Polymer grade Lactic acid monomer producing strain, construction method thereof and lactic acid manufacturing technique
A technology of lactic acid monomer and manufacturing technology, applied in the field of microbial application, can solve the problems of complex culture medium, unsatisfactory optical purity of lactic acid, incapable of large-scale production of D-lactic acid and L-lactic acid of extremely high optical purity, etc., and achieve efficient preparation effect of the process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0118] Example 1 - Mutation Cassette ldhA::kan-cI ts 857-p R -p L build
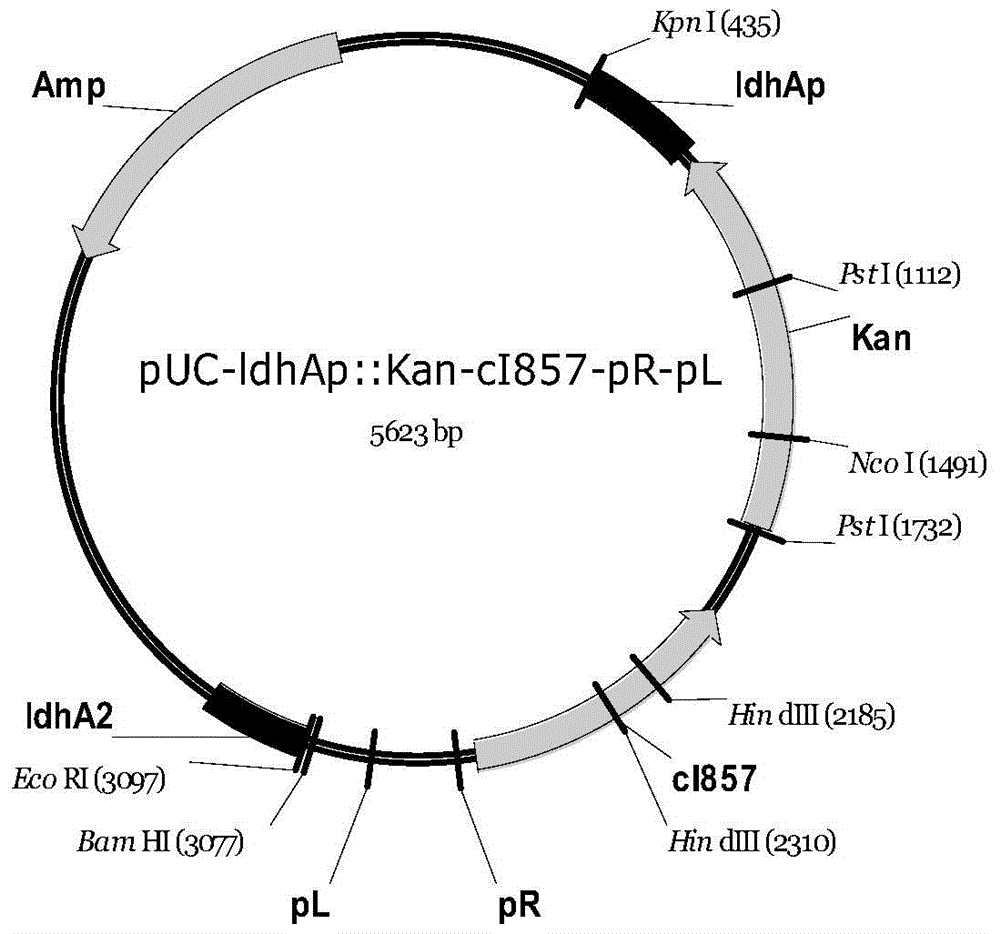
[0119] The ldhA gene fragment ldhA' on the B0013 chromosome was amplified by PCR with primers ldhA1 and ldhA2, and cloned into pUC18 vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pUC-ldhA'. Plasmid pPL451 was amplified by inverse PCR with primers PPL1 and PPL2, and combined with the kanamycin resistance gene fragment (plasmid pSK sym Km was digested with SmaI, and the 966bp fragment was recovered by gel) for ligation to obtain the recombinant plasmid pPL-Kan. Plasmid pPL-Kan was amplified by PCR with primers PPL3 and PPL4, and the product was double-digested with EcoRI and EcoRV, and then reverse-PCR amplified with primers Ec-RlA1 and Ec-RlA2 using pUC-ldhA' as a template and used EcoRI digested products were ligated to obtain the recombinant plasmid pUC-ldhAp::kan-cI ts 857-p R -p L . The physical map of the resulting recombinant plasmid is attached figure 1 shown. The recombinant plasmid pUC-ldhAp...
