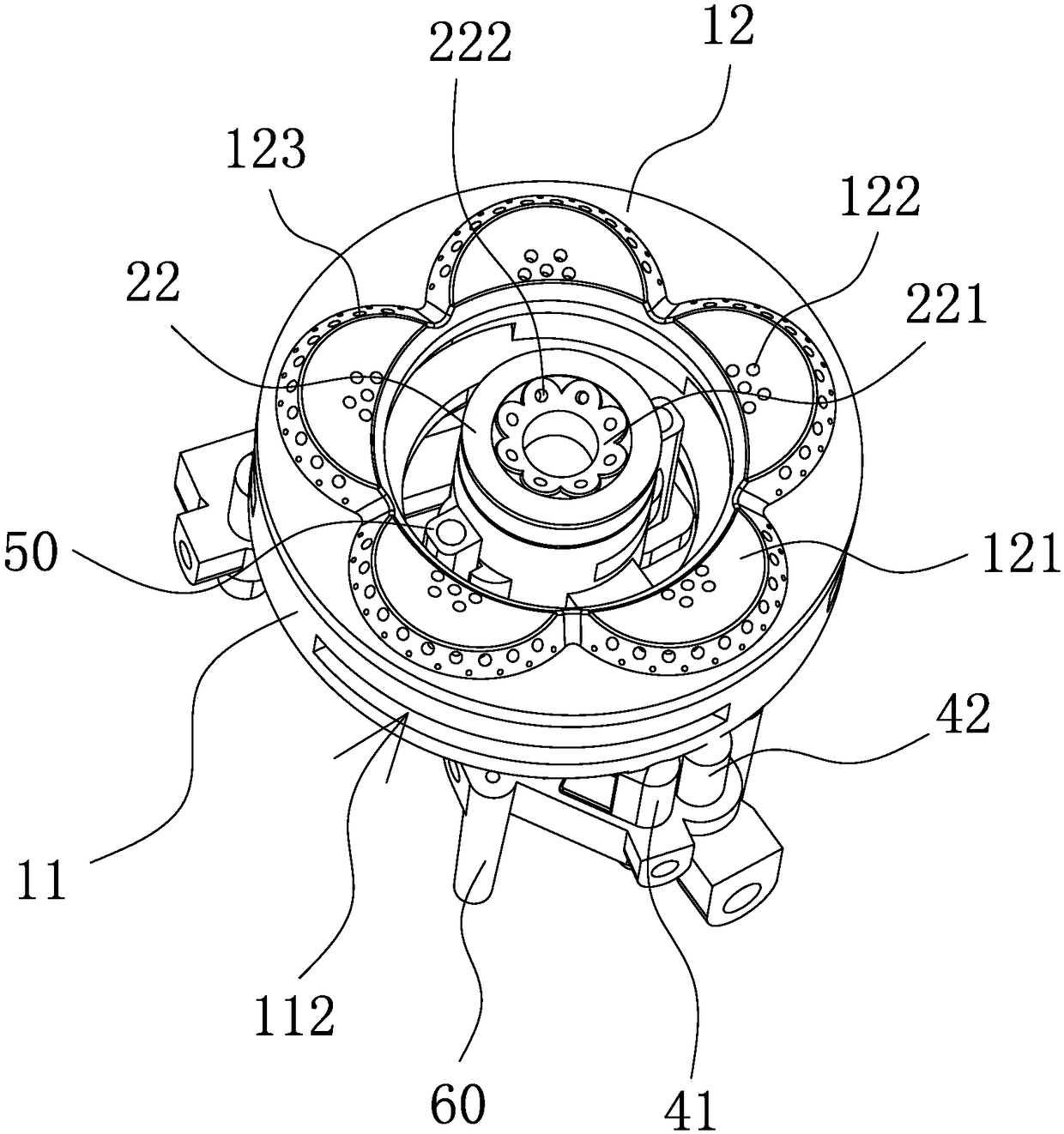
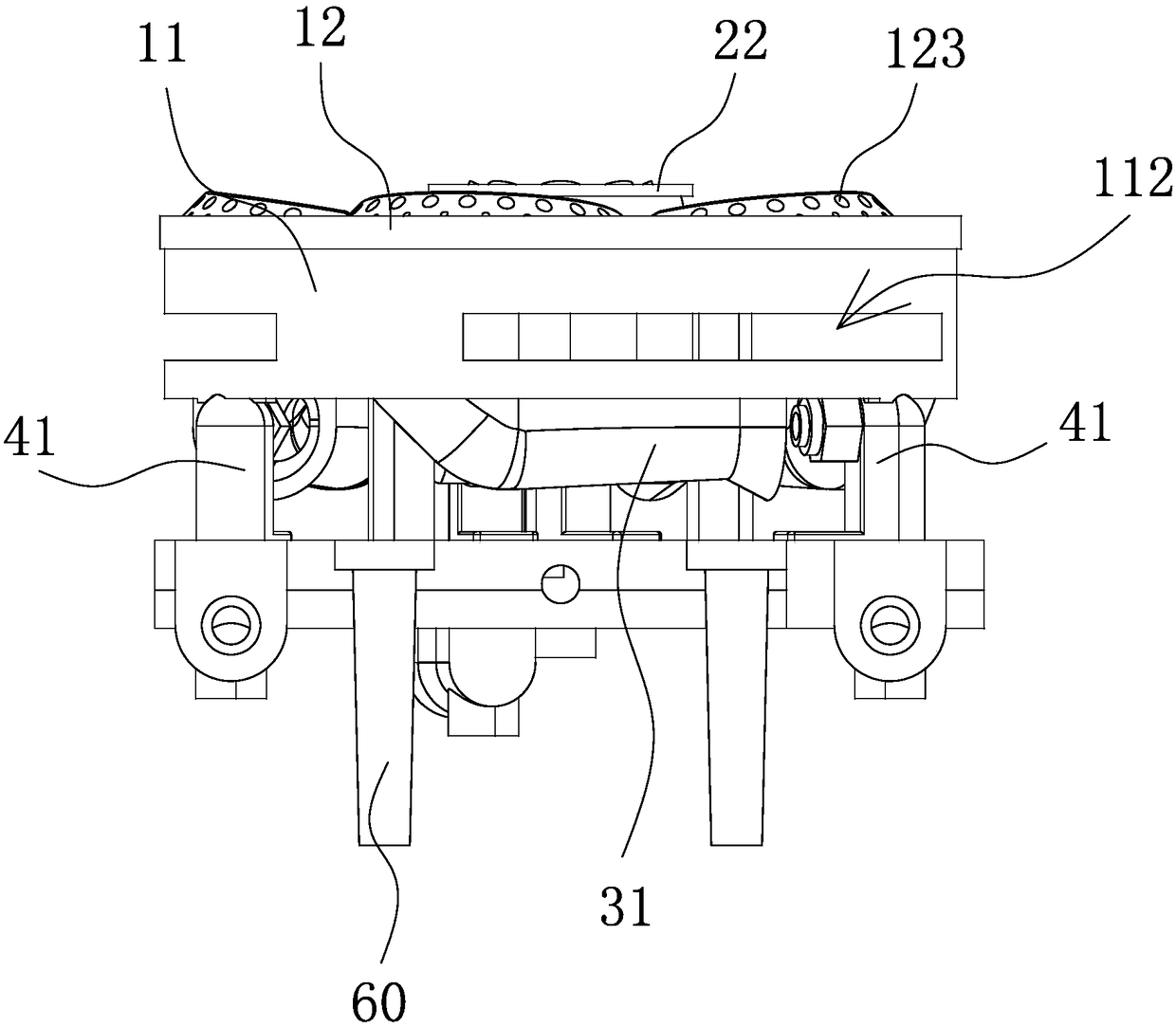
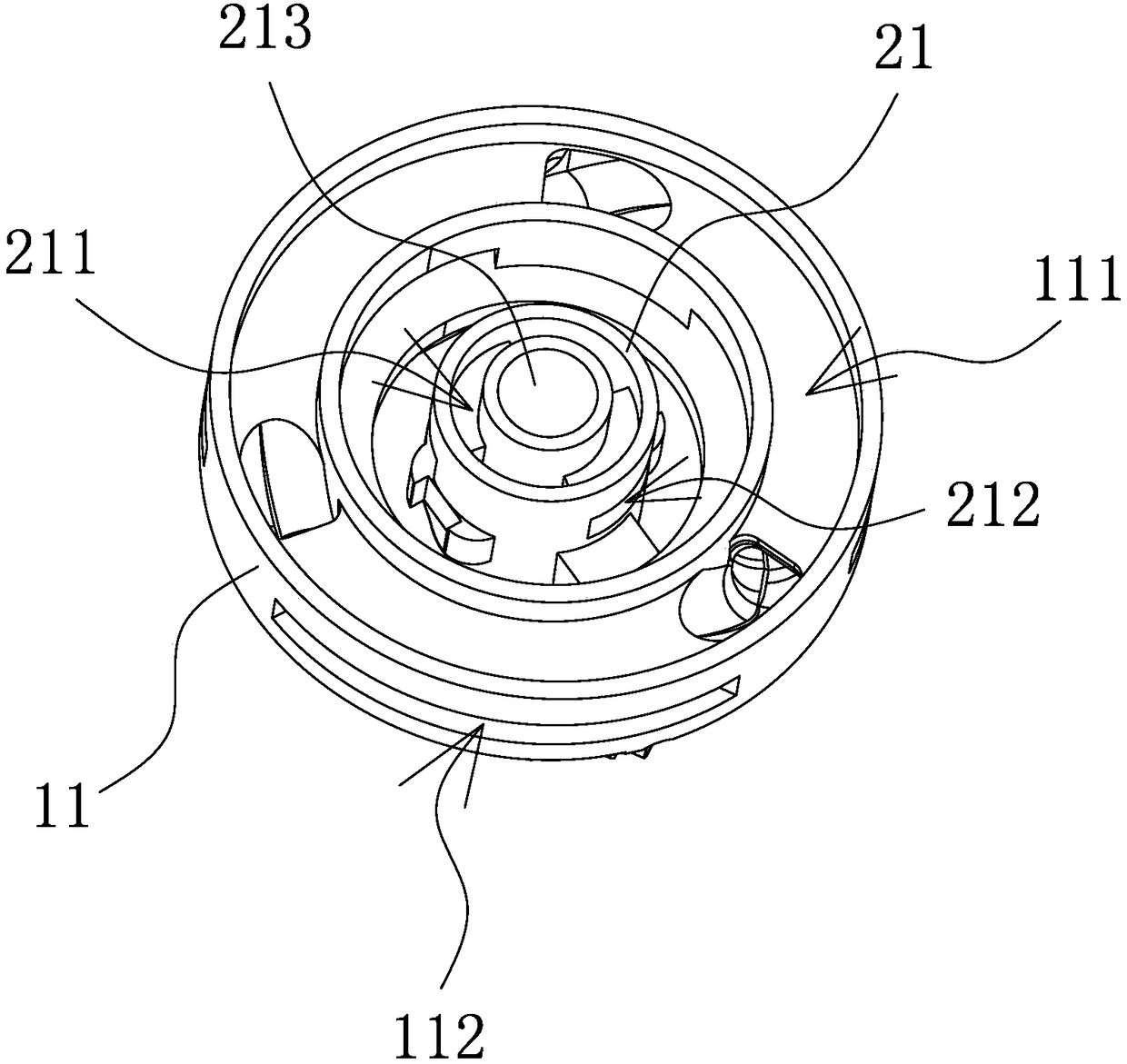
An improved burner
A burner, an improved technology, applied in the direction of burners, burners, burner material specifications, etc., can solve the problems of low safety, poor combustion effect, general strength, etc., and achieve reasonable structure design, prolong service life, gas Evenly distributed effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Pre-smelting treatment: according to the constituent elements and mass percentages of the magnesium alloy described in Table 1, Example 1, the charge is prepared, the charge is preheated to 160°C for use, and the crucible is preheated to dark red at 540°C for use;
[0069] Melting: Melt the prepared charge at 715°C into molten magnesium, stir evenly and continue to heat up to 755°C, refine and remove slag under the protection of argon;
[0070] Die-casting: Cool the magnesium liquid after refining and slag removal to 700°C, and then pour it into the mold cavity that has been preheated to 270°C for die-casting to obtain die-casting parts; among them, the pouring temperature is 725°C and the injection speed is The injection pressure is 9.2m / s, the injection pressure is 30MPa, and the filling time is 24ms.
