Semiconductor heterostructure, its preparation method and application
A heterogeneous structure, semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems that affect the quality of AlInN crystals and device performance, uneven material composition, fluctuations in In composition, etc., to achieve Achieve high-quality epitaxial growth, improve immiscibility, and eliminate reliability problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1 The Al contained in the device of this embodiment x In y Ga 1-x-y The N / GaN heterojunction can be fabricated as follows, where Al x In y Ga 1-x-y The specific composition of N is: aluminum component x=33%, indium component y=7%, gallium component 1-x-y=60%.
[0054] I. Non-pulse growth mode
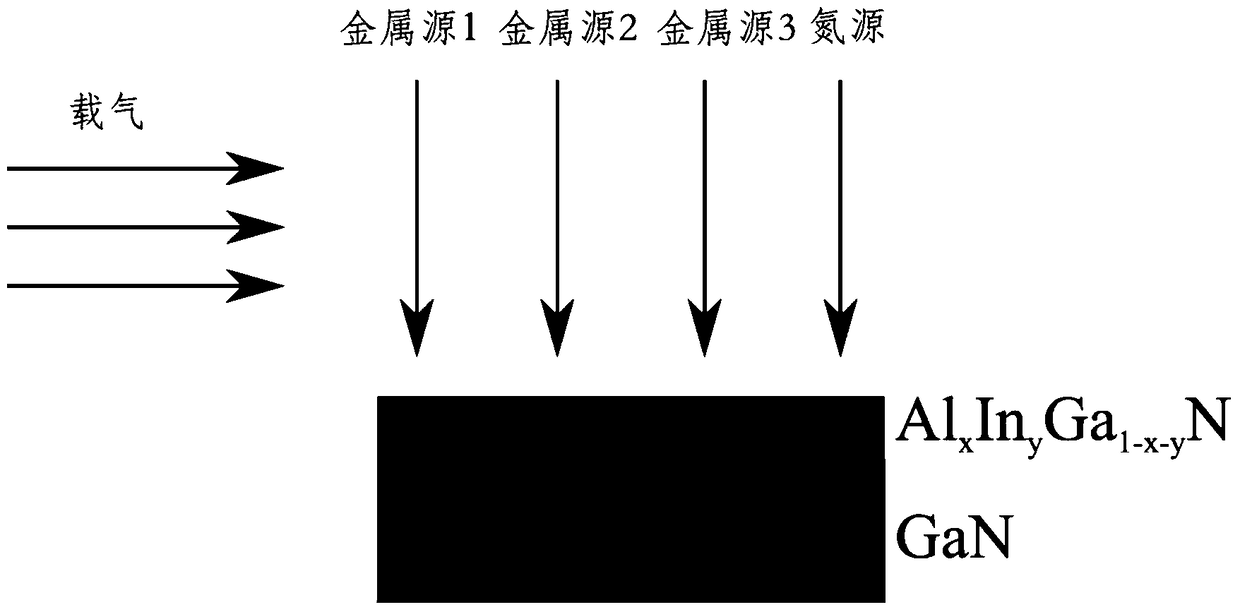
[0055] (1) GaN channel layer growth (assuming that the epitaxial growth of the nucleation layer, stress control layer, and buffer layer has been completed). The carrier gas is hydrogen, and the growth temperature is relatively high, 900-1200°C; the pressure of the reaction chamber is relatively high, 100-350mbar. The thickness of the GaN channel layer is more than 20nm, and the growth rate is 0.1-3μm / hr.
