A method for improving the hydrogen production of Chlamydomonas
A technology of Chlamydomonas and Rhine Chlamydia, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as high cost, achieve the effect of solving contradictions and broadening the range of symbiotic objects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] The hydrogen production cultivation of embodiment 1 algal bacteria
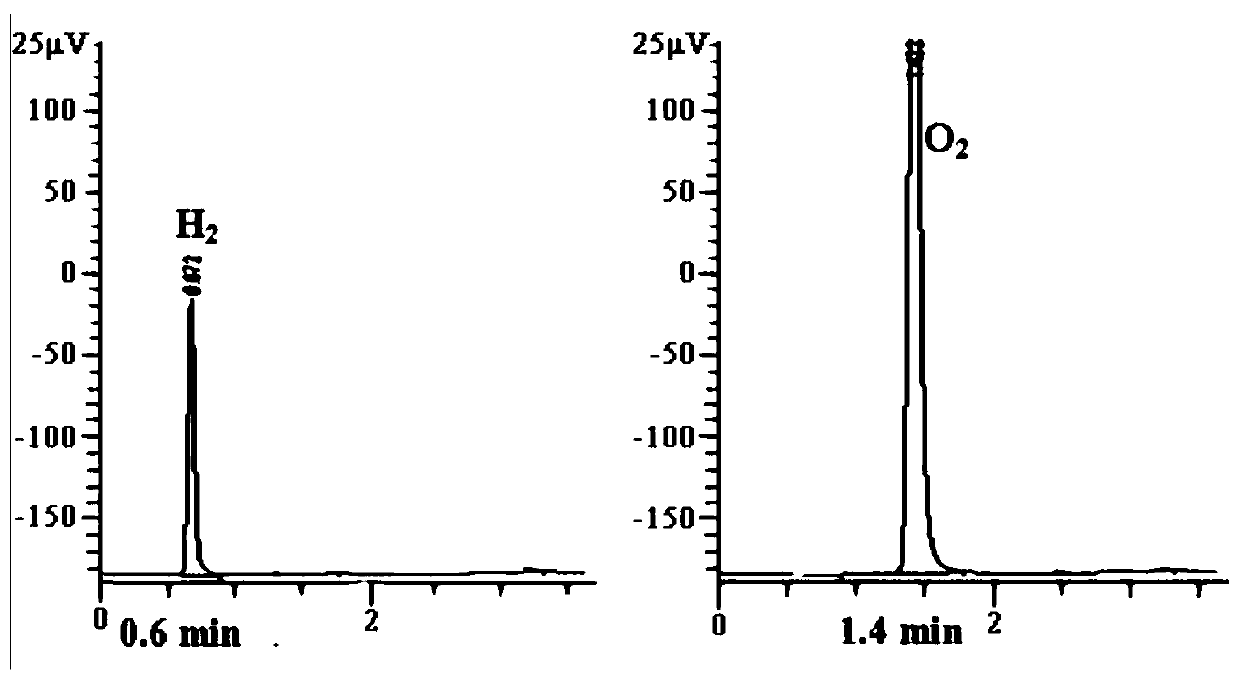
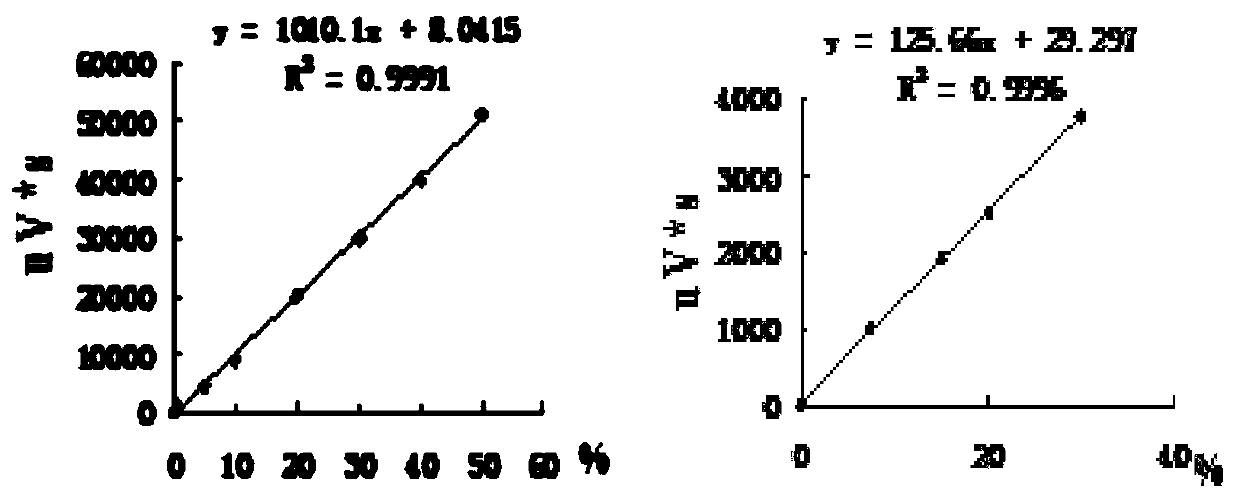
[0082] Chlamydomonas was cultured to saturation stage (OD 750 About 3.0), centrifuge at 5000rpm for 5min, remove the supernatant, add an appropriate amount of sulfur-deficient medium and resuspend 3 times to completely remove the sulfur in the original medium. The sulfur-deficient Chlamydomonas was transferred to a 60-ml hydrogen-producing culture flask at a chlorophyll concentration of 0.5 mg / L, and the volume was adjusted to 45 ml with a sulfur-deficient medium. The nitrogen-fixing bacteria (OD 600 =1) The bacteria and algae were added to the hydrogen-producing bottle with Chlamydomonas at the volume ratio of 1:80, 1:40, 3:80 and 1:20 respectively, and finally the bottle mouth was sealed with a rubber stopper. The culture system with only Chlamydomonas and only nitrogen-fixing bacteria was used as the control group, and the hydrogen-producing bottle was treated in the dark for 24 hours to consume...