Method and device for supergravity on-line preparation of nano zero-valent iron and synchronous treatment on nitrobenzene wastewater
A technology of nitrobenzene wastewater and nano-zero-valent iron, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of easy aggregation of nanoparticles, complicated preparation process, easy oxidation and deactivation, etc., and achieve rapid mixing Uniform, low cost, simple process effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
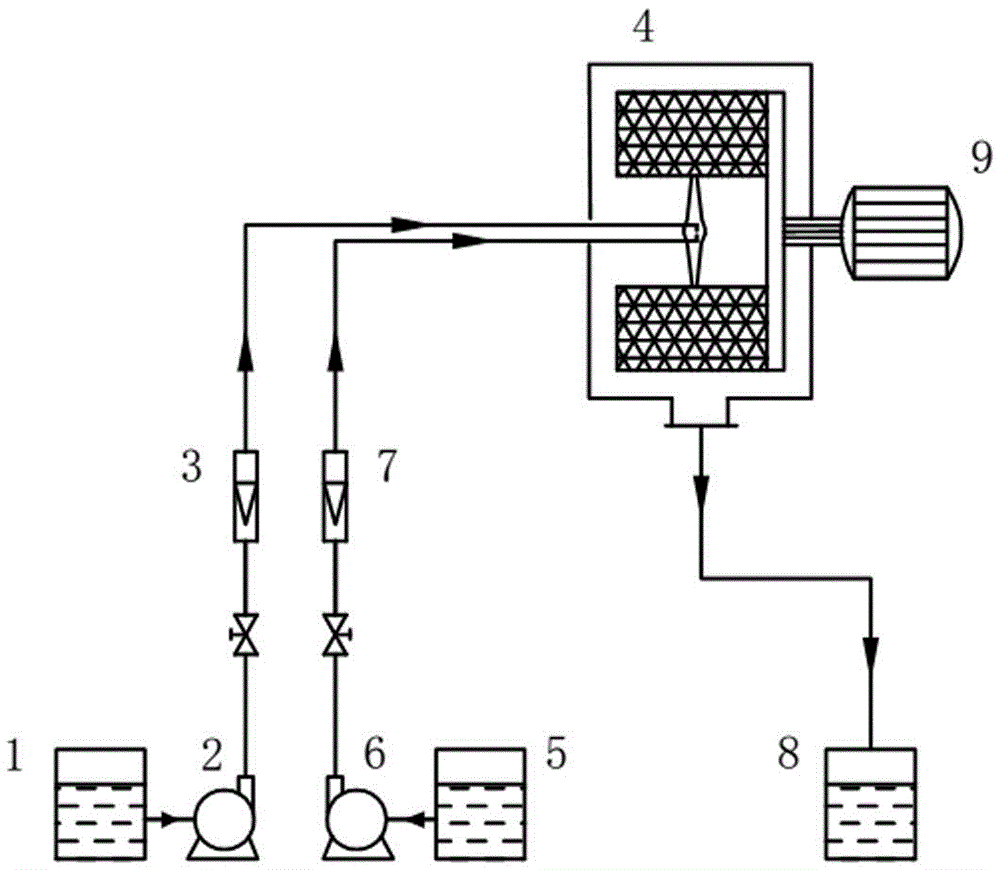
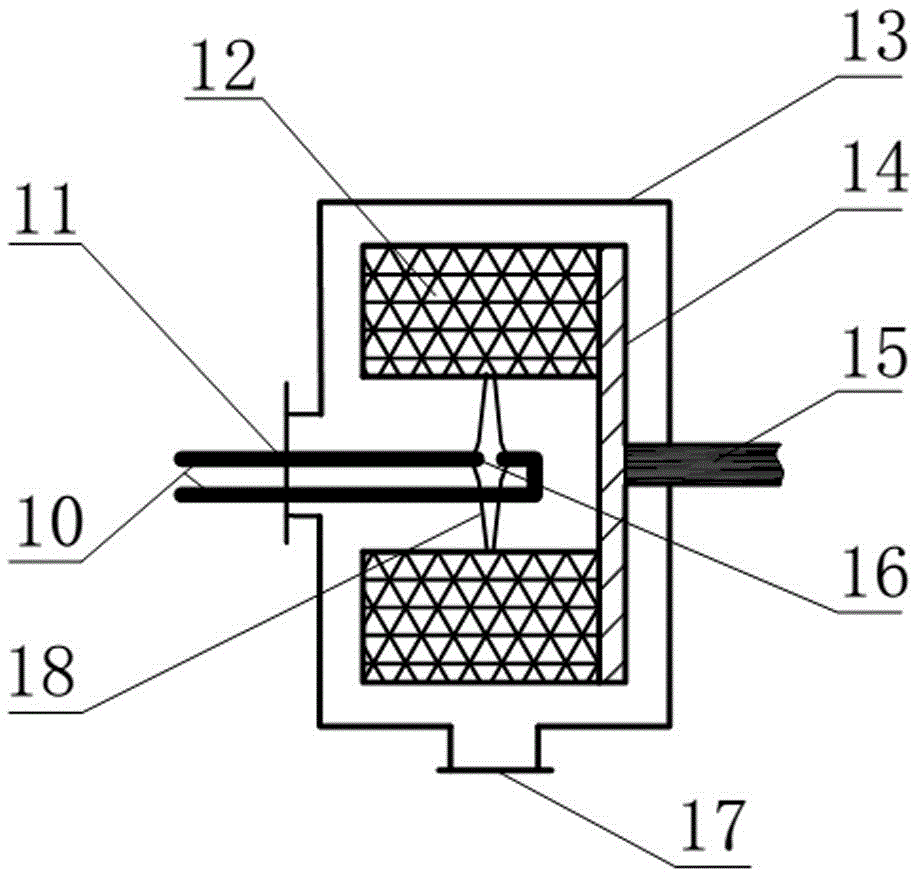
[0032] use figure 1 The process flow shown, the initial concentration of 250 mg L was treated at 20 °C -1 of nitrobenzene wastewater. Ferrous sulfate (FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O) The nitrobenzene wastewater dissolved in the liquid storage tank Ⅰ1 is formulated to contain FeSO 4 Nitrobenzene wastewater solution, FeSO 4 The concentration is 25 times the concentration of nitrobenzene, adjust the initial pH to 3.0; prepare NaBH with tap water 4 solution and placed in storage tank Ⅱ5, NaBH 4 The concentration is the FeSO 4 3 times the concentration. The two streams of liquid are respectively measured by the pumps I and II through the liquid flowmeters I and II, and then sprayed out from the feed pipes