Parallel prediction methods for protein folding
A protein folding and prediction method technology, applied in the fields of computer virtual reality technology and biological information technology, can solve the problems of limited folding, increased computational complexity, and reduced number of copies, and achieve the effect of accurate results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the examples.
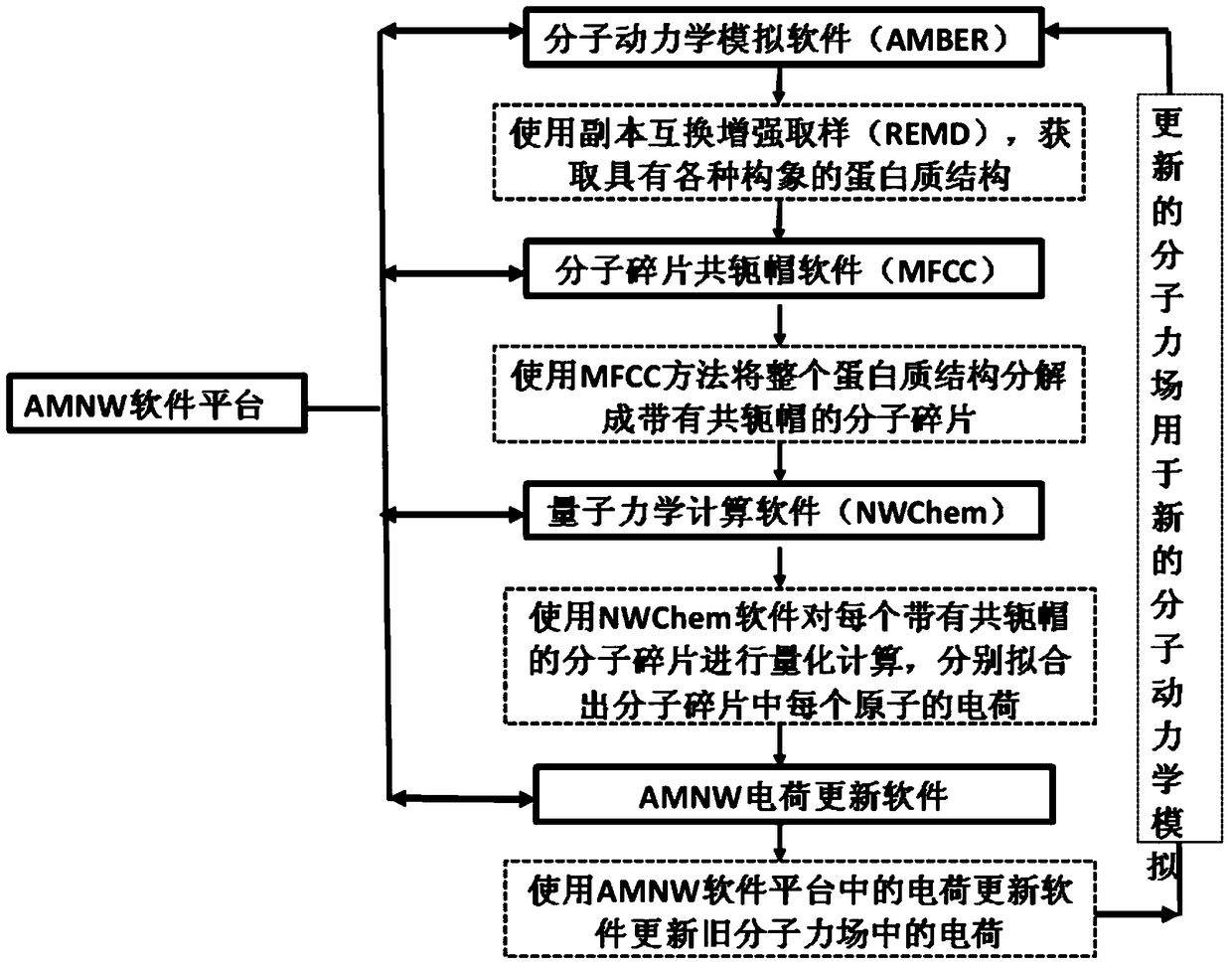
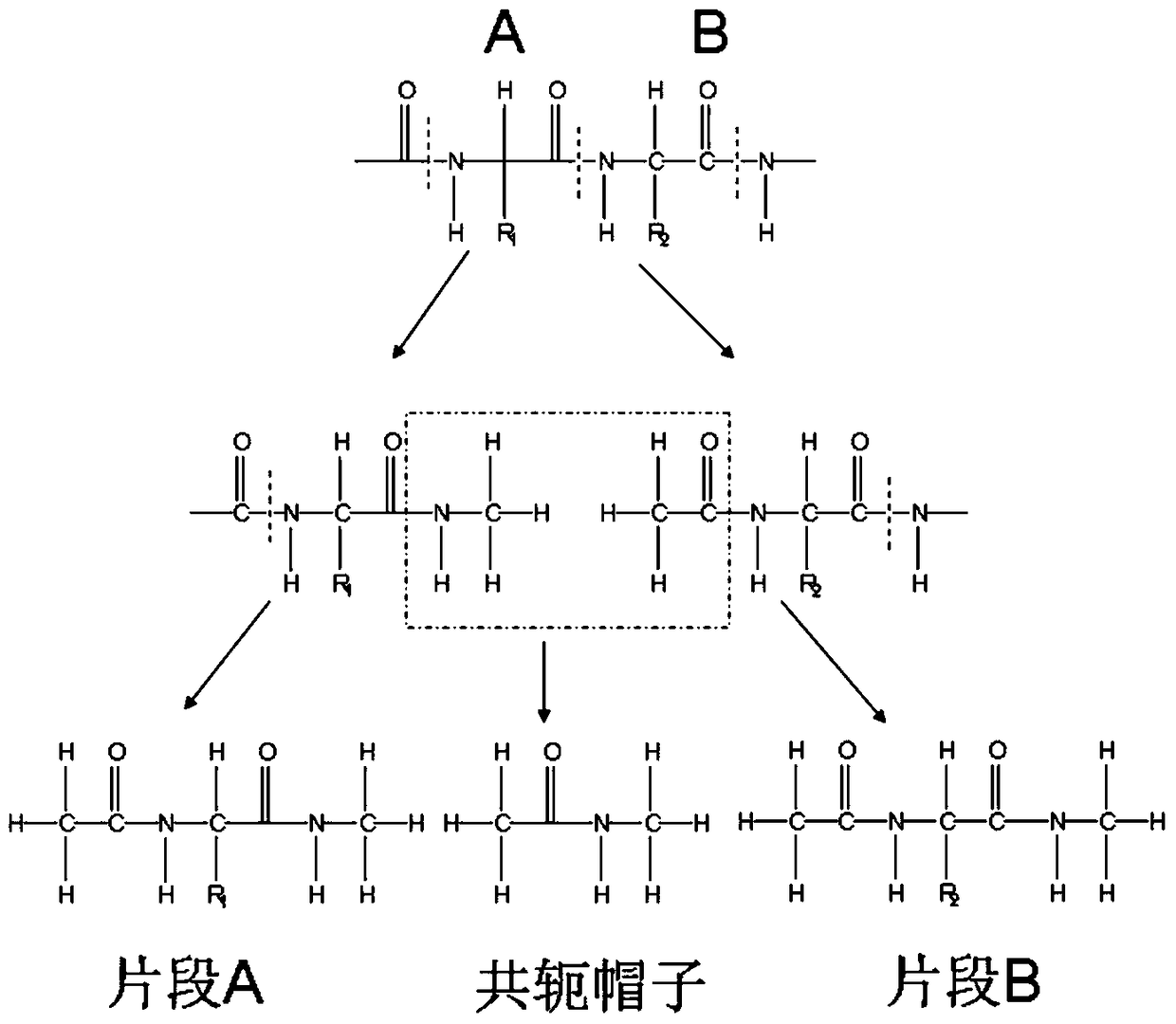
