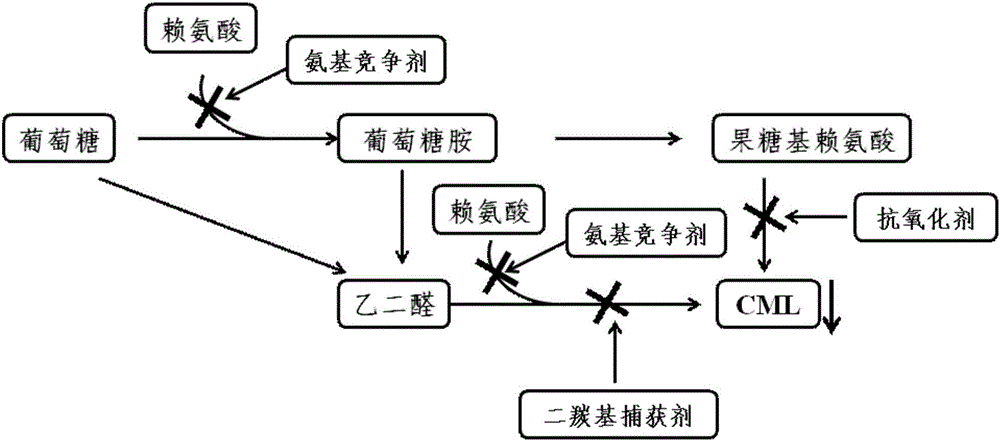
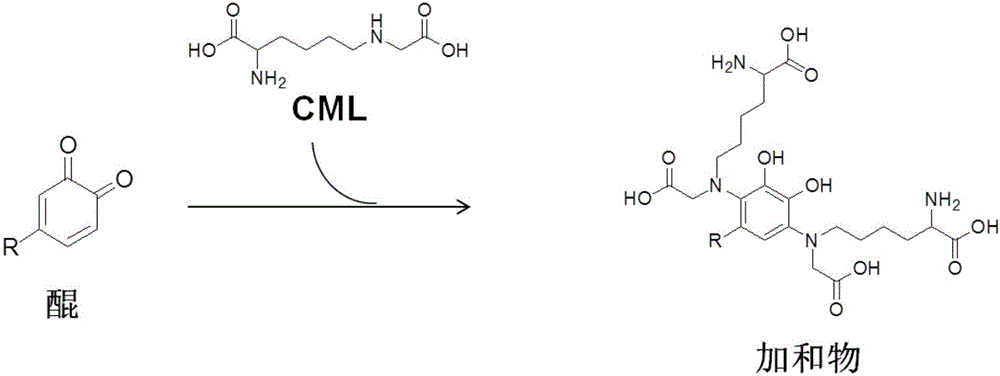
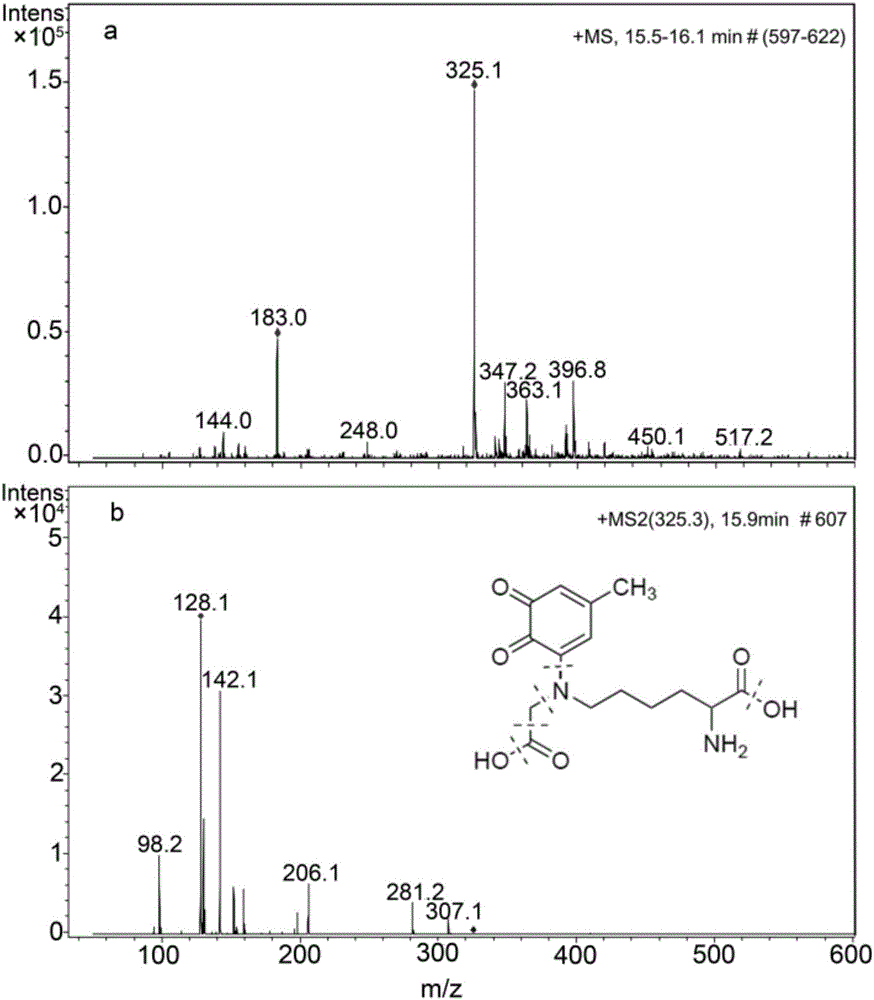
Class-I carboxymethyl lysine removing agent and application thereof
A carboxymethyllysine and elimination agent technology, which is applied in the field of carboxymethyllysine elimination preparations, can solve the problems of inability to eliminate and completely inhibit AGEs, and achieve the reduction of CML levels, compensation for the ineffectiveness of AGEs, and good elimination The effect of action
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] Identification of 4-methyl-phthaloquinone (4MBQ) capture CML ability and identification of the structure of the additive product, specifically including the following steps:
[0073] (1) Prepare 4MBQ solution with 0.2M phosphate buffer (pH 4.5) so that its concentration is 0.08mM;
[0074] (2) Prepare a solution of 1-10 mM CML with 0.2 M phosphate buffer, so that after mixing with the above (1) solution in equal volume, the pH is 5.0, 7.0 or 8.0;
[0075] (3) Use Stopped-flow to measure the reaction kinetics of 4MBQ and CML by monitoring the absorbance change of the reaction system in the ultraviolet-visible region (200-750nm) at 25°C;
[0076] (4) Prepare a solution in which CML is 10 mM and 4MBQ is 1 mM with 0.2 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.0);
[0077] (5) Stir the mixed liquid described in (4) at room temperature for 1 min, and process it through a 0.22 μm microfiltration membrane to obtain the test solution;
[0078] Finally, LC-ESI-MS / MS was used to detect the prepa...
Embodiment 2
[0097] The structural identification of epicatechin (EC) quinones capturing CML addition products specifically includes the following steps:
