A method for determining liquid production rate of a single gas well
A technology to determine the method and fluid production rate, which is applied in wellbore/well components, measurement, earthwork drilling and production, etc. It can solve the problems of gas reservoir evaluation, difficulty in well location deployment, and disputes over gas testing and drainage. Achieve the effect of solving the difficulty of deployment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] According to the principle of conservation of matter, in physical and chemical reaction mixing, the sum of the masses of the substances participating in the reaction mixing is equal to the sum of the masses of the substances produced after the reaction mixing. This law is also applicable to the mixing of produced water from gas wells. The water quality ions in the mixed liquid formed after mixing the produced water from multiple gas wells are equal to the sum of the corresponding water quality ions in the produced water from each gas well before mixing. Through the research and development of single well liquid extraction tools, combined with dynamic monitoring and liquid level testing, and through the analysis of the water samples taken and the water quality test results over the years, on the one hand, the ion content of water quality in most gas wells has not changed much within a period of time and is basically stable. Unless the reservoir changes or the source of wa...
Embodiment 2
[0027] In this embodiment, the method in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 is further described in detail. The collection of water samples and the measurement of the total liquid production in the above-mentioned step 2 are all collected in units of one day.
[0028] Various ions include chloride radical cl in step 2 - , Sulfate SO 4 2- , bicarbonate HCO 3 - , Sodium ion Na + , Potassium K + , calcium ion Ca 2+ , Magnesium ion Mg 2+ , in addition to these common ions, it can also be some other uncommon ions. The final selection should be based on the number of single wells. If the number of single wells is small, the final test can be completed with the content of common ions. If the number of single wells is large, the number of common ions cannot meet the quantity requirements of the equation, and common ions can also be used.
[0029] In step 3, the liquid production rate of each single well is calculated according to the following formulas:
[0030] V=V 1 +V 2 +…...
Embodiment 3
[0044] This embodiment is described with a specific experiment.
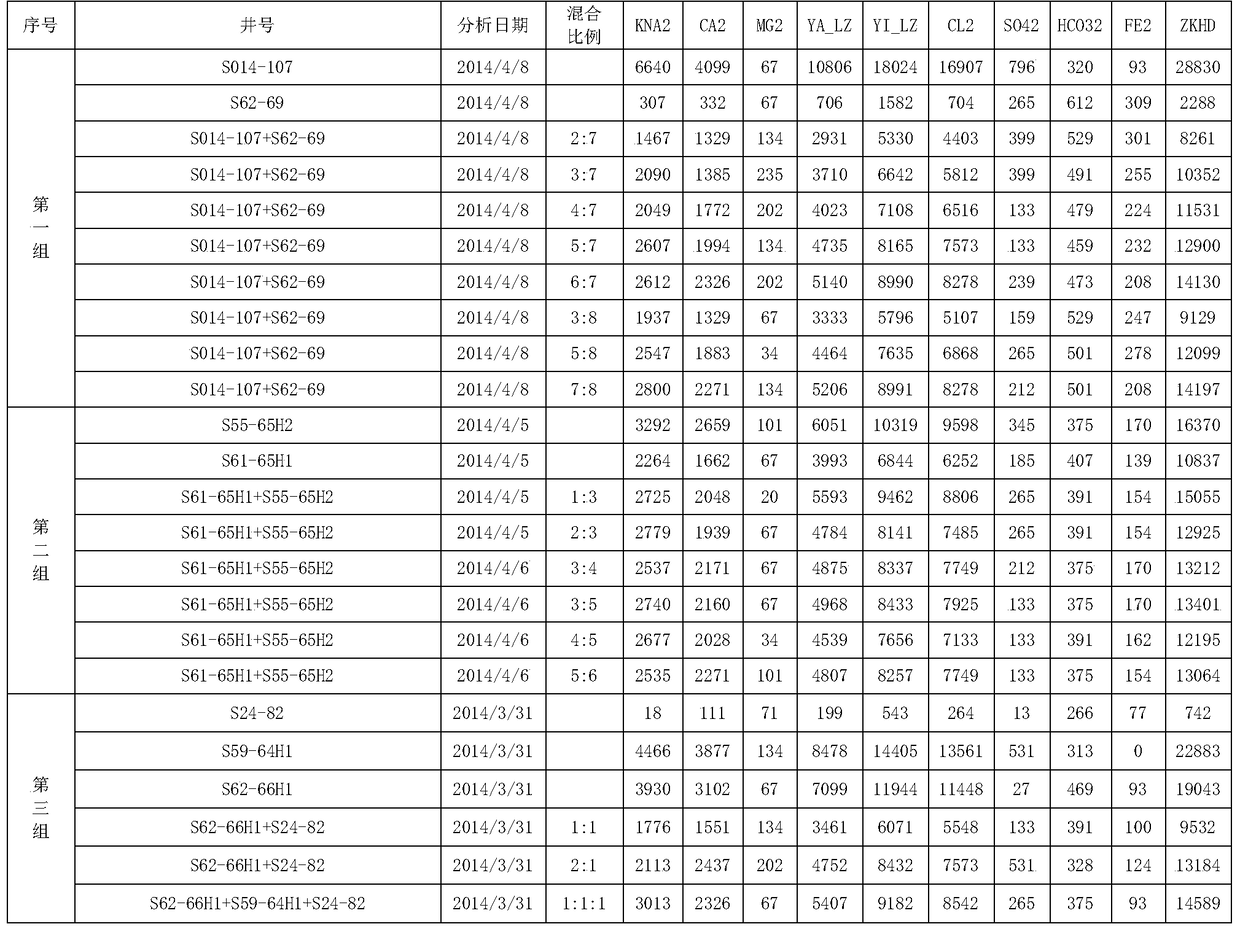
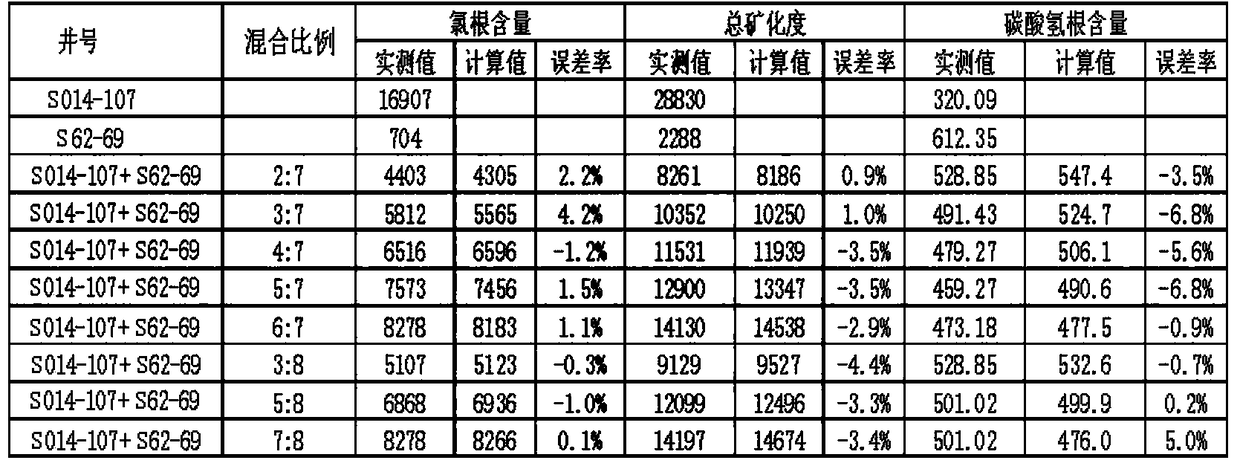
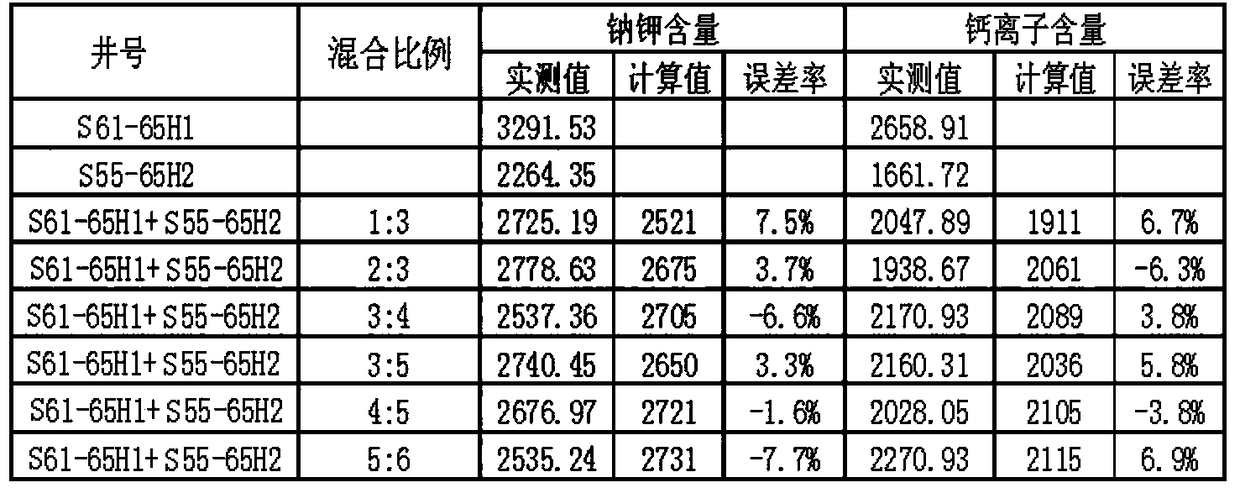
[0045] With the aid of a heating furnace to produce wells, water samples are collected from the wellhead, mixed according to different proportions, and the relationship between ions and volumes of single well liquid and mixed liquid is analyzed. The laboratory demonstrates that there is a certain correlation between the water quality ion content and the mixing volume ratio through a total of 17 kinds of ratio relationships in three groups of gas wells. The specific experimental data are shown in Table 1 below:
[0046] Table 1 Statistical table of test results of water quality analysis in three groups of experimental wells
[0047]
[0048] Mix in a 2:7 ratio:
[0049] Calculation of chlorine content=(16907*2+704*7) / 9=4305mg / l;
[0050] The measured chlorine content is 4402mg / l; the error rate is 2.2%.
[0051] Calculate the total salinity = (28829*2+2287*7) / 9=8186mg / l;
[0052] The measured total salinit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com