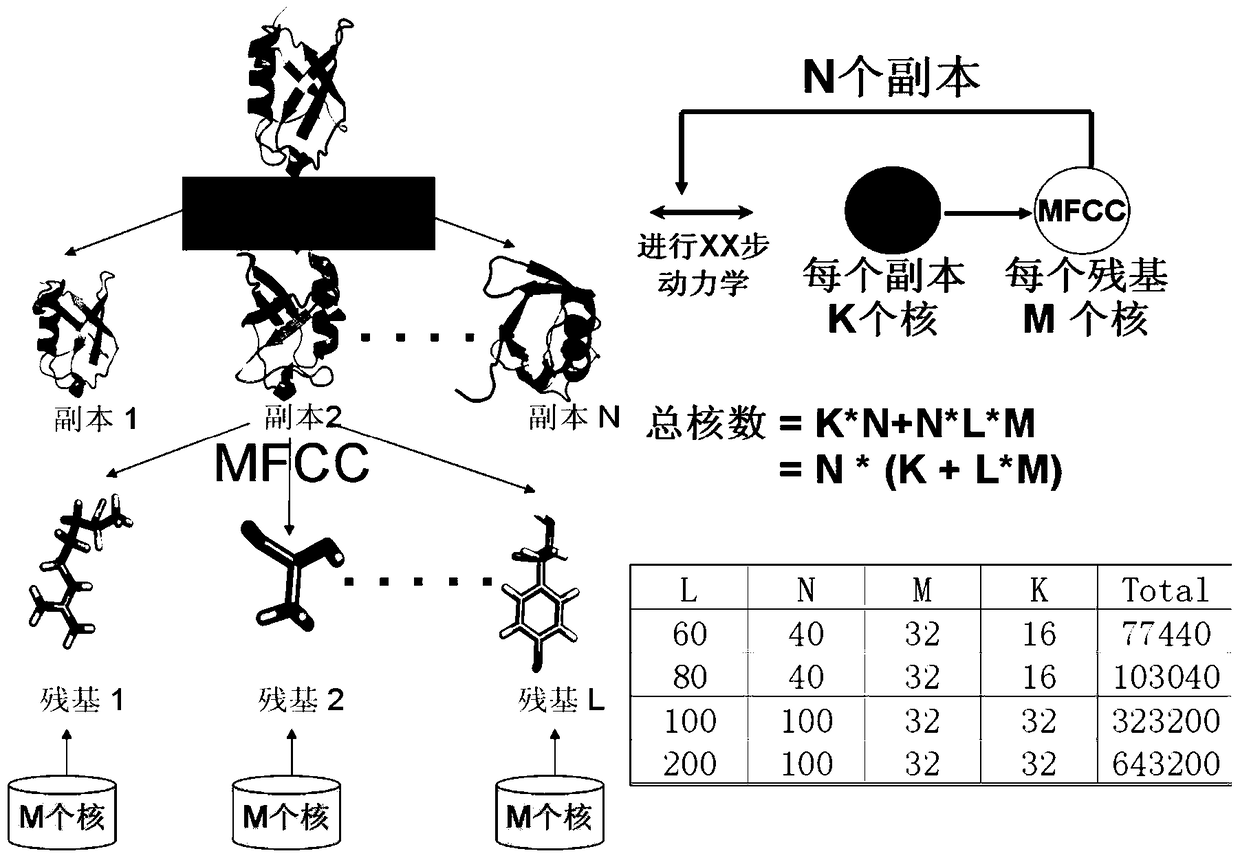
[0036] The present invention relates to a prediction method for studying protein folding in a living system, including the following content: Aiming at the problem of polarization effects, the method of quantum mechanics is used to calculate the charge properties of proteins, and in order to reflect the impact of the protein's surrounding environment on the structure in real time Influence, the environment around the protein is considered in real time during the simulation process, and the charge properties of the protein are continuously updated to account for the polarization effect of the protein. Aiming at the problem of protein conformation sampling, in order to reduce the number of copies required for routine copy exchange and improve efficiency, a recently developed efficient protein conformation sampling method based on generalized ensembles is proposed. And this ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com