Herbicide-tolerant plants and their applications
A herbicide and plant technology, applied in the fields of application, plant products, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve problems such as long cycle time and long-term safety evaluation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1. Construction of wheat mutant library and screening of herbicide-resistant mutants
[0032] Take commercially available wheat varieties—400kg of spring wheat Ningchun No. 4 seeds, 20kg of winter wheat Aikang 58 and Jimai 22 seeds, immerse the seeds in water for 4 hours, remove the seeds, and control the water. Then, the seeds were soaked with 0.5% (w / w) ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) for 12 hours, ensuring that the liquid surface was submerged in the seeds. After 12 hours, discard the EMS solution, change the tap water to soak the seeds, discard the tap water, repeat the soaking 5 times, soak for 5 minutes each time, then rinse the seeds with tap water for 2 hours, turn the seeds during the washing process, so that the EMS is washed, and air-dried slightly After sowing, the plants were harvested after maturity. Among them, the spring wheat Ningchun No. 4 harvested 3500 kg of M2 generation (2nd generation of mutant library) seeds, and the two varieties of Aikang ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2. Molecular level identification of herbicide-resistant positive plants
[0035] In order to prove the relationship between the herbicide-resistant mutants obtained in the present invention and the acetyl hydroxy synthetase mutation in the plants, this example carried out molecular identification on the obtained herbicide-resistant positive plants.
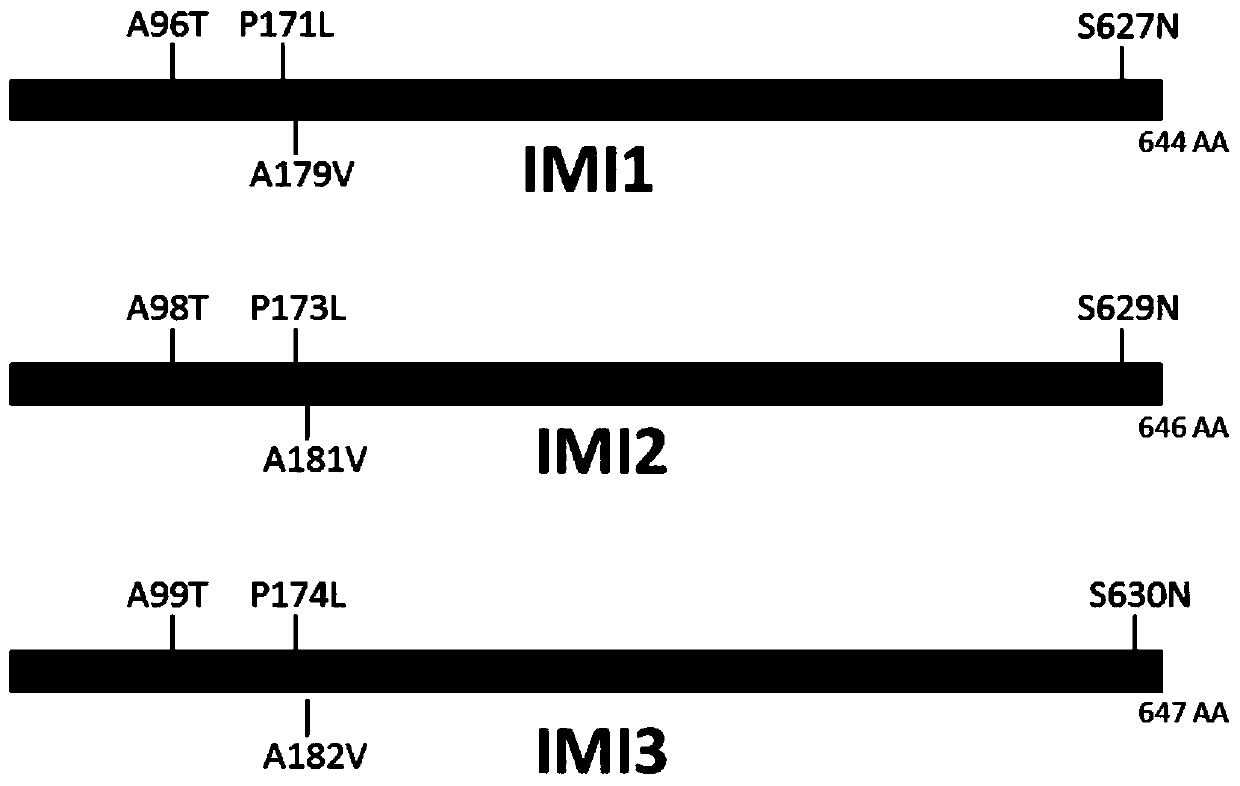
[0036] The three acetyl hydroxyl synthase genes IMI1, IMI2 and IMI3 in the wheat genome are located in the D genome, B genome and A genome, respectively. Take the leaves of suspected herbicide-resistant positive plants obtained by screening, together with the leaves of wild-type plants, extract genomic DNA from individual plants, and use genomic DNA as a template to polymerize the three acetyl hydroxyl synthases IMI1, IMI2 and IMI3 encoded in the wheat genome. The full-length genomic DNA sequence was amplified by enzyme chain reaction, and the amplification primers were:
[0037] TaImi1-F:TAAAGAAGCTAGCCCAATCTGAAC ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3. Tolerance phenotype of imidazolinone herbicides in field offspring of herbicide-resistant positive plants
[0044] The progeny of the line identified as the homozygous mutant was collected as a single plant, and a plot of about one square meter was planted in the field, and the wild type was planted next to it as a control. When the wheat grows to the three-leaf stage, it is sprayed with imazethapyr at a concentration of 500 mg / L, which is twice the commercially recommended dose. After one month of spraying, we investigated the death of seedlings. We found that the wild-type control almost stopped growing after spraying imazethapyr, and the newly grown leaves were completely withered and yellow, and then gradually withered. Positive seedlings then all presented the phenotype of complete tolerance to imazethapyr, and their normal growth and development were hardly affected (see image 3 with Figure 4 ), finally jointing and earing normally. This indicates ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com