I and II10 nozzles I and II, at a rate of 15 m s -1The initial collision, mixing and reaction are carried out in the collision region 18 at the collision initial velocity. Subsequently, the liquid enters the packing rotor with a rotation speed of 500 rpm from the inside to the outside al...
Embodiment 2
[0035] use figure 1 The process flow shown, the initial concentration of 100 mg L was treated at 10 ℃ -1 of nitrobenzene wastewater. Ferrous chloride (FeCl 2 ) dissolved in the nitrobenzene wastewater in the liquid storage tank Ⅰ1, made into FeCl-containing 2 Nitrobenzene wastewater solution, FeCl 2 The concentration is 20 times the concentration of nitrobenzene, adjust the initial pH to 7.0; prepare NaBH with tap water 4 solution and placed in storage tank Ⅱ5, NaBH 4 The concentration is the FeCl 2 2.5 times the concentration. Impinging flow - the rotational speed of the rotating packed bed is 2000 rpm, and the initial impacting velocity is 25 m s -1 . The treated nitrobenzene wastewater is discharged into the liquid storage tank 17 from the liquid outlet, and the sampling analysis shows that the removal rate of nitrobenzene is 98%. Sampling and analysis after standing for 3 minutes showed that the removal rate of nitrobenzene was 100%, and all of them were converted...
