Three-phase inverter topology structure with adjustable DC bus voltage and method of adopting structure to realize dynamic DC bus voltage adjustment
A DC bus voltage, three-phase inverter technology, applied in the direction of electronically commutated motor control, motor generator control, electromechanical brake control, etc., can solve the problems of increased motor loss, torque fluctuation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
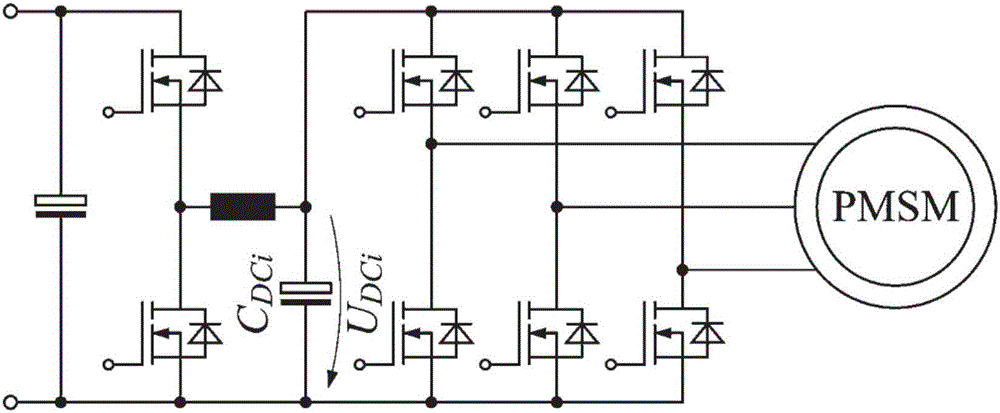
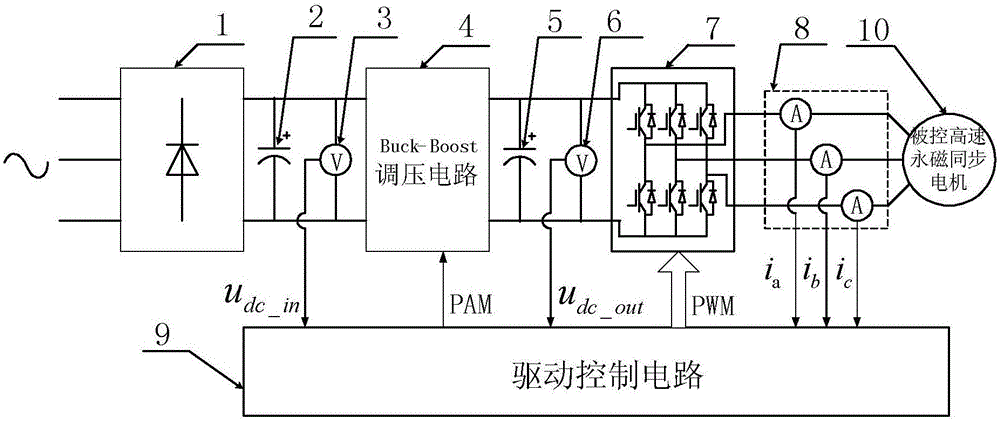
[0050] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 2 Describe this embodiment, the three-phase inverter topology structure with adjustable DC bus voltage described in this embodiment, which includes a three-phase rectifier bridge 1, a DC bus support capacitor 2, a DC bus input voltage detection module 3, and a Buck-Boost Voltage regulation circuit 4, DC bus output voltage stabilizing capacitor 5, DC bus output voltage detection module 6, three-phase half-bridge inverter circuit 7, three-phase current detection module 8 and drive control circuit 9;
[0051] The three-phase rectifier bridge 1 converts the received three-phase AC or single-phase AC into a DC voltage, and the DC voltage is stabilized by the DC bus support capacitor 2 and then input to the Buck-Boost voltage regulation circuit 4, and the Buck-Boost voltage regulation circuit 4 according to Drive the PAM control signal output by the control circuit 9 to adjust the voltage amplitude output by the Buck-Boost voltage...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0063] Specific implementation mode two: see figure 2 To illustrate this embodiment, the DC bus voltage dynamic adjustment method realized by the three-phase inverter topology structure with adjustable DC bus voltage described in the first specific embodiment, the specific process of the adjustment method is as follows:
[0064] First, the drive control circuit 9 detects in real time the DC voltage output by the three-phase rectifier bridge 1, the voltage output by the Buck-Boost voltage regulator circuit 4, and the three-phase current i output by the three-phase half-bridge inverter circuit 7 a , i b , i c ;
[0065] Among them, the output voltage of the three-phase rectifier bridge 1 is the input voltage u of the DC bus dc_in ,
[0066] The voltage output by the Buck-Boost voltage regulating circuit 4 is the output voltage u of the DC bus dc_out ;
[0067] Secondly, the drive control circuit 9 according to the external given instruction speed n cmd , to receive the i...
specific Embodiment approach 3
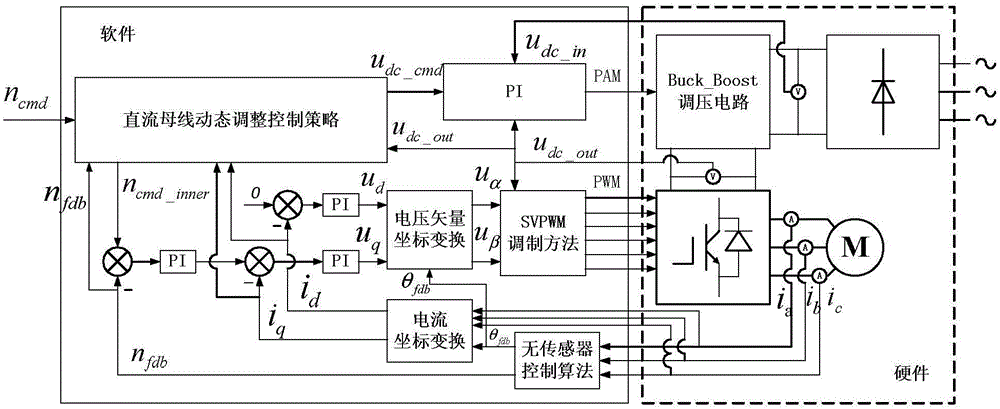
[0068] Specific implementation mode three: see image 3 This embodiment is described. The difference between this embodiment and the method for dynamically adjusting the DC bus voltage realized by using the three-phase inverter topology structure with adjustable DC bus voltage described in the second embodiment is that the drive control circuit 9 is based on External given command speed n cmd , to receive the input voltage u of the DC bus dc_in , the output voltage u of the DC bus dc_out and three-phase current i a , i b , i c process to make it generate a PAM control signal and a PWM control signal, and perform closed-loop control on the Buck-Boost voltage regulating circuit 4 through the PAM control signal, thereby controlling the output voltage u of the DC bus dc_out Perform dynamic adjustment, control the three-phase half-bridge inverter circuit 7 through the PWM control signal, thereby driving the controlled high-speed permanent magnet synchronous motor 10, and make ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com