[0071] Heat treatment: heat the die casting at 310°C for 12 hours, cool with the furnace, then raise the temperature to 390°C at a rate of 3.5°C / s and hold for 3 hours...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Pre-melting treatment: according to the constituent elements and mass percentages of the magnesium alloy described in Table 1, Example 2, the charge is prepared, the charge is preheated to 170°C for standby, and the crucible is preheated to dark red at 560°C for standby;
[0074]Melting: Melt the prepared charge into molten magnesium at 720°C, stir evenly and continue to heat up to 752°C, refine and remove slag under the protection of argon;
[0075] Die-casting: Cool the magnesium liquid after refining and slag removal to 710°C, and then pour it into the mold cavity that has been preheated to 275°C for die-casting to obtain die-casting parts; among them, the pouring temperature is 728°C and the injection speed is The injection pressure is 8.8m / s, the injection pressure is 32MPa, and the filling time is 25ms.
[0076] Heat treatment: heat the die casting at 305°C for 14 hours, cool with the furnace, then raise the temperature to 385°C at a rate of 3.2°C / s and keep it fo...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Pre-smelting treatment: according to the constituent elements and mass percentages of the magnesium alloy described in Table 1, Example 3, the charge is prepared, the charge is preheated to 155°C for standby, and the crucible is preheated to dark red at 520°C for standby;
[0079] Melting: Melt the prepared charge into molten magnesium at 710°C, stir evenly and continue to heat up to 758°C, refining and slag removal under the protection of argon;
[0080] Die-casting: Cool the magnesium liquid after refining and slag removal to 690°C, and then pour it into the mold cavity that has been preheated to 265°C for die-casting to obtain die-casting parts; among them, the pouring temperature is 722°C and the injection speed is The injection pressure is 10.2m / s, the injection pressure is 28MPa, and the filling time is 23ms.
[0081] Heat treatment: heat the die casting at 315°C for 12 hours, cool with the furnace, then raise the temperature to 395°C at a rate of 3.8°C / s and keep...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com