Optical reflection sensor and electronic device
A light reflection and sensor technology, applied in the direction of instruments, using re-radiation, re-radiation of electromagnetic waves, etc., can solve problems such as complex structures, achieve the effect of improving detection accuracy and preventing false detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
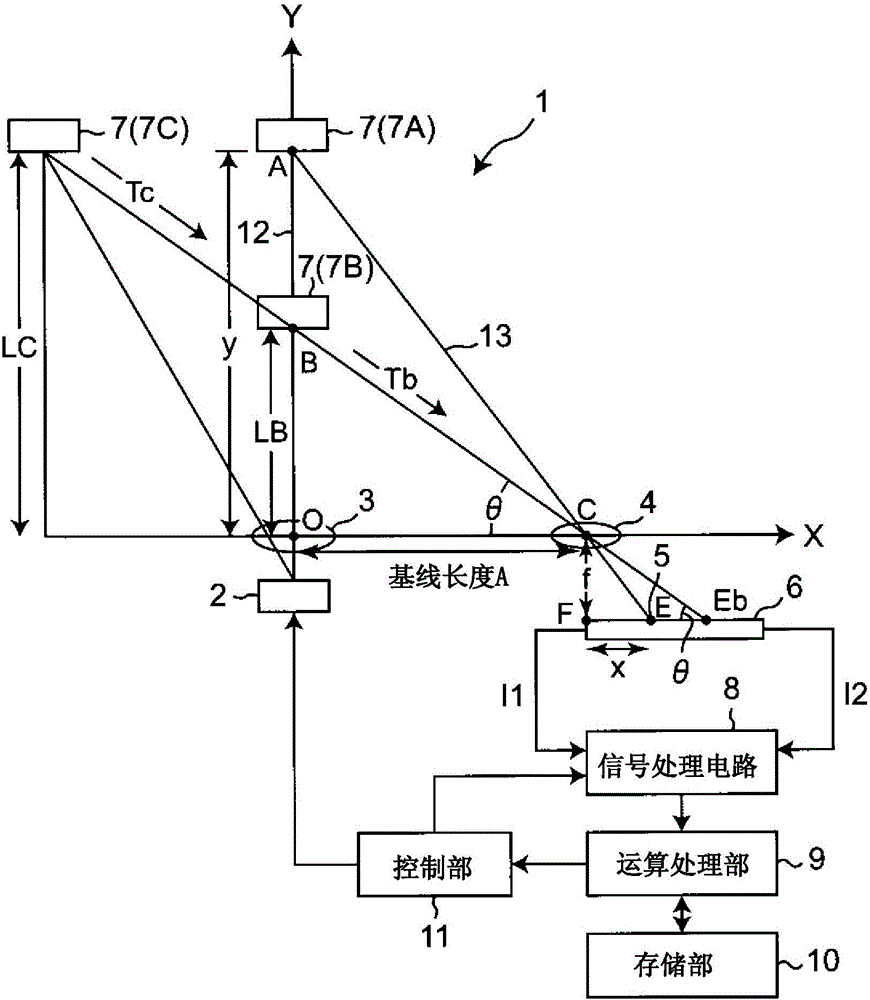
[0066] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram showing the structure of the light reflective sensor of this embodiment. The light reflective sensor of the present embodiment has a configuration in which both the above-mentioned triangulation distance measuring method and the above-mentioned TOF method are combined. exist figure 1 Among them, the light reflective sensor 1 includes: a light-emitting element 2 composed of the above-mentioned LED that irradiates light to a distance-measuring object (hereinafter simply referred to as object) 7 as an object of distance measurement; A light emitting lens 3; a light receiving lens 4 that condenses the reflected light from the object 7; In addition, other elements such as an infrared light emitting element or a laser diode may be used as the light emitting element 2 .
[0067] Assuming that the position of the above-mentioned light-emitting lens 3 is the origin O, the irradiation position of the light from the light-emitting element 2 ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
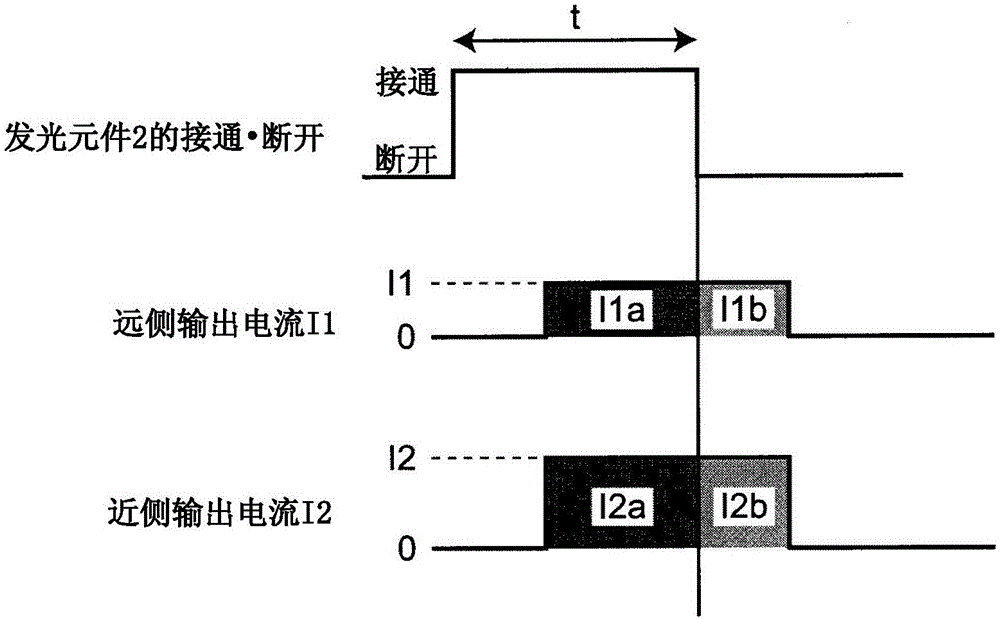
[0089] This embodiment relates to: a method of obtaining the position of the light spot 5 on the light receiving element 6 by using the above-mentioned signal processing circuit 8; The method of flight time T.
