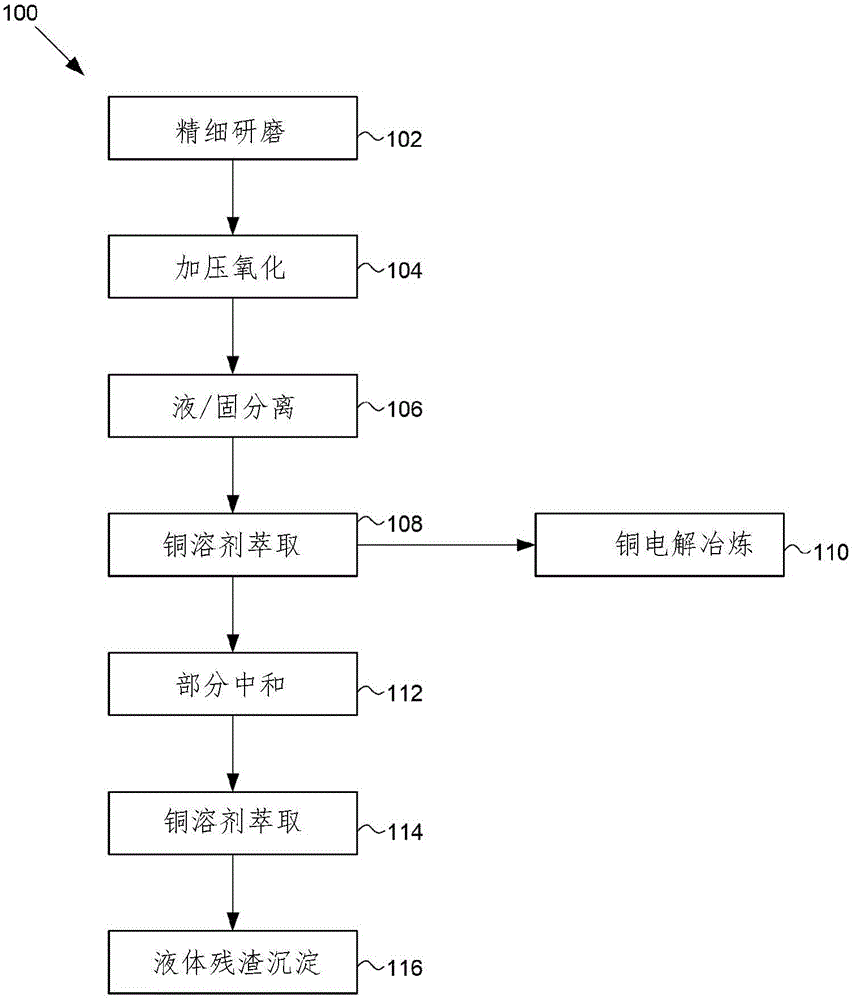
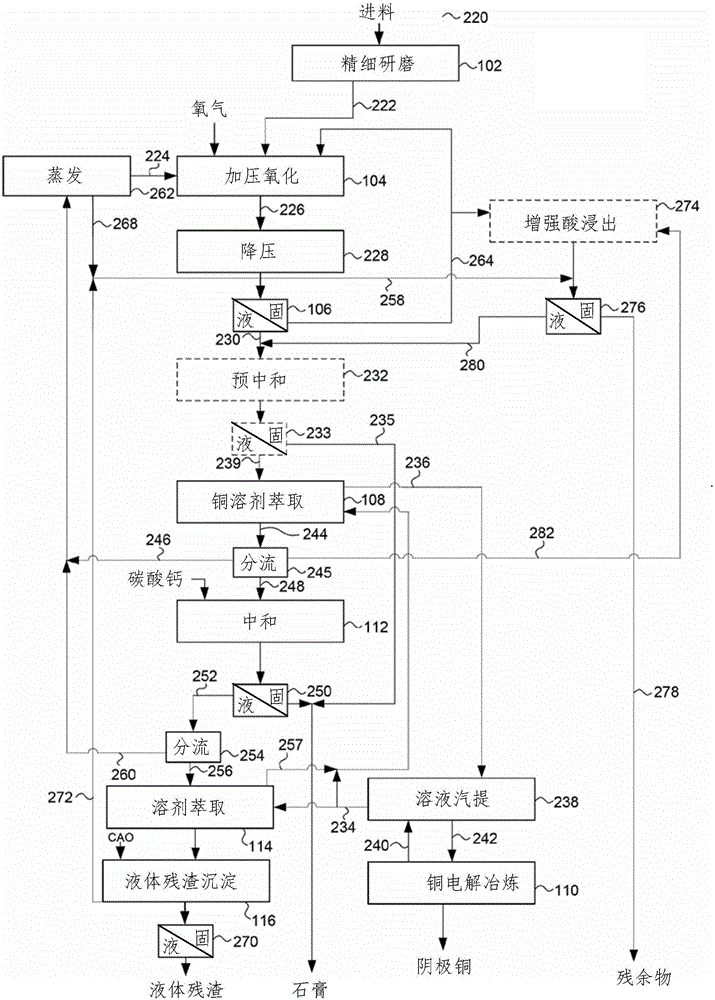
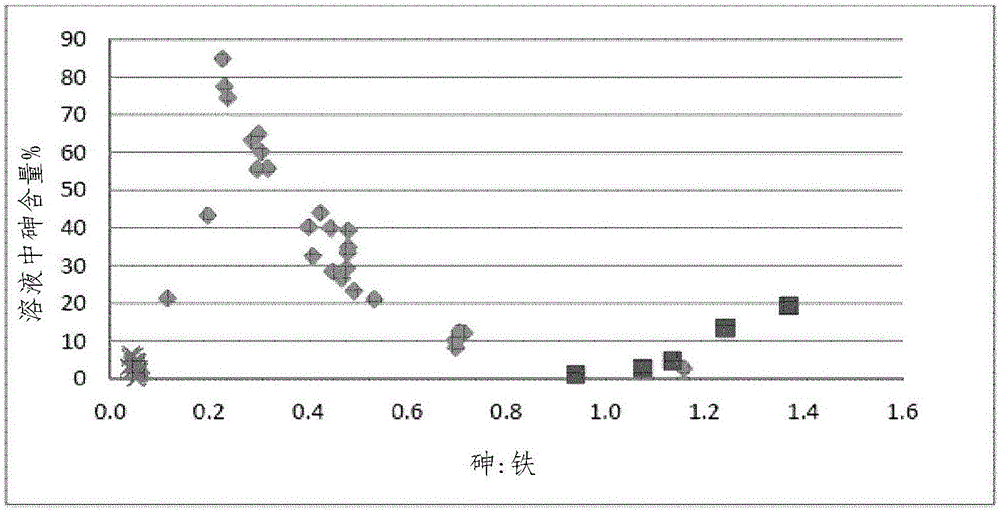
Process for recovery of copper from arsenic-bearing and/or antimony-bearing copper sulphide concentrates
A copper sulfide and copper recovery technology, which is applied in the field of copper recovery from arsenic- and/or antimony-containing copper sulfide concentrates, can solve the problems of high cost and uneconomical recovery of copper.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0154] The following example demonstrates the benefit of fine grinding in the leaching of arsenite containing material during pressure oxidation in the presence of chlorides and surfactants. 34% copper, 12% iron, 36% sulfur, and 12% arsenic were leached by pressurized oxidation under the following conditions (~64% arsenite, 1% arsenite, 8% chalcopyrite, 21% pyrite mine):
[0155] Total pressure of 200 psi (1378 kPa);
[0156] Temperature 150 degrees Celsius;
[0157] The residence time is 60 minutes;
[0158] Using a feed solution comprising 12 grams per liter of chlorine, 8 grams per liter of free acid and 15 grams per liter of copper;
[0159] Surfactant added o-phenylenediamine (OPD) is 5 kg per ton.
[0160] The degree of grinding was varied as indicated in Table 2.
[0161] Table 2
[0162] Effect of Grind Size on Copper Extraction
[0163] Grind size, P80-micron Copper extraction concentration, % 23 64.2 17 82.6 15 80.2 11 85.7 ...
Embodiment 2
[0169] The following examples demonstrate that the use of surfactants does not result in adequate copper recovery in the absence of chlorides when leaching chalbyite containing material during a pressure oxidation process.
