahertz signals. The terahertz signals pass through the polarization module 5 and the focusing lens A6-1, and are incident on the oscillating probe tip of the atomic force microscope ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com