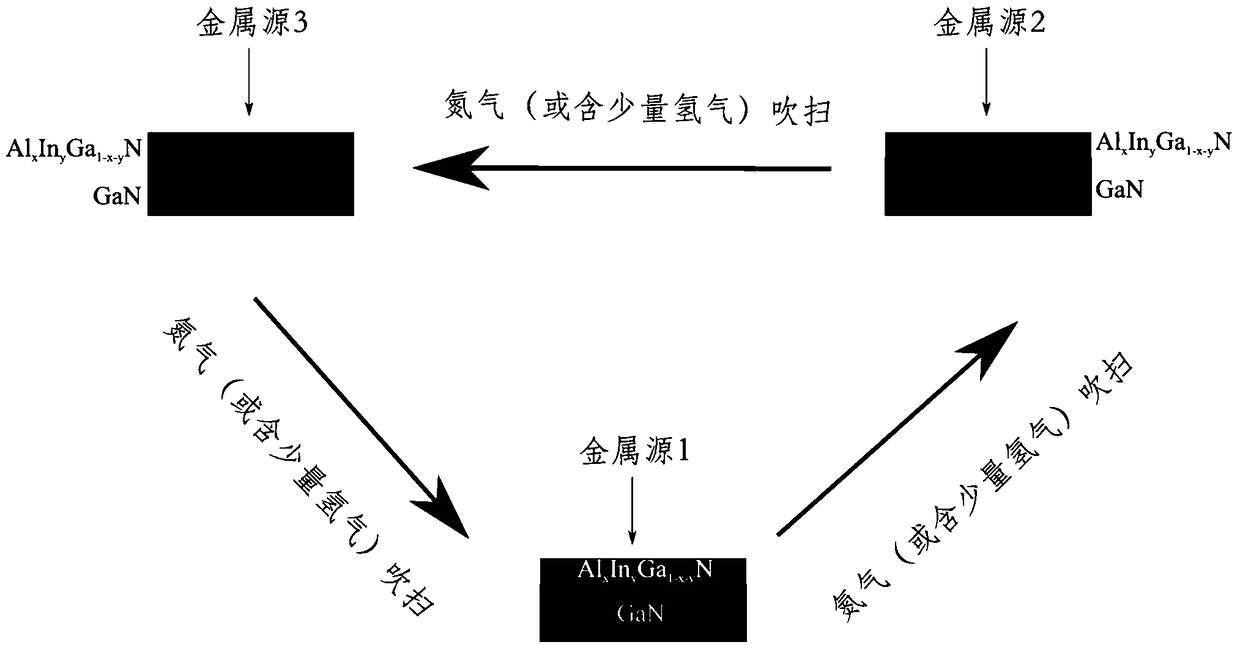
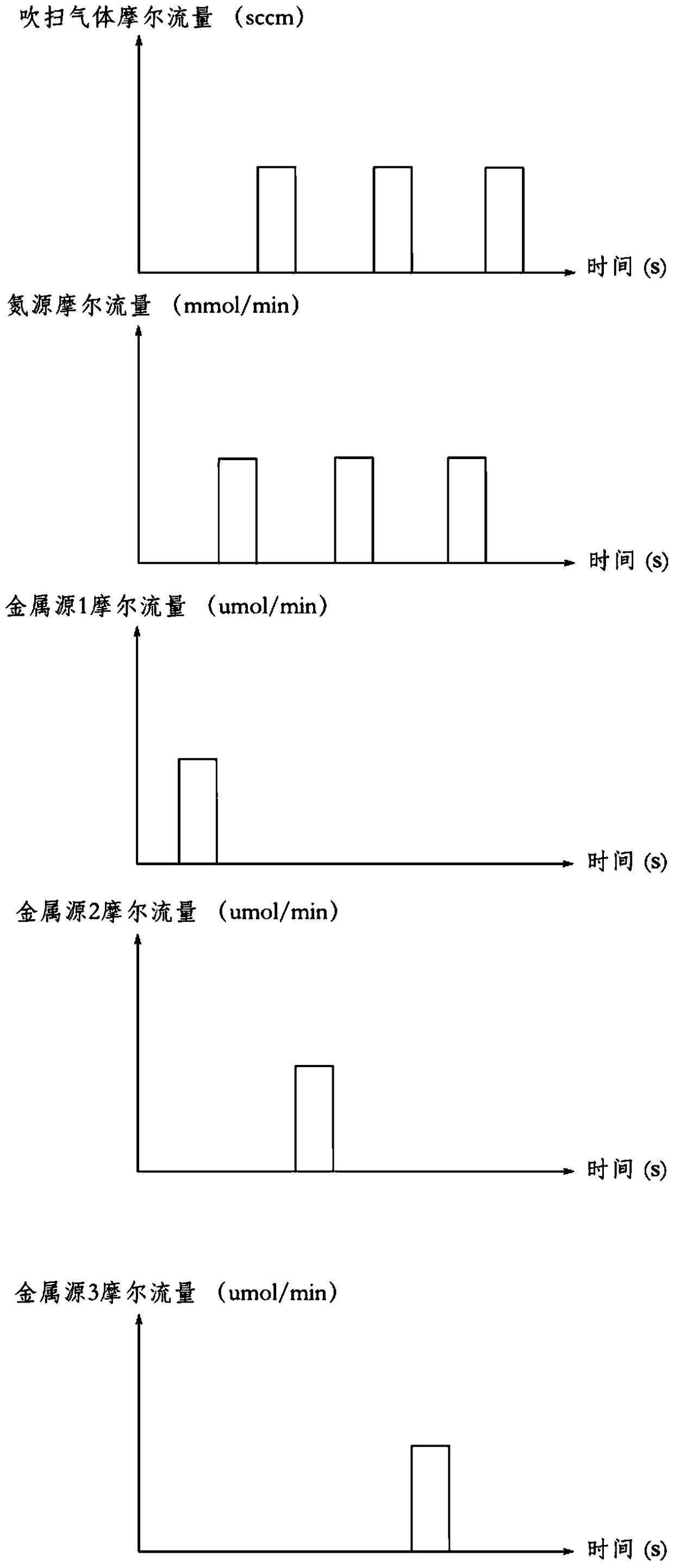
[0056] (2) Adjust the conditions of the reaction chamber to the growth conditions of the AlInGaN barrier layer. In the environment where ammonia (nitrogen source) is not turned off, the carrier gas is switched from hydrogen to nitrogen (or contains a small am...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2 The Al contained in the device of this embodiment x In y Ga 1-x-y The N / GaN heterojunction can be fabricated as follows, where Al x In y Ga 1-x-y The specific composition of N is: aluminum component x=66.01%, indium component y=13.99%, gallium component 1-x-y=20%
[0064]I. Non-pulse growth mode
[0065] (1) GaN channel layer growth (assuming that the epitaxial growth of the nucleation layer, stress control layer, and buffer layer has been completed). The carrier gas is hydrogen, and the growth temperature is relatively high, 900-1200°C; the pressure of the reaction chamber is relatively high, 100-350mbar. The thickness of the GaN channel layer is more than 20nm, and the growth rate is 0.1-3μm / hr.
[0066] (2) Adjust the conditions of the reaction chamber to the growth conditions of the AlInGaN barrier layer. In the environment where ammonia (nitrogen source) is not turned off, the carrier gas is switched from hydrogen to nitrogen (or contains a sma...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Embodiment 3 The Al contained in the device of this embodiment x In y Ga 1-x-y The N / GaN heterojunction can be fabricated as follows, where Al x In y Ga 1-x-y The specific composition of N is: aluminum component x=33.44%, indium component y=6.56%, gallium component 1-x-y=60%.
[0074] I. Non-pulse growth mode
[0075] (1) GaN channel layer growth (assuming that the epitaxial growth of the nucleation layer, stress control layer, and buffer layer has been completed). The carrier gas is hydrogen, and the growth temperature is relatively high, 900-1200°C; the pressure of the reaction chamber is relatively high, 100-350mbar. The thickness of the GaN channel layer is more than 20nm, and the growth rate is 0.1-3μm / hr.
[0076] (2) Adjust the conditions of the reaction chamber to the growth conditions of the AlInGaN barrier layer. In the environment where ammonia (nitrogen source) is not turned off, the carrier gas is switched from hydrogen to nitrogen (or contains a sm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com