[0170] The same feed as in Example 1 was used and leached in the absence of chloride. 34% copper, 12% iron, 36% sulfur, and 12% arsenic were leached by pressurized oxidation under the following conditions (~64% arsenite, 1% arsenite, 8% chalcopyrite, 21% pyrite mine)
[0171] Total pressure of 200 psi (1378 kPa);
[0172] Temperature 150 degrees Celsius;
[0173] The residence time is 90 minutes;
[0174] Using a feed solution comprising 40 grams per liter of free acid and 12 grams per liter of copper;
[0175] Surfactant added o-phenylenediamine (OPD) is 5 kg per ton.
[0176] As shown in Table 3, in the absence of chloride, the surfactant use was varied according to the size of the fine grind.
[0177] table 3
[0178] Effect of fine grinding and ...
Embodiment 3
[0183] The following examples demonstrate that the presence of chlorides and surfactants improves leaching and overall copper recovery when leaching chalbysite containing material during pressure oxidation.
[0184] Additional tests were performed in the presence of 12 grams per liter of chloride in the feed solution. Raw material assays and examples for 34% copper, 12% iron, 36% sulfur and 12% arsenic (~64% chalcopyrite, 1% arsenite, 8% chalcopyrite, 21% pyrite) Same as described in 2. Leaching by pressure oxidation under the following conditions:
[0185] Total pressure of 200 psi (1378 kPa);
[0186] Temperature 150 degrees Celsius;
[0187] The residence time is 90 minutes;
[0188] Using a feed solution comprising 12 grams per liter of chlorine, 40 grams per liter of free acid and 12 grams per liter of copper;
[0189] Surfactant added o-phenylenediamine (OPD) is 5 kg per ton.
[0190] The presence of surfactants was varied as indicated in Table 4.
[0191] Table 4...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com