Machine tool working step energy consumption monitoring method based on least square iterative algorithm
A least squares, iterative algorithm technology, applied in computer control, instruments, simulators, etc., can solve problems such as high price and easy environmental impact, performance or cost that are unacceptable to enterprises, and affecting the rigidity of machine tools.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
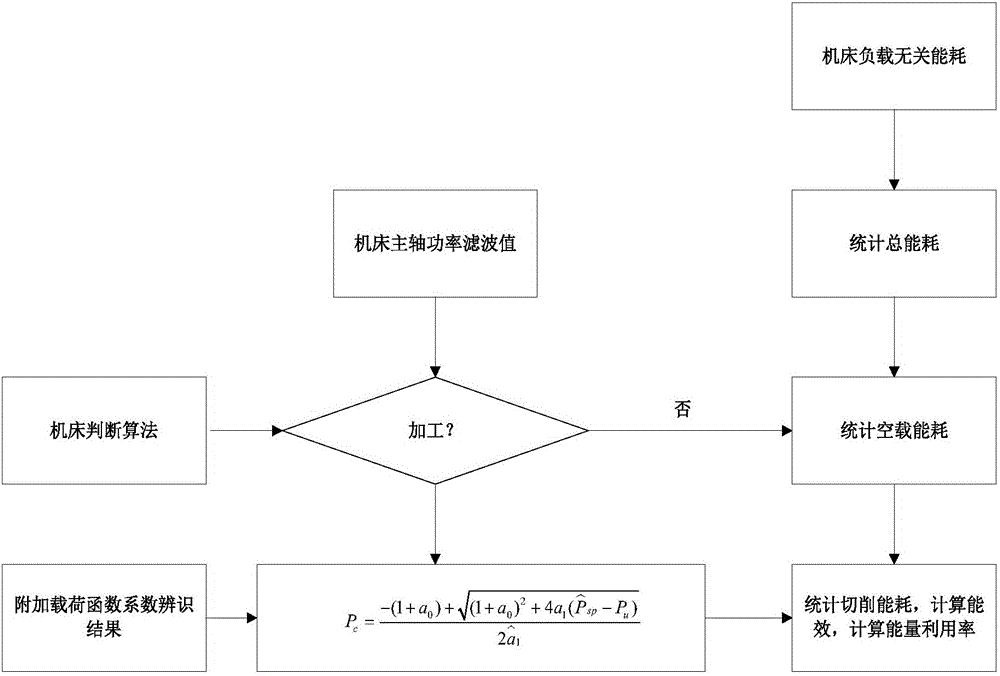
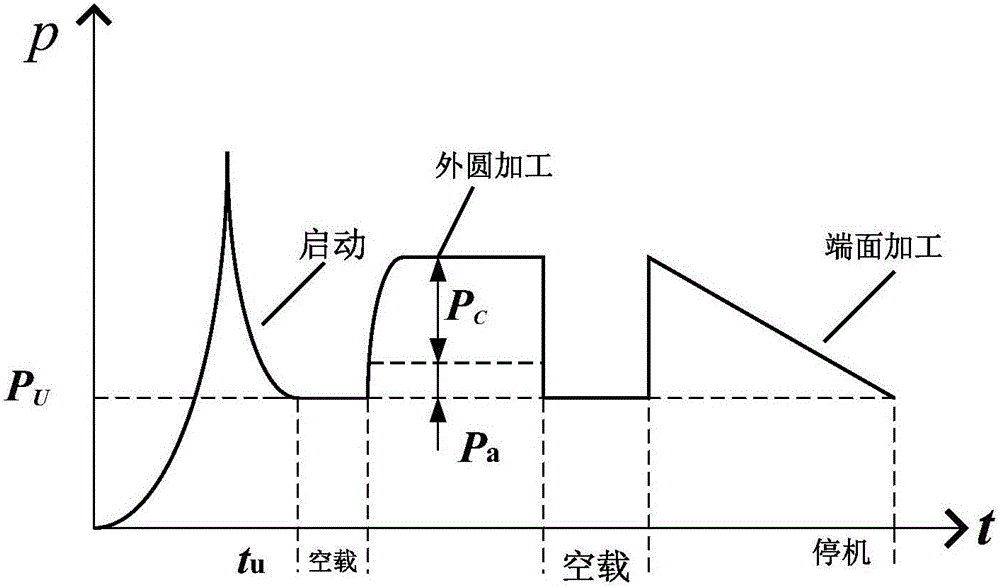
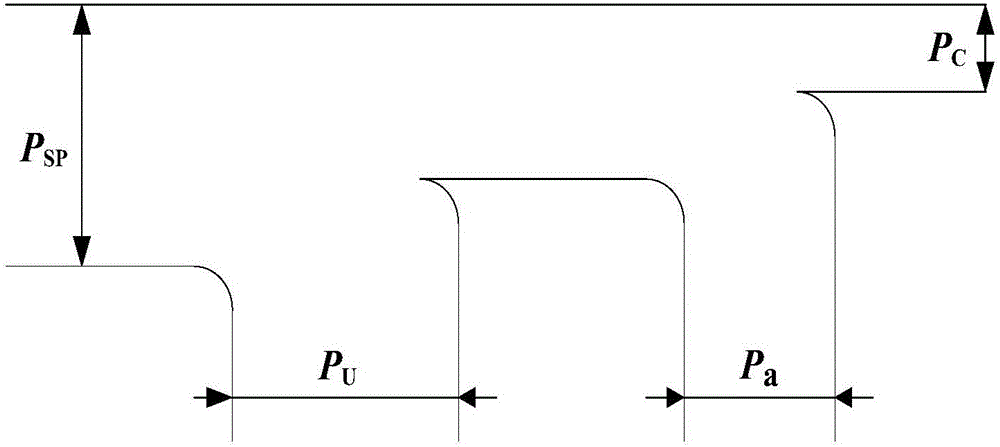
[0065] The invention establishes the on-line monitoring of the energy consumption state of the machine tool with the aim of obtaining the monitoring and acquisition of the energy consumption of the machine tool step, and accurately obtains the cutting power parameter by the least square iterative algorithm. The method specifically includes the following steps:
[0066] 1. Filter processing of power signal:
[0067] The working environment of the factory workshop is harsh, and the voltage and current of the power signal are susceptible to fluctuations and noise interference in this environment.
[0068] The present invention uses a sliding filter to estimate the no-load power.
[0069] P ^ s p ( n ) = 1 n ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com