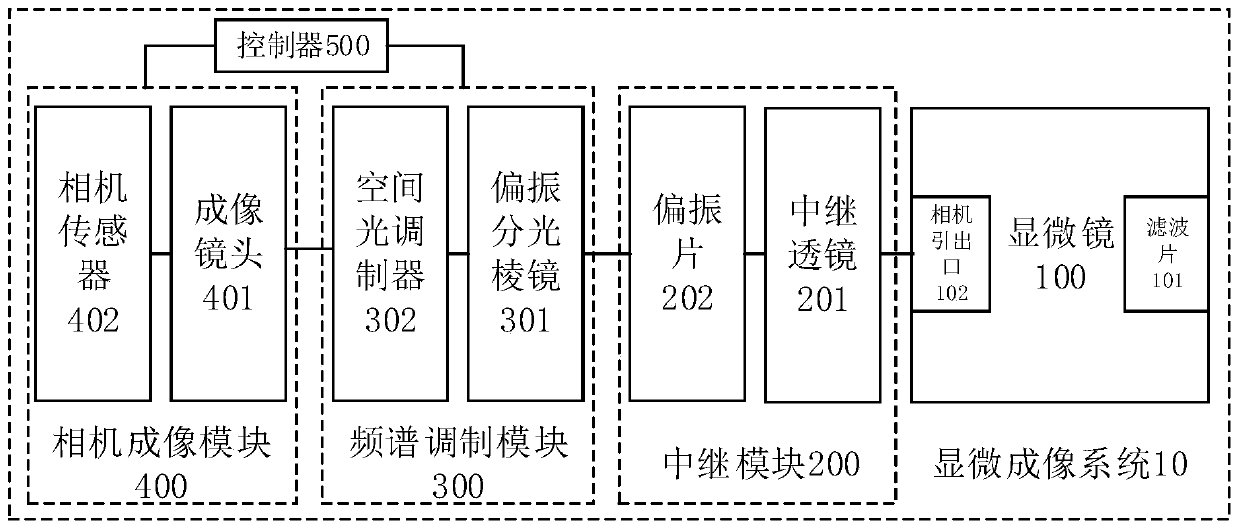
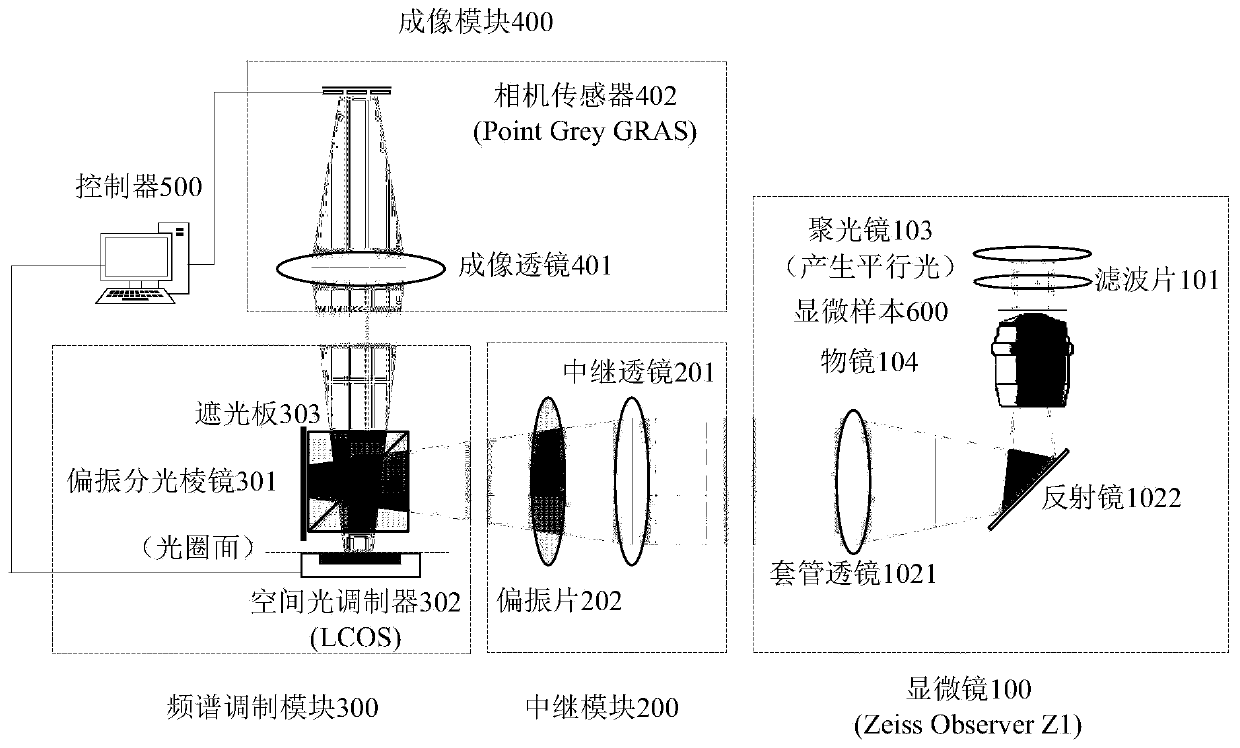
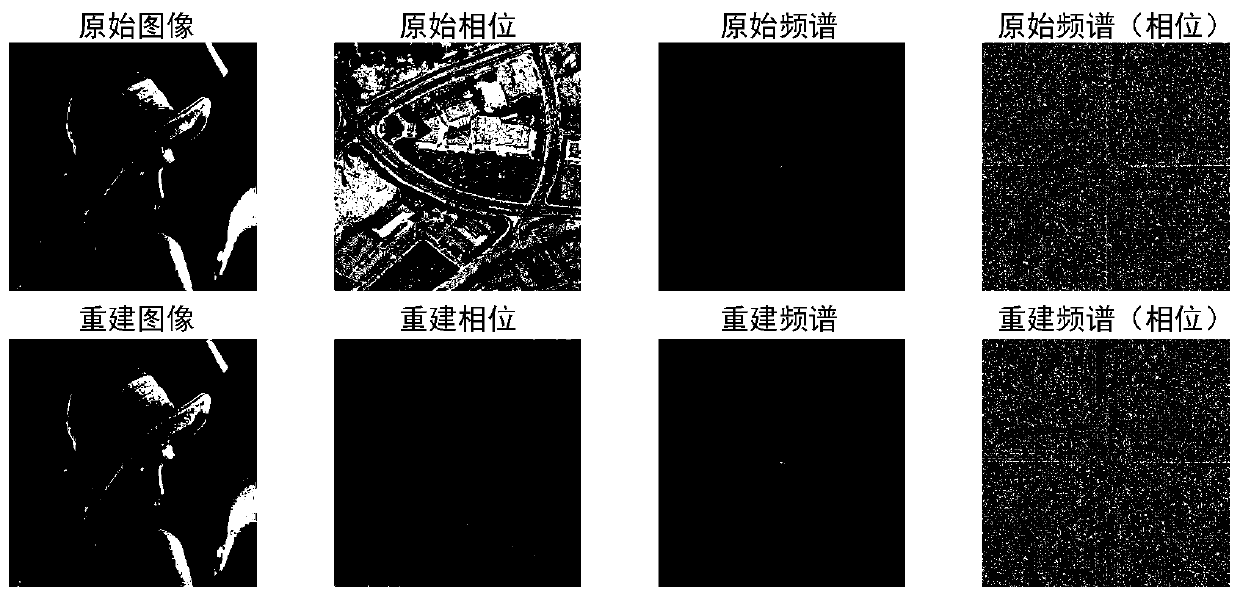
Frequency domain mosaic microscopy system based on spatial light modulator
A spatial light modulator and microscopic system technology, applied in microscopes, instruments, optics, etc., can solve problems such as low resolution, slow mechanical scanning speed, and lack of acquisition at the imaging end, achieving improved spatial resolution and flexible programming The effect of controlling and improving the collection speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] Embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below, examples of which are shown in the drawings, wherein the same or similar reference numerals designate the same or similar elements or elements having the same or similar functions throughout. The embodiments described below by referring to the figures are exemplary only for explaining the present invention and should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
[0033] In describing the present invention, it should be understood that the terms "center", "longitudinal", "transverse", "upper", "lower", "front", "rear", "left", "right", " The orientations or positional relationships indicated by "vertical", "horizontal", "top", "bottom", "inner" and "outer" are based on the orientations or positional relationships shown in the drawings, and are only for the convenience of describing the present invention and Simplified descriptions, rather than indicating or implying that the device or element refe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com