Patient movement demand-based assistance lower limb rehabilitation robot self-adaptation control method
A technology of rehabilitation robot and self-adaptive control, which is applied in the direction of sports accessories, passive exercise equipment, gymnastic equipment, etc. It can solve the problems of low control precision, poor anti-interference, and difficulty in realizing adaptive control, so as to reduce costs and improve intelligence. The effect of personalized, continuous and seamless auxiliary control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
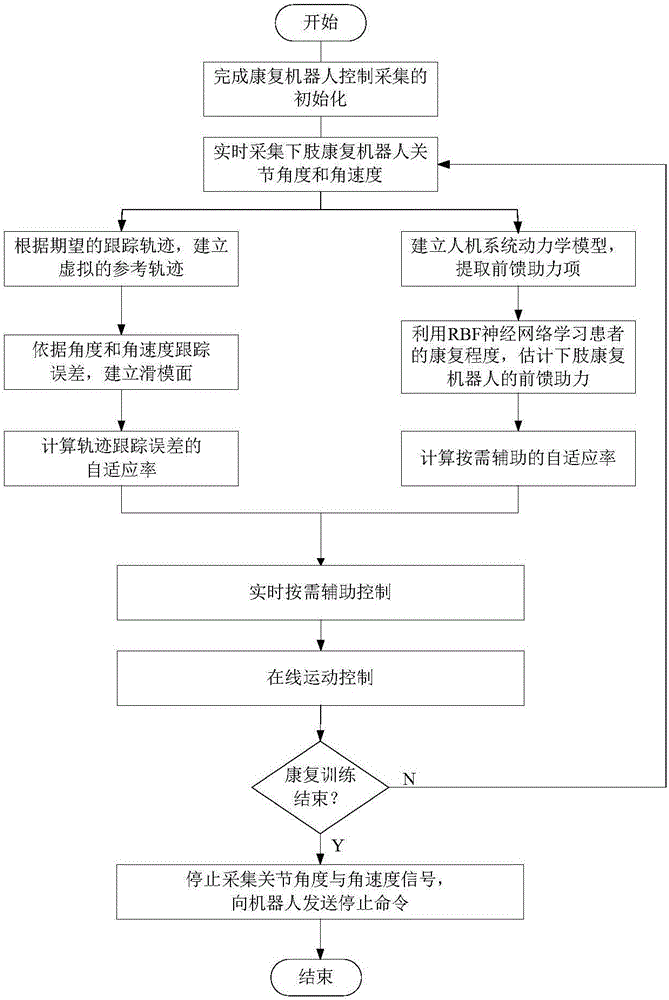
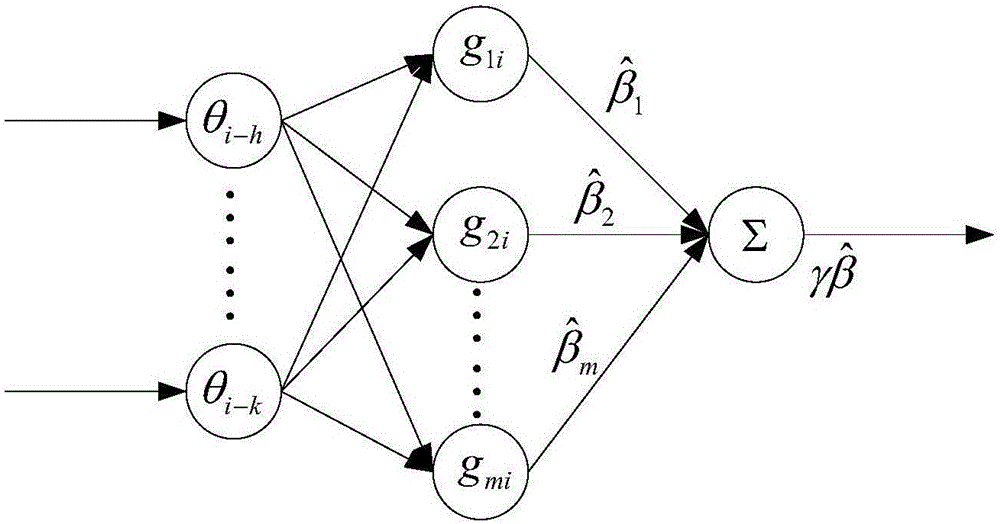
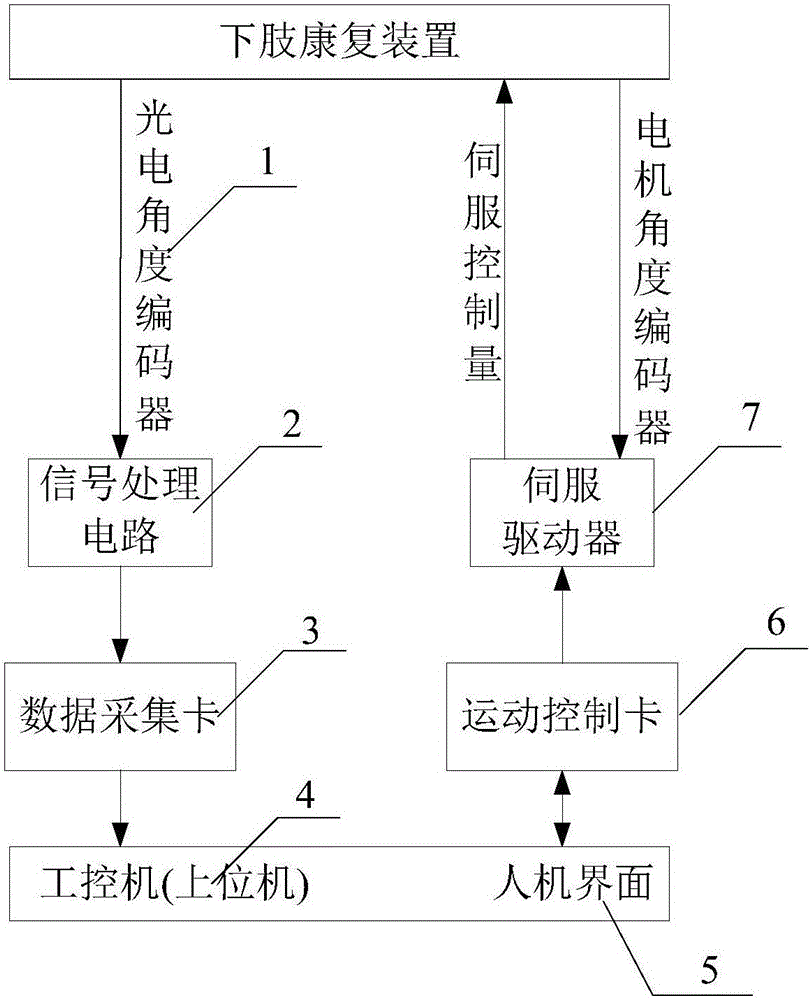
[0047] see figure 1 and image 3 , the self-adaptive control method of the lower limb rehabilitation robot that is continuously and seamlessly assisted by the patient's movement needs: firstly, the joint angle and joint angular velocity signals of the patient's lower limb hip joint and knee joint are collected in real time, and the robust variable structure control method is used to achieve the desired Trajectory adaptive tracking control; then, combined with the dynamics model of the human-machine system, the RBF (Gaussian Radial Basis) neural network is used to learn the patient's rehabilitation degree and active movement ability in real time, and then estimate the feedforward assistance of the lower limb rehabilitation robot; again, Adaptively attenuate the real-time assistance of the robot based on the trajectory tracking error, maximize the active movement ability of the patient, and realize the continuous adaptive auxiliary control according to the patient's rehabilitati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com