Preparation method and application of tissue engineering material for promoting directional differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
A bone marrow mesenchymal and tissue engineering technology, applied in the field of biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of inability to produce insulin-secreting cells, low differentiation efficiency, and short lifespan of insulin-secreting cells.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
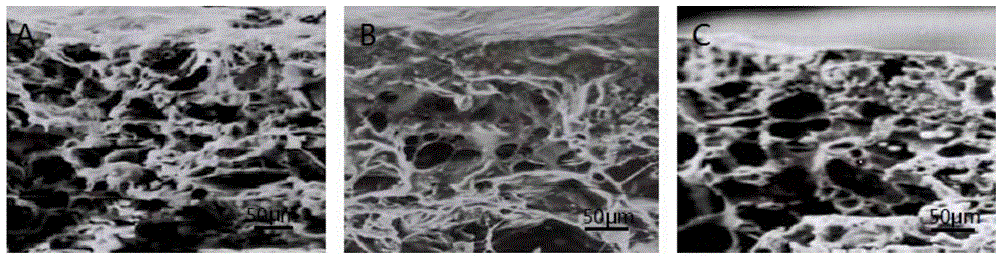
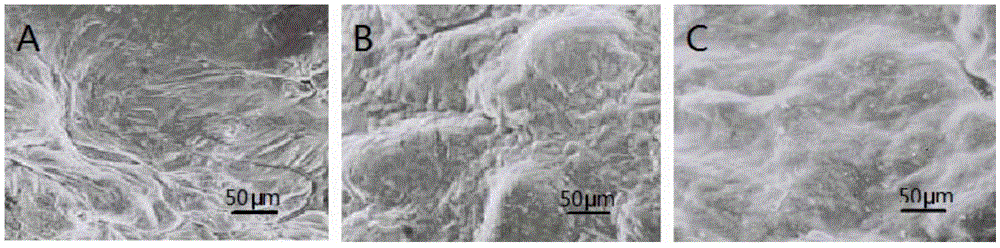
[0039] Embodiment 1: the preparation of porous PLGA scaffold
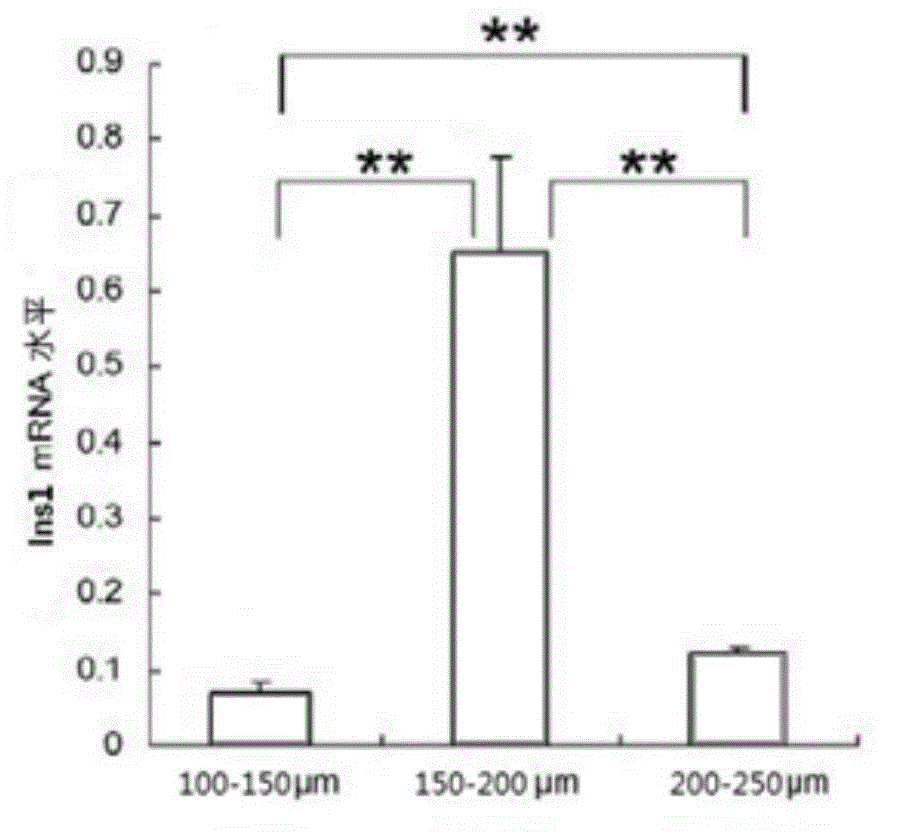
[0040] Dissolve 0.5g of PLGA (molecular weight 15KD) (PLA:PGA is 85:15, purchased from Shandong Provincial Institute of Medical Devices) raw materials in 1,4-dioxane solution, and prepare a PLGA concentration of 10% (w / v) solution. Add NaCl particles with a particle size of 150-200 μm and a ratio of 50% (w / w) to the above-mentioned polylactic-glycolic acid solution with a concentration of 10% w / v, and stir to obtain a uniform suspension. ×8cm petri dish. Drying at room temperature for 48h, freeze-drying for 48h. After demolding, use distilled water to filter out the NaCl in the porous film, and dry it at room temperature for 48 hours. Stir the deionized water in the beaker to accelerate the dissolution of NaCl particles. After the NaCl particles are completely dissolved, dry the film and seal it for storage.
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2: the preparation of porous PLGA scaffold
[0042] Dissolve 0.5g of PLGA (molecular weight 15KD) (PLA:PGA is 85:15, purchased from Shandong Provincial Institute of Medical Devices) raw materials in 1,4-dioxane solution, and prepare a PLGA concentration of 10% (w / v) solution. Add NaCl particles with a particle size of 150-200 μm and a ratio of 25% (w / w) to the above-mentioned polylactic-glycolic acid solution with a concentration of 10% w / v, and stir to obtain a uniform suspension. ×8cm petri dish. Drying at room temperature for 48h, freeze-drying for 48h. After demolding, use distilled water to filter out the NaCl in the porous film, and dry it at room temperature for 48 hours. Stir the deionized water in the beaker to accelerate the dissolution of NaCl particles. After the NaCl particles are completely dissolved, dry the film and seal it for storage. The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the ratio of NaCl particles added during the pr...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: the preparation of porous PLGA scaffold
[0044] Dissolve 0.5g of PLGA (molecular weight 15KD) (PLA:PGA is 85:15, purchased from Shandong Provincial Institute of Medical Devices) raw materials in 1,4-dioxane solution, and prepare a PLGA concentration of 10% (w / v) solution. Add NaCl particles with a particle size of 150-200 μm and a ratio of 75% (w / w) to the above-mentioned polylactic-glycolic acid solution with a concentration of 10% w / v, and stir to obtain a uniform suspension. ×8cm petri dish. Drying at room temperature for 48h, freeze-drying for 48h. After demolding, use distilled water to filter out the NaCl in the porous film, and dry it at room temperature for 48 hours. Stir the deionized water in the beaker to accelerate the dissolution of NaCl particles. After the NaCl particles are completely dissolved, dry the film and seal it for storage. The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the ratio of NaCl particles added during the pr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com