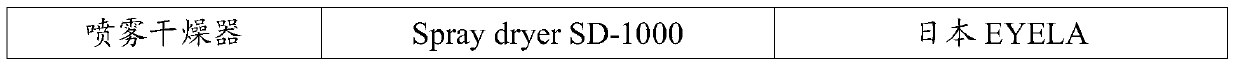High-protein yeast extract with mellow taste and preparation method and application thereof
A yeast extract, high-protein technology, applied in application, food science, food coating and other directions, can solve the problem of inability to solve the taste effect, and achieve the effect of enriching the taste experience, enhancing the mellow feeling, and enhancing the edge taste.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0057] In a preferred embodiment, the preparation method of the high-protein yeast extract with a unique mellow taste comprises the following steps: (1) set the concentration of high-protein yeast, perform autolytic enzymolysis, and obtain enzymes that meet the requirements and (2) centrifuging the enzymatic hydrolyzate obtained in step (1), and getting the light phase to concentrate or dust.
[0058] Preferably, in the above method for preparing yeast extract, in step (1), the enzymes added are mainly food-based enzymes, such as papain, yeast extract enzyme, nuclease, transglutaminase and the like.
[0059] In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the protein content of the raw material high-protein yeast in step (1) should reach more than 55% dry weight, preferably more than 68wt%, and the specific process of autolytic enzymolysis is: Heat the yeast solution at 90-100°C, react for 20-40 minutes, cool down at 45-68°C, pH 5.5-6.8, add food enzymes, perform enzymatic...
Embodiment 1
[0078] To prepare a high-protein yeast extract with a mellow taste, the steps are as follows:
[0079] (1) Fixed solution of high-protein yeast: Take 150 g of yeast (dried) and deionized water to prepare 1000 mL of solution, so that the mass fraction of yeast is 15%.
[0080] (2) Autolytic enzymolysis: Add the solution of step (1) into the autolytic enzymolysis tank, heat up to 95°C, react for 25 minutes, cool down to 55°C, adjust the pH of the solution to 6.0, add 0.3g papain, 0.15g nucleic acid Enzymes, 0.15 g of transglutaminase and 0.3 g of extractase, were used for enzymatic hydrolysis for 19 hours.
[0081] (3) Enzyme inactivation process: heat the product of step (2) to 85° C., and inactivate the enzyme for 1 hour.
[0082] (4) Cool down to 65°C and keep warm, use a centrifuge to centrifuge for 10 minutes at a speed of 5000r / min, take the light phase and evaporate it to a solid content of 40% in a concentrated evaporator, and use a spray dryer to obtain KOKUMI flavor ...
Embodiment 2~ Embodiment 6
[0084] According to the process conditions listed in Table 3 and Table 4, the operations of Embodiment 2 to Embodiment 6 were carried out.
[0085] The process condition of table 3 embodiment 1-embodiment 6
[0086] Process conditions Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Example 4 Example 5 Example 6
[0087] Initial heating temperature (°C) 95 95 90 100 90 100 Heating reaction time (min) 25 25 20 25 30 40 Temperature after cooling down (°C) 45 55 50 60 68 65 Autolysis time (h) 19 17 17 19 18 18 pH 6.0 5.5 6.8 6.0 6.0 6.5
[0088] Table 4 The amount of food enzymes added in Examples 1 to 6 (g)
[0089] Food enzyme / g Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Example 4 Example 5 Example 6 papain 0.3 0.25 0.35 0.3 0.3 0.25 nuclease 0.15 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.15 0.1 transglutaminase 0.15 0.1 0.2 0.15 0.15 0.15 extractase 0.3 0.25 0.3 0.25 0.25 0.2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com