[0090] figure 2 Shown in order from the top: the timing of turning on (on) and off (off) of the above-mentioned driving signal output from the above-mentioned control unit 11 to the light-emitting element 2 (that is, turning on and off of the light-emitting element 2 ); a change in the far-side output current as a detection signal on the far side of the element 6 ; and a change in the near-side output current as a detection signal on the near side of the light receiving element 6 .
[0091] Here, the far side of the light receiving element 6 refers to the side where the reflected light from the distant object 7 forms the light spot 5 in the light receiving element 6 which is a PSD. In addition, the near side of the light receiving element 6 refers to the side where ...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
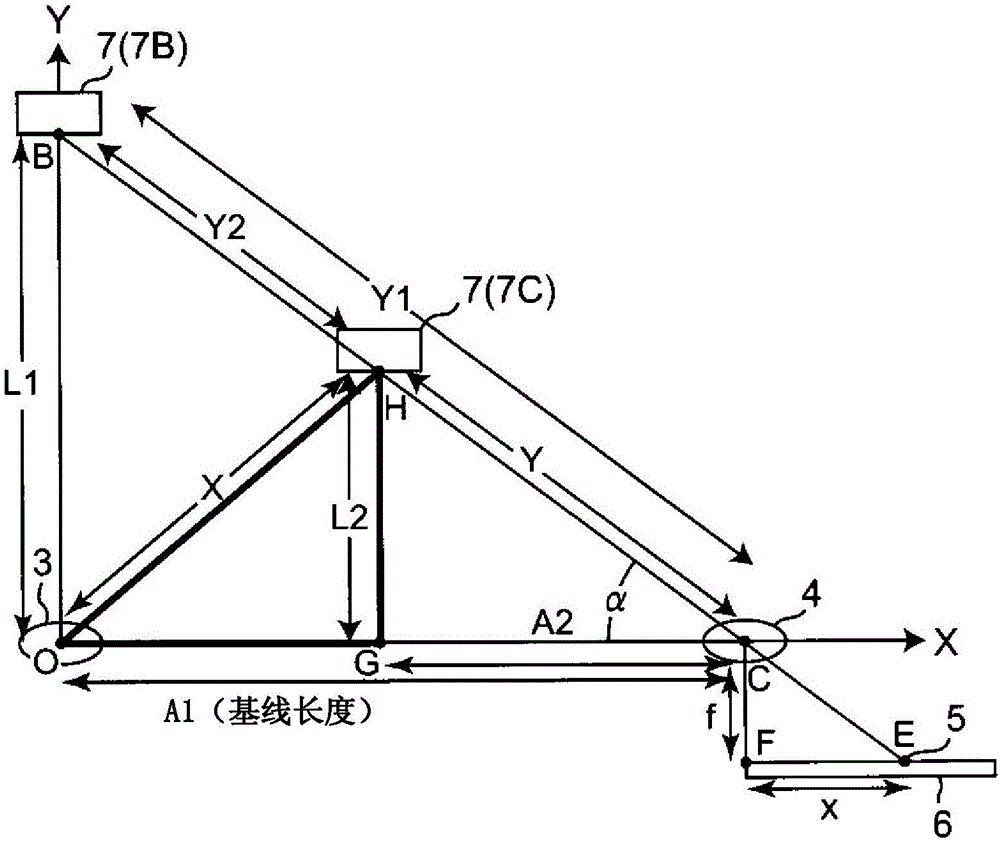
[0100] This embodiment relates to obtaining the deviation from the base line to the position on the optical axis of the light-emitting element 2 when the light emission angle of the light-emitting element 2 is expanded without using the time-of-flight lookup table of the first embodiment. The method of the distance of the object 7 of the position.
[0101] In this embodiment, if image 3 As shown, assume a case where an object 7C to be measured is located at an intermediate position between the light-emitting lens 3 and the light-receiving lens 4 .
[0102] The above-mentioned signal processing circuit 8 first obtains the position of the light spot 5 on the light-receiving element 6 based on the far-side output current I1 and the near-side output current I2 from the light-receiving element 6 as a PSD, for example, through the processing of the above-mentioned second embodiment. , measure the length (distance x) of side FE of triangle FCE. Furthermore, using the arithmetic pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com