Embodiment 2
[0120] Example 2 - Construction of Mutation Cassette thiE::difGm
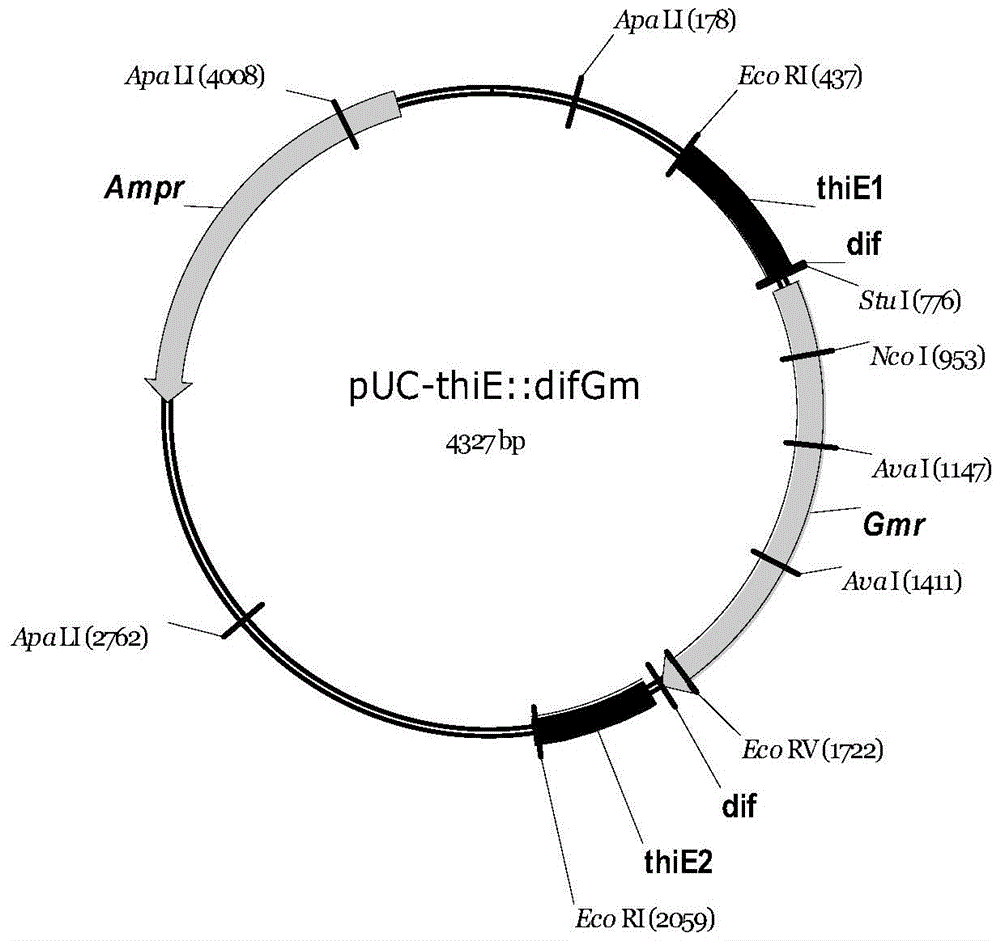
[0121] Using E. coliB0013 chromosomal DNA as template, ThiE1p and ThiE2p as primers, the partial sequence of thiE gene with a length of 0.6kb was amplified. This was cloned into pUC18 to obtain the recombinant plasmid pUC-thiE. The 1.2kb difGm fragment was cloned into the StuI site in the middle of thiE to obtain the recombinant plasmid pUC-thiE::difGm. The physical map of the resulting recombinant plasmid is attached figure 2 shown. The recombinant plasmid pUC-thiE::difGm was digested with ApaLI, and the linearized plasmid was recovered by gel, and PCR amplification was performed with primers ThiE1p and ThiE2p to obtain the thiE::difGm gene fragment.