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Example 2 Contribution of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and nitrogen-fixing bacteria to hydrogen production in co-culture system
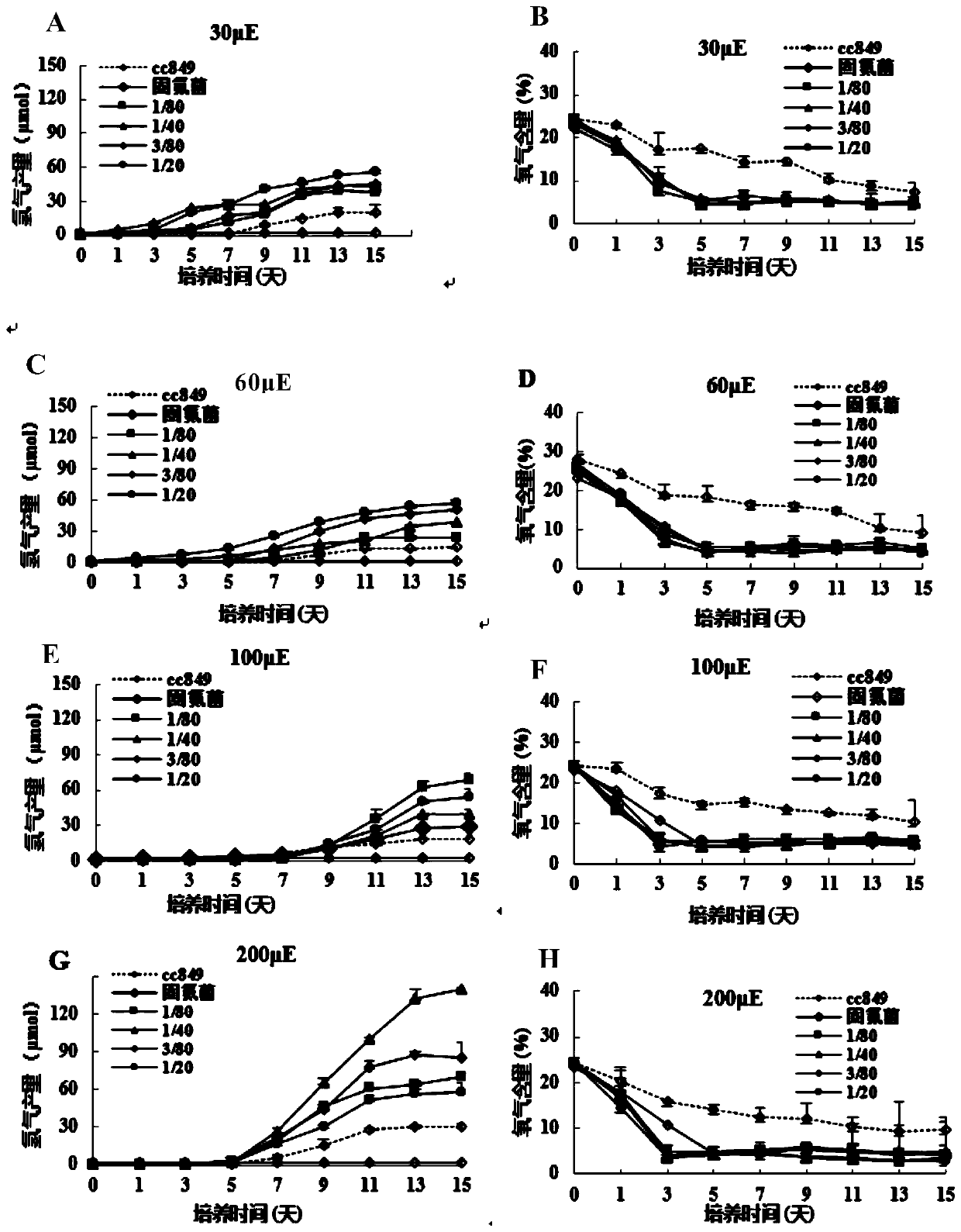
[0100] In order to understand the contribution of algae and bacteria to the increase of hydrogen production in the mixed co-culture system of Chlamydomonas and nitrogen-fixing bacteria, the pure Chlamydomonas culture system, pure nitrogen-fixing bacteria culture system, and Chlamydomonas-nitrogen-fixing bacteria co-culture system with optimal hydrogen production conditions were combined. The culture system and the optimal mixing ratio of Chlamydomonas lysate (that is, algae treated with liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw treatment) - nitrogen-fixing bacteria co-cultivation system (a total of 4 different culture systems) were continuously measured for hydrogen after 24 hours of darkness. The results are as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0101] It can be seen from the results that the pure nitrogen-fixing bacteria culture system and the Chlamydomonas lysat...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Growth status and distribution pattern of Chlamydomonas and nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the co-cultivation system of embodiment 3 algae
[0106] 1. In order to detect the growth of Chlamydomonas after co-cultivation with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, the co-cultivation conditions with the best hydrogen production were detected in the normal TAP medium and the hydrogen-producing TAP-S medium respectively. The growth of the following two algae.
[0107] The co-cultivation operation of algal bacteria under normal culture conditions is as follows: culture nitrogen-fixing bacteria in logarithmic phase (OD600 is about 1.0), centrifuge at 5000rpm for 5 minutes, remove the supernatant, and resuspend three times with the same volume of TAP to completely remove nitrogen-fixing bacteria For the culture medium, the resuspended nitrogen-fixing bacteria are mixed with Chlamydomonas according to the ratio of bacteria and algae under the optimal hydrogen production conditions, and added ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com