Method for recovering rare earth metals from waste sulphates
A rare earth metal and sulfate technology, which is applied in the field of rare earth metal recovery from waste sulfate materials, can solve the problem of undisclosed chemical preparation of rare earth compounds and the like, and achieve the effect of cost saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
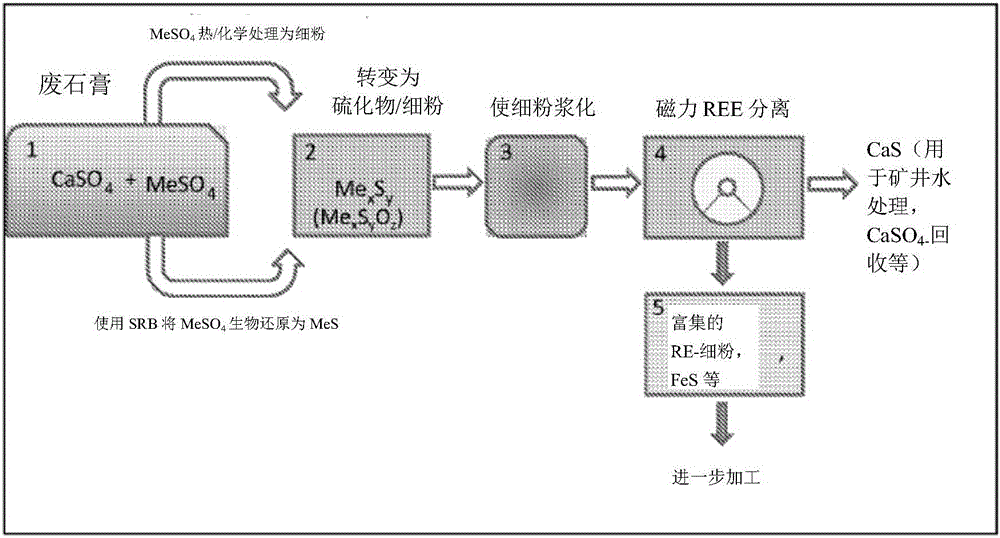
[0045] Firstly, the phosphogypsum samples were dried in an oven (105 °C, 20 h). Gypsum leachate was then prepared by adding dry phosphogypsum powder to water (50 g / L) and mixing in Erlenmeyer glass flasks for 24 h. The solution obtained was filtered (0.45 μm) in order to remove phosphogypsum particles. The clarified solution was used for sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) studies. Filled with N through a 0.22 μm pore size filter 2 After anaerobic exposure of the phosphogypsum filtrate to gas for 1 hour, the flask containing the gypsum leachate was sealed with an airtight butyl rubber stopper and the top screw cap was removed. With 0.2g yeast extract and 3.75ml lactate L -1 Correction of phosphogypsum leachate. Pre-grown Desulfovibrio desulfurum was added to a volume of 25 L of phosphogypsum leachate.
[0046] The culture formed a precipitate which was collected by vacuum filtration on a 0.22 μm pore size filter funnel. The precipitate was rinsed from the filter with sterile...
Embodiment 2
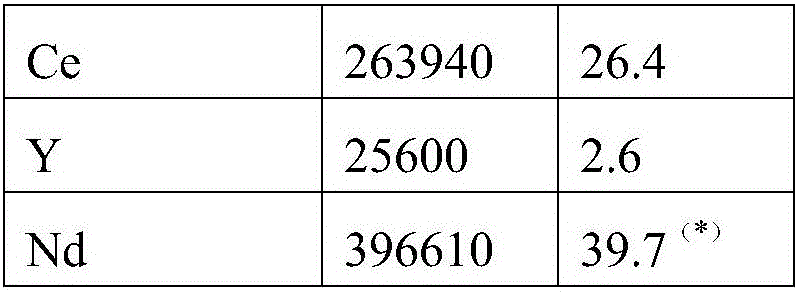
[0053] The experiment described in Example 1 was likewise repeated to test the reproducibility of the procedure. In Experiment 2 SRB precipitation, the contents of La, Ce and Y were observed to be 33900, 77300 and 5200 ppm (mg / kg), respectively. The Nd-content of the SRB precipitate was 38900 ppm.
[0054] By using a magnetic separation similar to Experiment 1, the final concentrate is shown in Table 2:
[0055] Table 2. Rare earth metal content in recovered concentrates
[0056] components
[0057] (*) From a separate trial (FI101787B)
Embodiment 3
[0059] Phosphogypsum samples of the same origin as used in the aforementioned patent FI101787B were dried in an oven (105° C., 20 h). Gypsum leachate was prepared by adding dry phosphogypsum powder to water (50 g / L) followed by mixing in Erlenmeyer glass flasks for 24 h. The solution obtained was filtered (0.45 μm) to remove solid phosphogypsum particles. The clarified solution was used for sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) studies.
[0060] Continuously operated sulfate reduction and REE precipitation experiments were performed in a 0.7-liter UASB (upflow anaerobic sludge bed) column, which was also equipped with a solution circulation line with a powerful pump to regulate the fluidization of the sludge so that Mix and homogenize the sludge in the column if necessary. The column was primed with 500 ml of anaerobic granular sludge from an operating wastewater treatment plant and filled to a total volume of 700 ml with sulphate-enriched water. Microbial activity is ensured by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com