Method for terminating lncRNA diallele transcription
A biallelic and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low incidence of homologous recombination, difficulty, and failure to give, and achieve the effects of accurate gene function identification, accurate success rate, and improved accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] This Example 1 provides how to apply the method of the present invention to the targeted knockout of the MALAT1 gene. Among them, MALAT1 (located in the first intron of MALAT1) was selected as the target region, and homologous recombination vectors MALAT1-CMV-PuroR-BGH PolyA and MALAT1-CMV-NeoR-BGH PolyA containing double antibiotic genes were constructed, and CRISPR / Cas9-mediated DNA double-strand breaks were inserted into the downstream of the MALAT1 promoter through homologous recombination to terminate the expression of the MALAT1 gene, and finally the dual-allelic knockout cell lines were obtained by efficient screening using dual antibiotic genes.
[0034] According to different target genes, this method can be applied to different target genes including human by designing and modifying the corresponding homology arm sequence of the desired target gene and the gRNA sequence (of the gene targeted by CRISPR / Cas). Species cell line gene transcription termination.
...
Embodiment 2
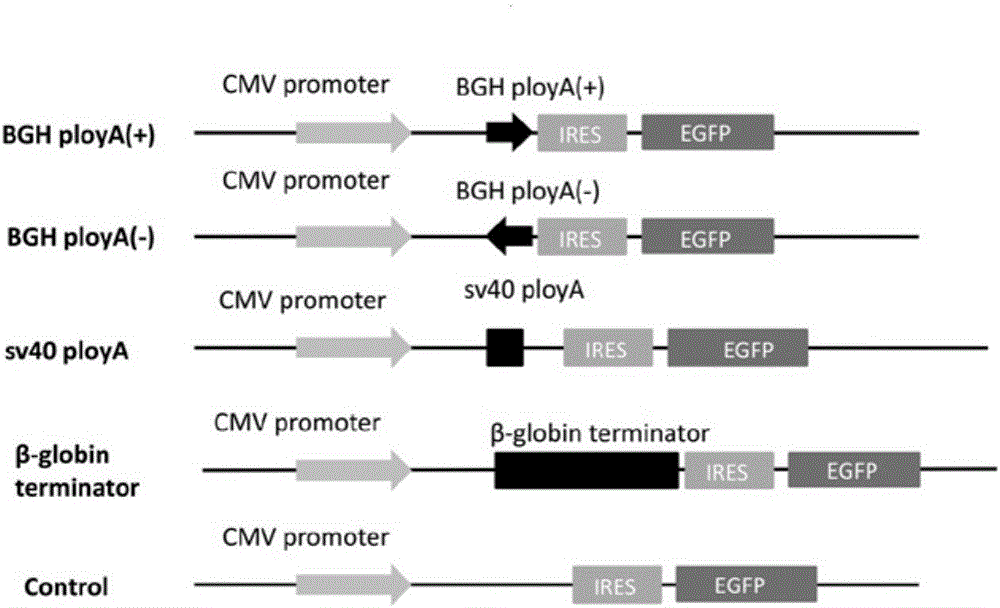
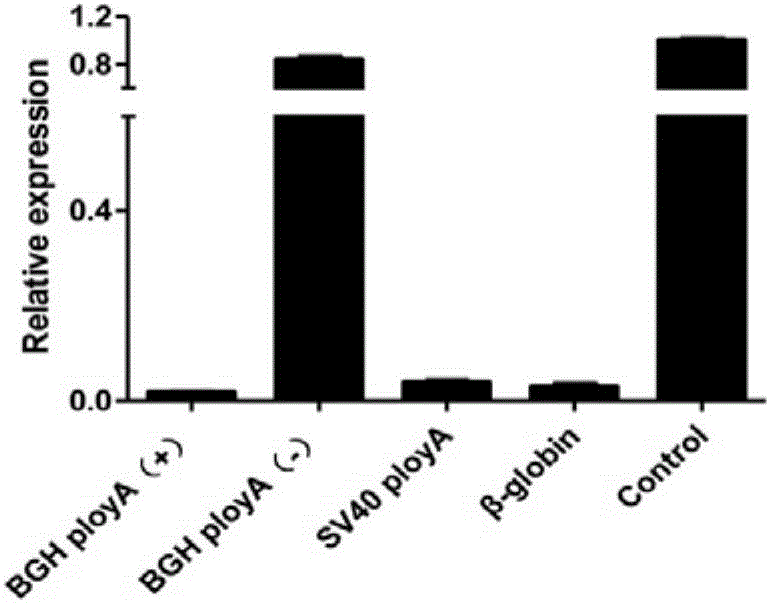
[0075] This example 2 provides the optimized comparison of transcription termination signal SV40PolyA (Simian vacuolating virus40PolyA), BGH PolyA (bovine growth hormone PolyA) and β-globin teminator in the present invention in terms of termination efficiency, molecular weight, and reverse sequence termination efficiency (See figure 1 ). Among them, SV40PolyA (Simian vacuolating virus 40PolyA) and BGH PolyA (bovine growth hormone PolyA) are transcription termination signals that can be widely used in molecules; and β-globin teminator is the termination signal of gene β-globin, which is a more thorough study of transcription termination Signal. Using these three transcription termination signals, compare their termination efficiencies, molecular weights, and reverse sequence termination efficiencies, see figure 1 .
[0076] Specifically include the following steps:
[0077] a) Design PCR amplification primers for SV40PolyA, β-globin teminator and BGH PolyA. SV40PolyA is am...
Embodiment 3
[0091] In Example 3, monoclonal cell lines were obtained from the polyclonal cell lines obtained in Example 1 by using the limiting dilution method, and the transcription of MALAT1 was detected by RT-qPCR.
[0092] Specifically include the following steps:
[0093] a) When using the limiting dilution method to obtain a monoclonal cell line, firstly dilute the cells obtained after screening in Example 1. About 50 cells in 10ml medium, inoculate 100μl in each well of a 96-well plate, and culture for 15 days;
[0094] b) DNA and RNA were extracted according to the instructions of TRIzol reagent (purchased from Life Company);
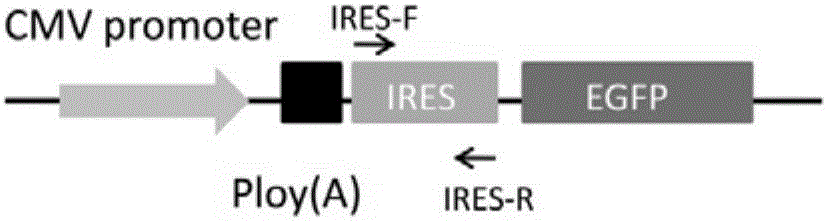
[0095] c) Using the genotyping PCR method, the upstream and downstream primers of the homologous recombination region such as Figure 7 As indicated, the extracted sample DNA was used as a template for PCR detection ( Figure 8 ). The nucleotide sequences of the primers used in this detection method are as follows:
[0096] MALAT1-HDR-F: 5'-CCCTCGGAGTT...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com