[0098] (1) Use 0.2M phosphate buffer (pH 8.0) to prepare solutions with 0.1M lysine (Lys) and 0.1M glucose (Glu) respectively to simulate the food system;
[0099] (2) Take 1mL of the simulated food system described in (1), and add 2mM EC quinone;
[0100] (3) Heat the sample in a water bath at 80°C for 1 hour;
[0101] (4) Take 1 mL of the heated sample, add distilled water to make up to 5 mL;
[0102] (5) Take 1 mL of the diluted solution and pass it through a 0.22 μm microfiltration membrane, and use UPLC-ESI-MS / MS to carry out structural identification of the adduct.
[0103] Described UPLC adopts Agilent SB1290 model, and detection condition is:
[0104] Column: Agilent SB-C 18 Chromatographic column 2.1×50mm, 1.8μm
[0105] Column temperature: 25°C
[0106] Mobile phase: A) formic acid: water = 1:1000 (v:v), B) acetonitrile ...
Embodiment 3
[0119] The structural identification of epicatechin (EC) quinones capturing CML addition products specifically includes the following steps:
[0120] (1) Use 0.2M phosphate buffer (pH 8.0) to prepare solutions with 0.1M lysine (Lys) and 0.1M glucose (Glu) respectively to simulate the food system;
[0121] (2) Take 1mL of the simulated food system described in (1), and add 2mM EC quinone;
[0122] (3) Heat the sample in a water bath at 100°C for 1 hour;
[0123] (4) Take 1 mL of the heated sample, add distilled water to make up to 5 mL;
[0124] (5) Take 1 mL of the diluted solution and pass it through a 0.22 μm microfiltration membrane, and use UPLC-ESI-MS / MS to carry out structural identification of the adduct.
[0125] Described UPLC adopts Agilent SB1290 model, and detection condition is:
[0126] Column: Agilent SB-C 18 Chromatographic column 2.1×50mm, 1.8μm
[0127] Column temperature: 25°C
[0128] Mobile phase: A) formic acid: water = 1:1000 (v:v), B) acetonitrile...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com