Method for removing disinfection by-products in water
A technology for disinfection by-products and water removal, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of restricting the application of ultraviolet disinfection methods, high toxicity, instability, etc., and achieve the effects of improving anti-microbial pollution performance, prolonging service life, and low system operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
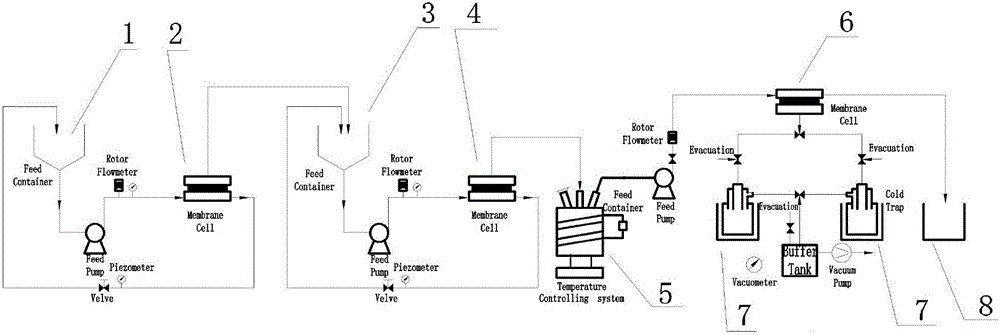
[0048] The present embodiment is a method for removing disinfection by-products in water. The equipment and process used are as shown in Figure 1. The water sample to be treated is swimming pool water after disinfection in a certain swimming pool, wherein the types of DBPs are THMs and HAAs (haloacetic acids). Mainly, THMs and HAAs fluctuate between 230μg / L-260μg / L and 140μg / L-420μg / L respectively. The method includes the following steps:
[0049] (1) Enhanced coagulation:
[0050] Adding water to polyferric sulfate with an iron content of 25wt% makes it a coagulant with a concentration of 5 mg / L;
[0051] Add water to cationic polyacrylamide with a molecular weight of 3000kDa to prepare a coagulant aid with a concentration of 20mg / L;
[0052] Put the coagulant and coagulant aid into the water sample to be treated, the dosage is 50mg / L and 0.15mg / L in turn, adjust the pH value to 8 and then stir, the stirring speed is 400r / min, the stirring time for 15 minutes, then let stan...
Embodiment 2
[0065] This embodiment is a method for removing disinfection byproducts in water. The water sample to be treated is tap water in a certain city as an example. THMs and HAAs fluctuate between 10 μg / L-35 μg / L and 1.4 μg / L-4.5 μg / L respectively. Method steps are similar to embodiment 1, difference is:
[0066] (1) Enhanced coagulation:
[0067] Adding water to polyferric sulfate with an iron content of 15wt% makes it a coagulant with a concentration of 15mg / L;
[0068] Add water to cationic polyacrylamide with a molecular weight of 3000kDa to prepare a coagulant aid with a concentration of 23mg / L;
[0069] Put the coagulant and coagulant aid into the water sample to be treated, the dosage is 40mg / L and 0.10mg / L in turn, adjust the pH value to 7.5 and then stir, the stirring speed is 60r / min, the stirring time for 15 minutes, then stand still for 15 minutes;
[0070] (2) Ultrafiltration:
[0071] The ultrafiltration membrane module 2 comprises an ultrafiltration membrane, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0079] This embodiment is a method for removing disinfection byproducts in water. The water sample to be treated is tap water in a certain city as an example. THMs and HAAs fluctuate between 10 μg / L-35 μg / L and 1.4 μg / L-4.5 μg / L respectively. Method steps are similar to embodiment 1, difference is:
[0080] (1) Enhanced coagulation:
[0081] Adding water to polyferric sulfate with an iron content of 20wt% makes it a coagulant with a concentration of 15 mg / L;
[0082] Add water to cationic polyacrylamide with a molecular weight of 3000kDa to prepare a coagulant aid with a concentration of 24mg / L;
[0083] Put the coagulant and coagulant into the water sample to be treated, the dosage is 45mg / L and 0.096mg / L in turn, adjust the pH value to 6.41 and then stir, the stirring speed is 200r / min, the stirring time for 20min, then stand still for 20min;
[0084] (2) Ultrafiltration:
[0085] The ultrafiltration membrane module 2 comprises an ultrafiltration membrane, and the ultraf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com