Embodiment 3
[0122] Example 3 - Construction of Mutation Cassette dld::difGm
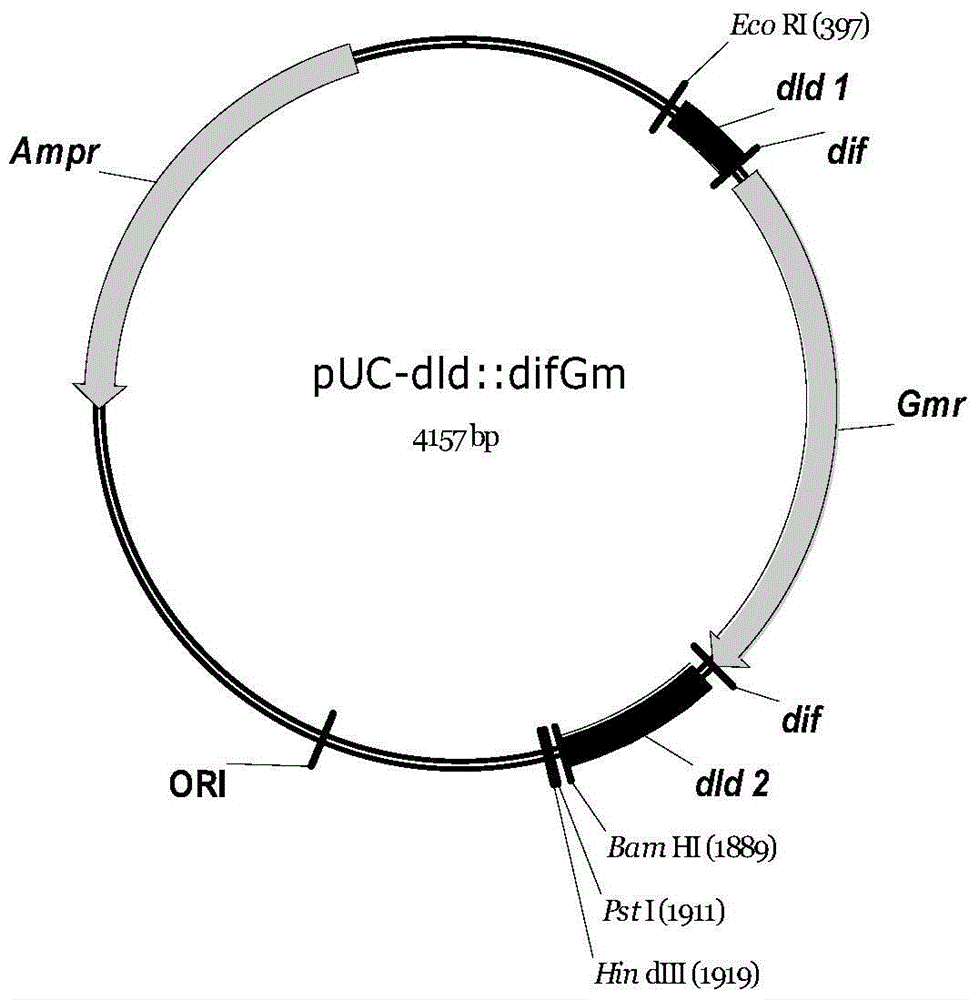
[0123] Using the chromosomal DNA of bacterial strain B0013 as a template, the dld' gene fragment (0.9kb) was amplified by PCR with primers Dld1 and Dld2, and the PCR product was cloned into the vector pUC18SmaI site to obtain the recombinant plasmid pUC-dld'. Digest the recombinant plasmid with EcoRV, remove the 0.4 kb gene fragment in the middle of the dld' gene, and clone into the dif-Gm-dif fragment to obtain the recombinant plasmid pUC-dld'::difGm. The physical map of the resulting recombinant plasmid is attached image 3 shown. The recombinant plasmid pUC-dld'::difGm was digested with EcoRI, and the linearized plasmid was recovered by gel, and PCR amplification was performed with primers Dld1 and Dld2 to obtain the dld'::difGm gene fragment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com