Acrylic fiber treatment agent and use thereof
A technology of acrylic fiber and treatment agent, applied in the direction of fiber treatment, fiber type, fiber chemical characteristics, etc., can solve the problems of broken wire operability, sintering furnace damage, narrowing of fiber bundle interval, etc., to prevent stable operability , The effect of preventing melt adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
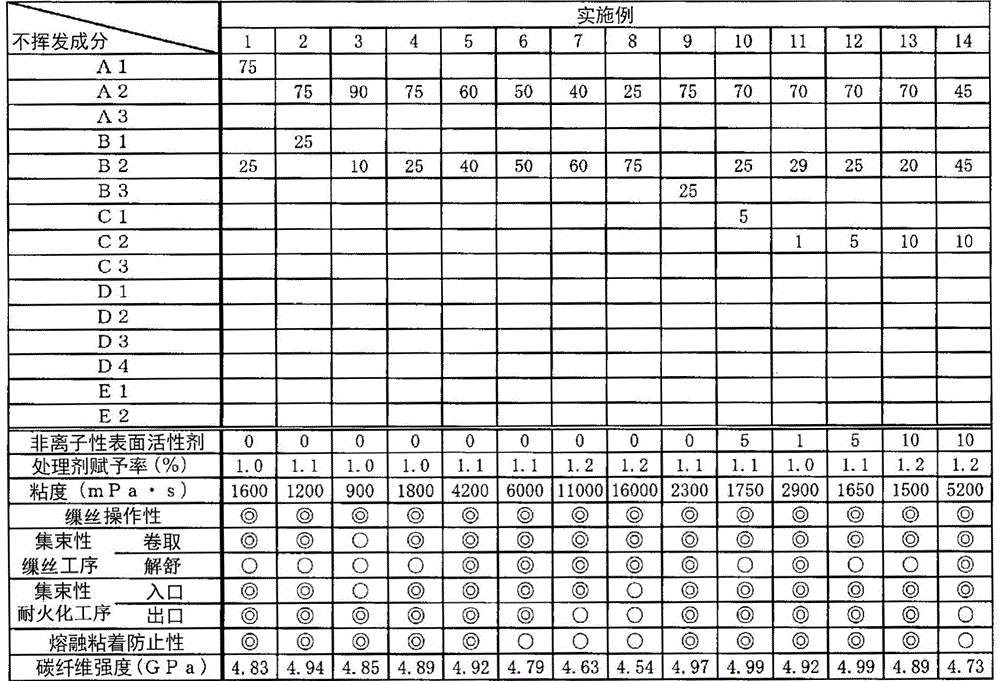
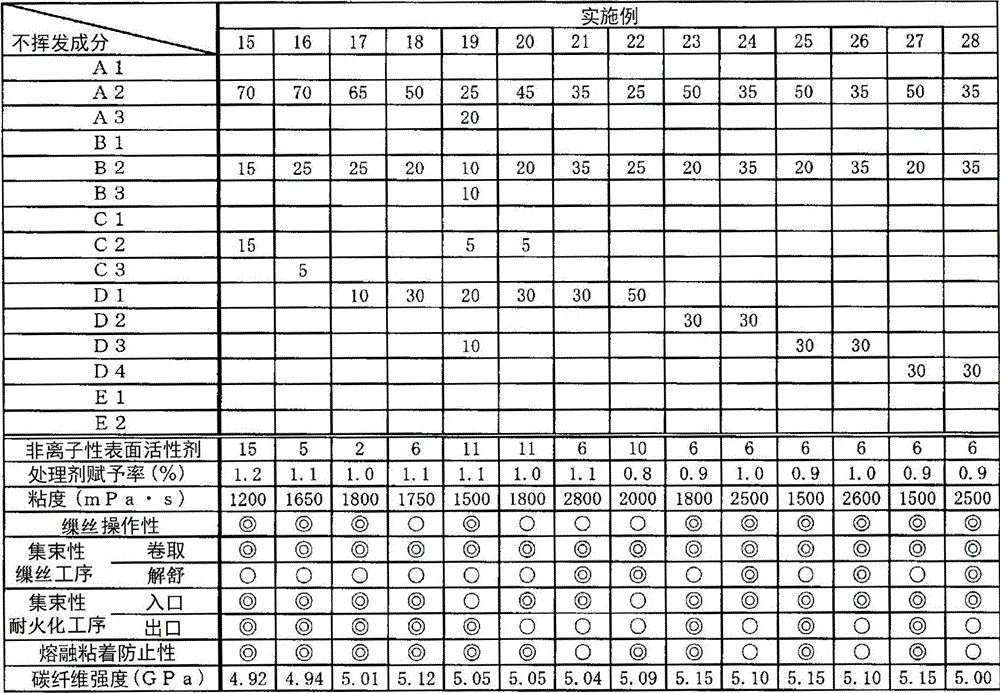
Embodiment 1~28、 comparative example 1~13
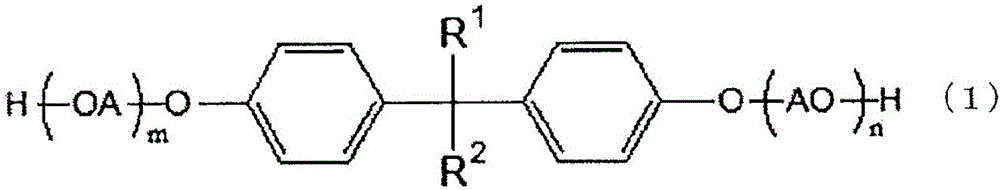
[0147] Water-based emulsification using the following compounds A1-A3, polyether compounds B1-B3, nonionic surfactants C1-C3, modified silicone D1-D4 prepared above, and ester-based compounds E1-E2 and water were mixed and stirred according to the non-volatile components shown in Tables 1 to 3 to prepare acrylic fiber treatment agents whose non-volatile components accounted for 20% by weight in the treatment agent. In addition, the numerical value in a table shows the weight ratio of each component in the non-volatile content of a processing agent. For example, the numerical values of the compounds A1 to A3 in the table represent the weight ratios of the compounds A1 to A3 in the non-volatile components of the treatment agent. In addition, the numerical value of the "nonionic surfactant" of Tables 1-3 shows the weight ratio (weight%) which a nonionic surfactant (total amount) occupies in a nonvolatile component.
[0148] Next, the prepared treatment agents were further dilu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com