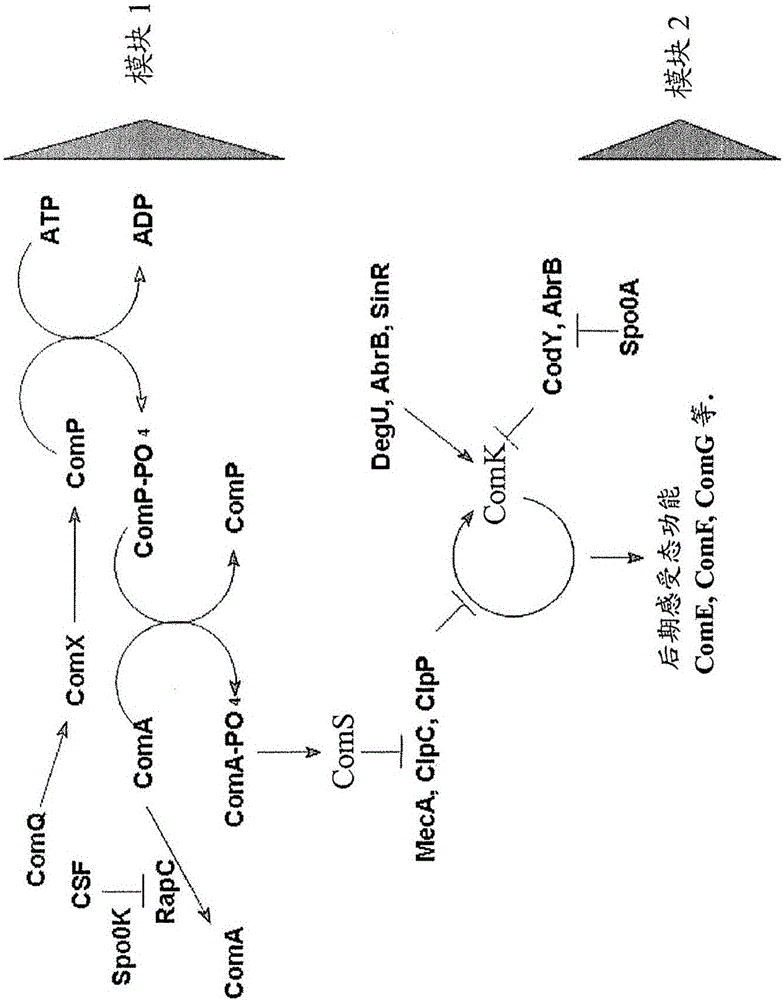
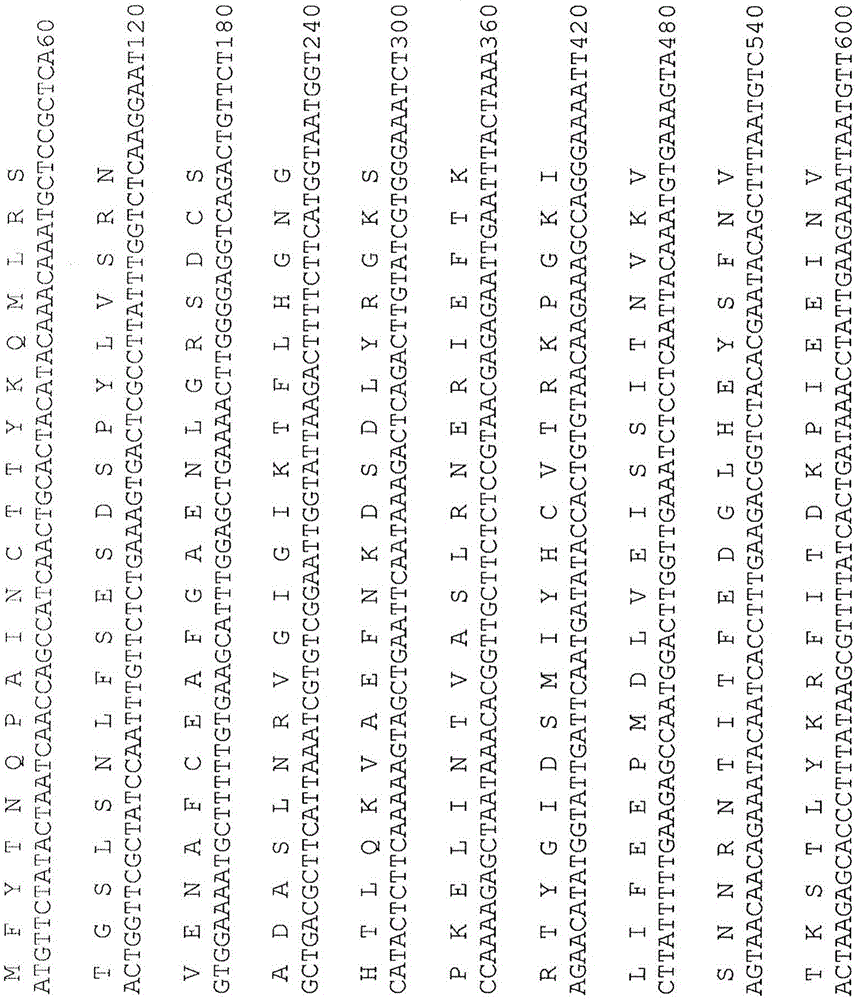
Methods of obtaining genetic competence in bacillus cells
A technology of Bacillus genus and competence, which is applied in the field of obtaining genetic competence, and can solve problems such as the inability to prove the transformation of Bacillus licheniformis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0260] DNA sequencing
[0261] Using Applied Biosystems Model 3130X Genetic Analyzer (3130X Genetic Analyzer) (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), utilize dye terminator chemistry (dye terminatorchemistry) (Giesecke etc., 1992, Journal of Virol.Methods 38:47- 60) Perform DNA sequencing. Sequences were assembled with sequencing specific primers using phred / phrap / consed (University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA).
[0262] coli strain
[0263] Use ONE TOP10 chemically competent Escherichia coli cells (Invitrogen Corporation, Carlsbad, CA, USA), Competent E. coli cells (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA), XL1-Blue competent E. coli cells (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA), and Gold supercompetent E. coli cells (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA) were used for routine plasmid construction and propagation.
[0264] Bacillus strains
[0265] B. subtilis 168Δ4 is derived from B. subtilis type strain 168 (BGSC 1A1, Bacillus Genetic Stock Center, Columbus, OH, USA) and has dele...
Embodiment 1
[0283] Example 1: Determination of the Genome Sequence of Bacillus licheniformis Strain SJ1904
