A method for imitating ecological reproduction and healthy and efficient breeding of snakeheads
A breeding method and a technology of imitating ecology, which are applied in the field of imitation ecological reproduction and healthy and high-efficiency breeding of the moon snake, can solve the problems of not fully grasping the growth characteristics of the moon snake, inconvenient operation, and the survival rate of commercial fish is less than 60%. The effect of reducing the incidence of skin and internal organs, reducing the difficulty and cost of construction, saving bait and labor costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
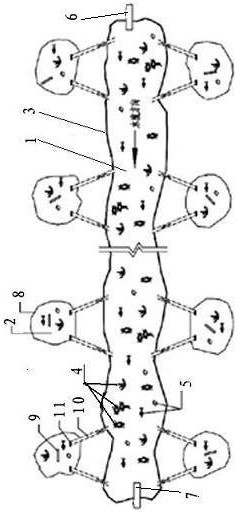
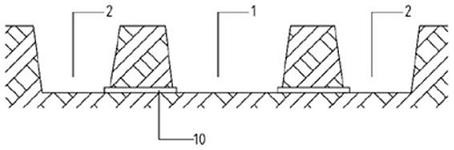
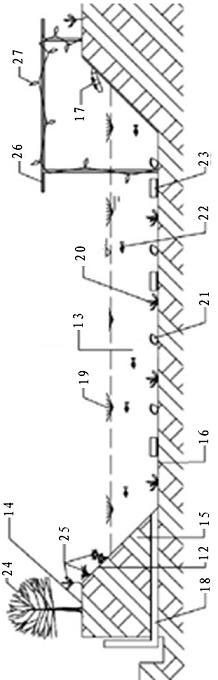
[0051] see figure 1 —— image 3 The technical solution adopted by the present invention to solve its technical problems is: the present invention is a method for imitating ecological reproduction and healthy and efficient breeding of snakeheads, including the construction of breeding mud ditch and the construction of breeding mud ponds, the imitation of ecological reproduction and healthy and efficient breeding of snakeheads, The breeding process is as follows: selection of fish species and cultivation before March of the first year - natural pairing of fish species into the spawning cultivation pond to spawn from April to August of the first year - hatching and cultivation of fish eggs from May to September of the first year Cultivation of seedlings - from June to October, the seedlings are graded and put into breeding mud ponds for cultivation - the adult fish will start to market in January of the second year.
[0052] Specific steps are as follows:
[0053] Step 1: Breed...
Embodiment 2
[0086] see figure 1 —— image 3 , the operation method step of embodiment 2 is identical with embodiment 2, and difference is that the length of breeding mud ditch body is 20m, and ditch width is 1.5m--2.0m, and ditch depth is 50cm--60cm. 20 spawning ponds were built on both sides of the ditches, and 24 pairs of preliminary classified species were put in. For details, see Example 1——Example 3 Effect Comparison Table
Embodiment 3
[0088] see figure 1 —— image 3 , the operation method step of embodiment 3 is identical with embodiment 1, and difference is that the length of breeding mud ditch body is 30m, and ditch width is 1.5m--2.0m, and ditch depth is 50cm--60cm. Build 30 spawning ponds on both sides of the ditches, and release 36 pairs of preliminary classified fish.
[0089] Embodiment 1——Example 3 breeding effect comparison table
[0090] Example Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Breeding mud ditch length (m) 10 20 30 Number of spawning ponds (units) 10 20 30 The number of primary species of fish (pair) 12 24 36 Number of successfully paired fish species (pairs) 9 19 29 Breeding fish pairing rate (%) 75 79.1 80.6 Annual spawning times (times / year) 4 4 4 Average number of eggs laid per year (grass / pair) 14000 13140 13120 Fertilization rate (%) 85.3 85.5 85.2 Hatch rate (%) 90.2 90.8 90.6 Seed survival rate (%) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com