Method for preparing novel Mn (IV) ion activated red luminescence material
A red light-emitting, ion technology, applied in the direction of light-emitting materials, chemical instruments and methods, can solve the problems of fluoride toxicity, limited application prospects, etc., to achieve the effect of high luminous efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0012] Mix 1.9734 g of barium carbonate, 4.0976 g of germanium dioxide, and 0.0522 g of manganese dioxide in an agate mortar, then pre-calcine in a high-temperature muffle furnace at 600 ° C for 4 hours, and finally calcined at 1200 ° C for 4 hours, The obtained white powder is the final product.
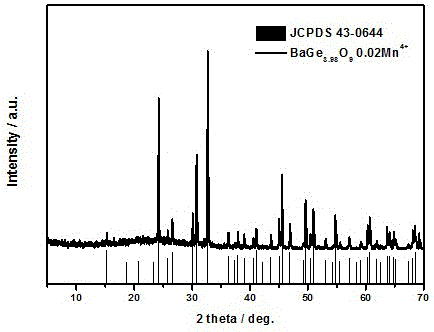
[0013] The XRD diffraction pattern of this fluorescent powder is attached figure 1 shown, with the standard card JCPDS 43-0644 (BaGe 4 o 9 ) in contrast, the two are completely consistent, and no diffraction peaks of any heterogeneous phases are observed, which indicates that the samples we synthesized have a single crystal phase.
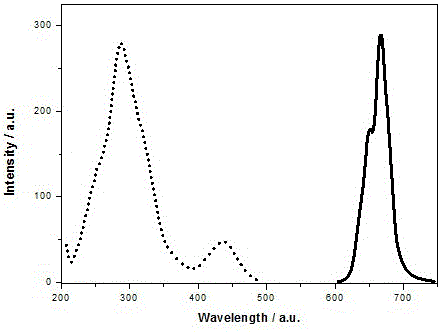
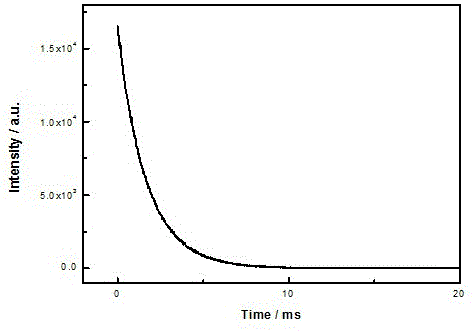
[0014] attached figure 2 Shown are the room temperature excitation spectrum (monitored at 667 nm) and emission spectrum (excited at 430 nm) of the sample. The sample has strong broadband excitation in the ultraviolet light region (240 nm ~ 380 nm) and blue light region (400 nm ~ 500 nm). Under the excitation of 430 nm light, the emission of the sam...
Embodiment 2
[0017] Mix 1.7761 g of barium carbonate, 0.1000 g of calcium carbonate, 4.0976 g of germanium dioxide, and 0.0348 g of manganese dioxide in an agate mortar, then pre-fire in a high-temperature muffle furnace at 600 °C for 4 hours, and finally at 1300 °C Lower calcining for 4 hours, the white powder obtained is the final product.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Mix 1.9734 g of barium carbonate, 3.6879 g of germanium dioxide, 0.3200 g of titanium dioxide, and 0.0522 g of manganese dioxide in an agate mortar, then pre-fire in a high-temperature muffle furnace at 600 °C for 4 hours, and finally at 1400 °C Calcined for 6 hours, the obtained white powder was the final product.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com