[0284]From contigs generated using 454 DNA sequencing technology (Margulies et al., 2005, Nature 437:376-380), random paired reads using Sanger sequencing technology, and for closing gaps and resolving repetitive sequences Reads from PCR fragments of genomic DNA, determining the genome sequence of the complete chromosome of Bacillus licheniformis strain SJ1904. Sequencing data was assembled using Phrap and edited and viewed in Consed. Gene models were predicted from genomic DNA sequences using Glimmer (Delcher et al., 1999, Nucleic Acids Research 27:4636-4641). Use an E-value threshold of 1X10 -5 BLASTP for machine annotation of gene models by comparison with the non-redundant database PIR-NREF (Wu et al., 2002, Nucleic Acids Research 30:35-37).
Embodiment 2
[0285] Example 2: Identification of Bacillus licheniformis M.Bli1904II DNA methyltransferase gene
[0286] The deduced amino acid sequence of the gene model of B. licheniformis strain SJ1904 was compared with the protein sequence from REBASE (Roberts, R.J., Macelis, M., Rebase. 2005) using BLASTP (Altschul et al., 1997, Nucleic Acids Research 25:3389-3402). Compare. Because DNA methyltransferases have a moderate level of sequence conservation, this analysis identified all putative DNA methyltransferases in this genome. The cytosine-specific DNA methyltransferase signature in M.Bli1904II was identified using Prints-S version 16 performed by InterProScan version v3.3. In addition, six highly conserved motifs (motifs) found in cytosine-specific DNA methyltransferases were also conserved in Bacillus licheniformis M. Bli1904II DNA methyltransferase.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com