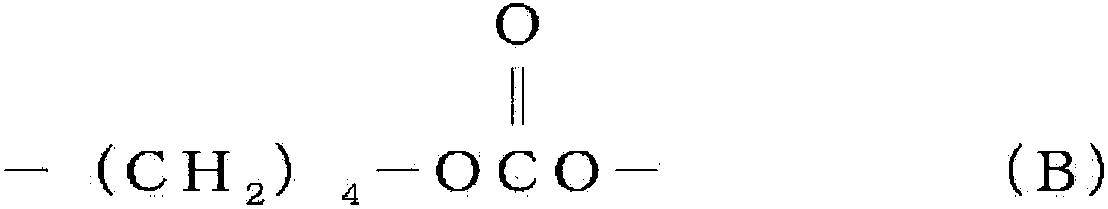polycarbonate diol
A polycarbonate diol and repeating unit technology, applied in polyurea/polyurethane coatings, coatings, etc., can solve problems such as strong interaction, poor dispersion stability, and high viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
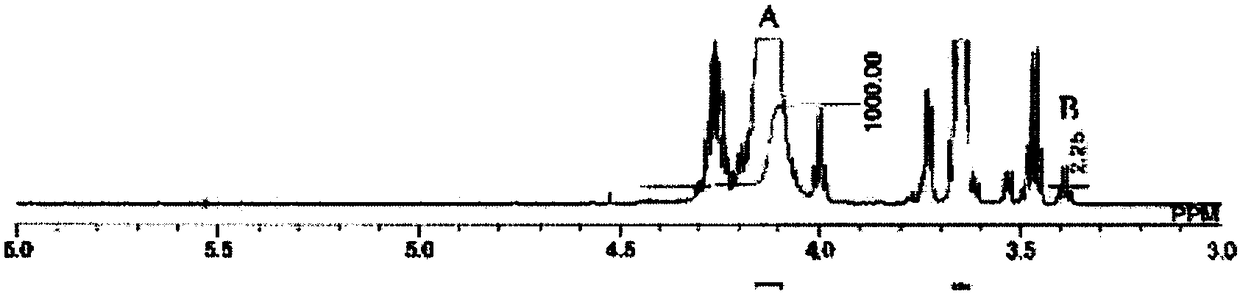
[0145] Put 275g (3.1mol) of dimethyl carbonate, 500g (4.8mol) of 1,5-pentanediol, 490g (4.2mol) of ) 1,6-hexanediol. 0.2 g of tetrabutyl titanate was added as a catalyst to the aforementioned flask, and the mixture in the aforementioned flask was stirred and heated under normal pressure. The reaction temperature was set at 190° C., and the reaction was carried out for 12 hours while distilling off a mixture of methanol and dimethyl carbonate generated. Thereafter, the pressure in the flask was reduced to 12 kPa, and the reaction was further performed at 195° C. for 5 hours while distilling off diol and dimethyl carbonate. Thereafter, 0.22 g of 2-ethylhexyl acid phosphate was added as a phosphorus compound to the flask, and the mixture in the flask was heated at 120° C. for 5 hours to obtain polycarbonate diol. Table 1 shows the analysis results of the obtained polycarbonate diol. This polycarbonate diol is abbreviated as PC-1. The obtained polycarbonate diol has a repeatin...
Embodiment 2
[0147] 310g (3.4mol) of dimethyl carbonate, 500g (4.8mol) of 1,5-pentanediol, 490g (4.2mol) of ) 1,6-hexanediol. 0.2 g of tetrabutyl titanate was added as a catalyst to the aforementioned flask, and the mixture in the aforementioned flask was stirred and heated under normal pressure. After distilling off the mixture of produced methanol and dimethyl carbonate, the reaction temperature was set at 160° C. to react for 2 hours, and then the reaction temperature was increased to 190° C. to further react for 12 hours. Thereafter, the pressure in the flask was reduced to 12 kPa, and the reaction was further performed at 195° C. for 5 hours while distilling off diol and dimethyl carbonate. Thereafter, 0.22 g of 2-ethylhexyl acid phosphate was added as a phosphorus compound to the flask, and the mixture in the flask was heated at 120° C. for 5 hours to obtain polycarbonate diol. Table 1 shows the analysis results of the obtained polycarbonate diol. This polycarbonate diol is abbrev...
Embodiment 3
[0149] In a 2L glass flask equipped with a rectification column filled with a regular packing and a stirring device, put 350g (3.9mol) of dimethyl carbonate, 500g (4.8mol) of 1,5-pentanediol, 490g (4.2mol) ) 1,6-hexanediol. 0.2 g of tetrabutyl titanate was added as a catalyst to the aforementioned flask, and the mixture in the aforementioned flask was stirred and heated under normal pressure. After distilling off the mixture of produced methanol and dimethyl carbonate, the reaction temperature was set at 150° C. to react for 3 hours, and then the reaction temperature was increased to 190° C. to further react for 12 hours. Thereafter, the pressure in the flask was reduced to 12 kPa, and the reaction was further performed at 195° C. for 5 hours while distilling off diol and dimethyl carbonate. Thereafter, 0.22 g of 2-ethylhexyl acid phosphate was added as a phosphorus compound to the flask, and the mixture in the flask was heated at 120° C. for 5 hours to obtain polycarbonate d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com