Low-activity martensitic steel with high-temperature mechanical performance and heat treatment process
A technology of mechanical properties, martensitic steel, applied in the field of low activation martensitic steel with high temperature mechanical properties and heat treatment process, can solve the problem of inability to quickly enter the industrial application stage, poor stability between batches, single batch Small output and other problems, to achieve the effect of large-scale industrial production, simple method and good industrial base
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] (1) According to the composition ratio: Cr 9.0%, W 1.5%, V 0.2%, Ta 0.15%, Mn 0.45%, C0.10%, N 0.01~0.05%, Ni≤0.005%, Nb≤0.001%, Co ≤0.005%, Cu≤0.005%, Mo≤0.005%, P≤0.005%, S≤0.005%, O≤0.01%, Al≤0.01%, and the rest is Fe element and alloy burning loss ratio raw materials.
[0016] (2) In the vacuum induction furnace, raw materials are added sequentially according to the burning loss and volatilization characteristics of the alloy elements. The easy-to-oxidize alloy elements are added after they are fully deoxidized. The volatile alloy elements are added under the protection of the atmosphere or at the end of the smelting process. After smelting, an ingot with qualified composition is prepared.
[0017] (3) The prepared ingot is smelted by vacuum consumable arc to further reduce the impurity content.
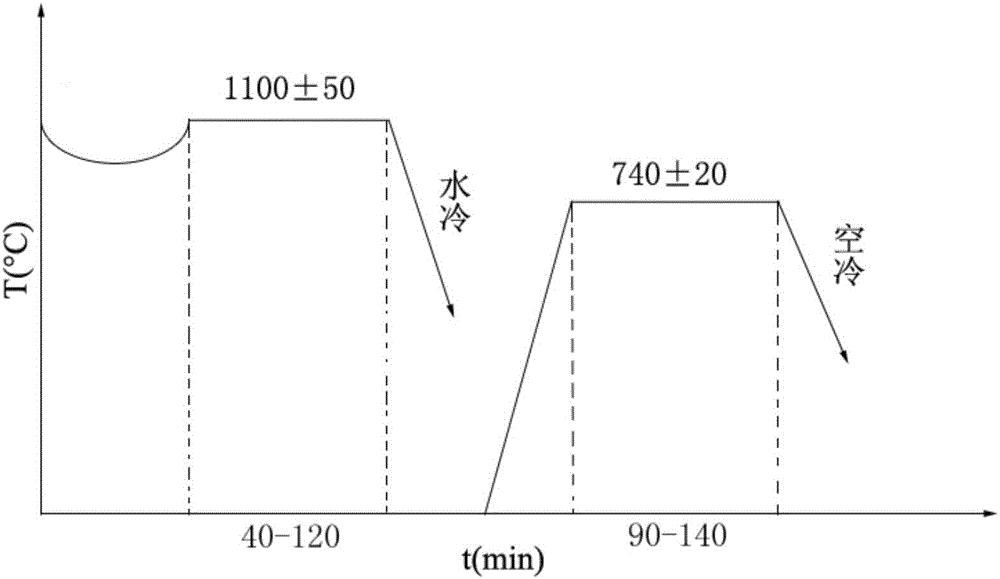
[0018] (4) Forging the ingot obtained in step (3), the initial forging temperature is 1150°C, the heat preservation is 60min, and the final forging temperature is 850°C. ...
Embodiment 2
[0025] (1) According to the composition ratio: Cr 9.0%, W 1.5%, V 0.2%, Ta 0.15%, Mn 0.45%, C0.10%, N 0.01~0.05%, Ni≤0.005%, Nb≤0.001%, Co ≤0.005%, Cu≤0.005%, Mo≤0.005%, P≤0.005%, S≤0.005%, O≤0.01%, Al≤0.01%, and the rest is Fe element and alloy burning loss ratio raw materials.
[0026] (2) In the vacuum induction furnace, raw materials are added sequentially according to the burning loss and volatilization characteristics of the alloy elements. The easy-to-oxidize alloy elements are added after they are fully deoxidized. The volatile alloy elements are added under the protection of the atmosphere or at the end of the smelting process. After smelting, an ingot with qualified composition is prepared.
[0027] (3) The prepared ingot is smelted by vacuum consumable arc to further reduce the impurity content.
[0028] (4) Forging the ingot obtained in step (3), the initial forging temperature is 1150°C, the heat preservation is 60min, and the final forging temperature is 850°C. ...
Embodiment 3
[0035](1) According to the composition ratio: Cr 9.0%, W 1.5%, V 0.2%, Ta 0.15%, Mn 0.45%, C0.10%, N 0.01~0.05%, Ni≤0.005%, Nb≤0.001%, Co ≤0.005%, Cu≤0.005%, Mo≤0.005%, P≤0.005%, S≤0.005%, O≤0.01%, Al≤0.01%, and the rest is Fe element and alloy burning loss ratio raw materials.
[0036] (2) In the vacuum induction furnace, raw materials are added sequentially according to the burning loss and volatilization characteristics of the alloy elements. The easy-to-oxidize alloy elements are added after they are fully deoxidized. The volatile alloy elements are added under the protection of the atmosphere or at the end of the smelting process. After smelting, an ingot with qualified composition is prepared.
[0037] (3) The prepared ingot is smelted by vacuum consumable arc to further reduce the impurity content.
[0038] (4) Forging the ingot obtained in step (3), the initial forging temperature is 1150°C, the heat preservation is 60min, and the final forging temperature is 850°C. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com