Embodiment 3
[0038] use figure 1 As shown in the process flow, the initial concentration of 500 mg L was treated at 25 °C -1 of nitrobenzene wastewater. FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O dissolved in the nitrobenzene wastewater in the liquid storage tank Ⅰ1, made into FeSO 4 Nitrobenzene wastewater solution, FeSO 4 The concentration is 25 times the concentration of nitrobenzene, adjust the initial pH to 3.0; prepare KBH with tap water 4 solution and placed in reservoir II5, KBH 4 The concentration is the FeSO 4 4 times the concentration. Impinging flow - the rotational speed of the rotating packed bed is 800 rpm, and the initial impacting velocity is 5 m s -1 . The treated nitrobenzene wastewater was discharged from the liquid outlet into the liquid storage tank 17 for sampling and analysis, and the removal rate of nitrobenzene was 92%. After standing for 3 minutes, the removal rate of nitrobenzene was 97%.
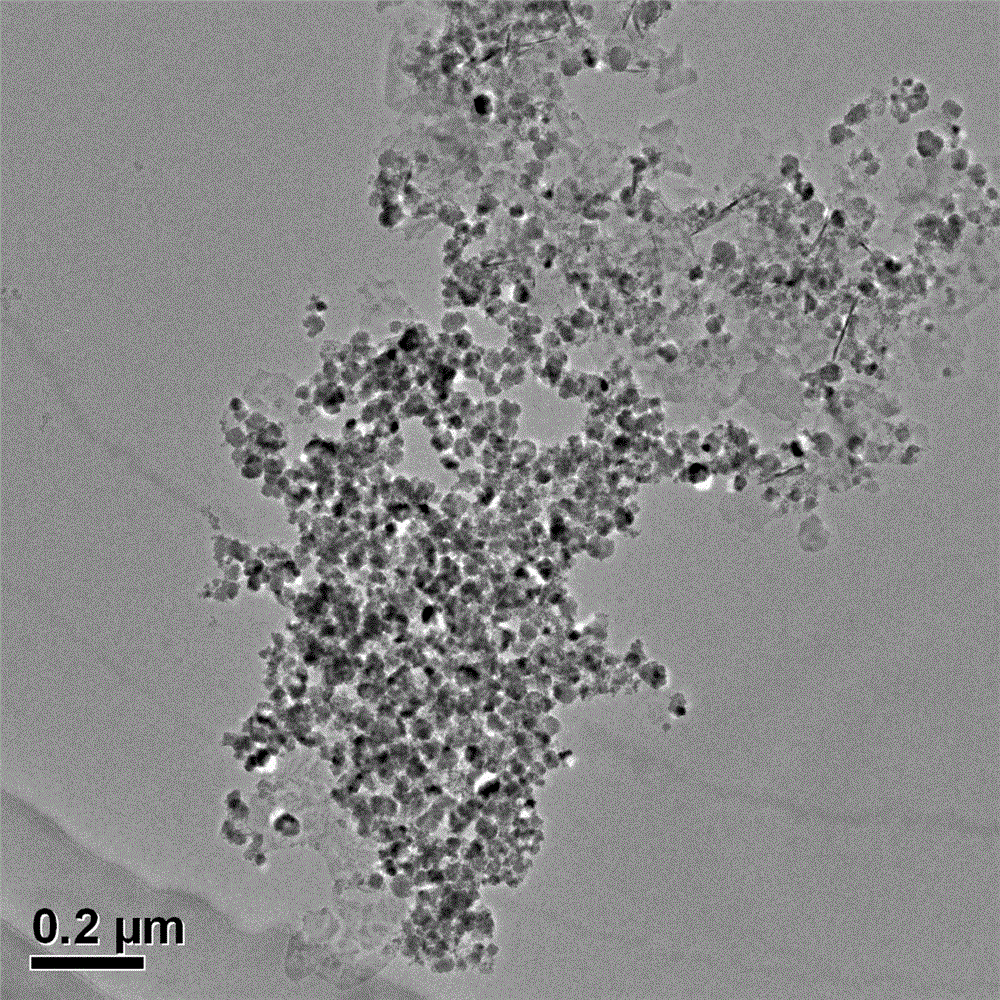
[0039] This method uses supergravity technology to realize online preparation of nanometer...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com