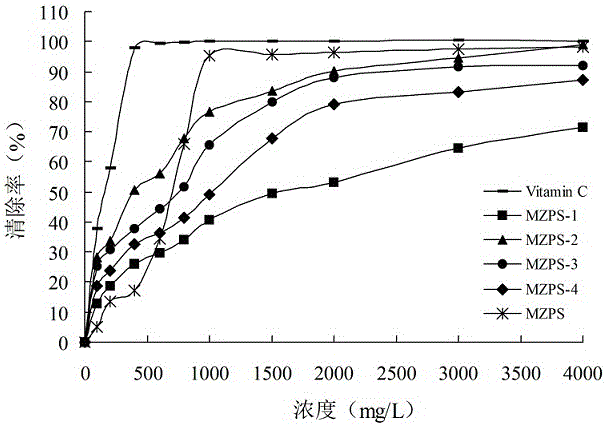
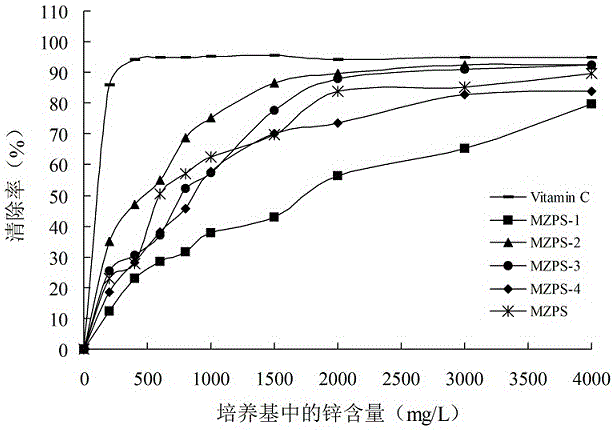
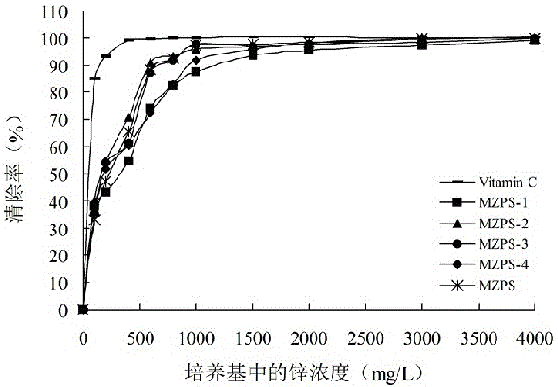
Thelephora ganbajun mycelium polysaccharide as well as preparation method and application of thelephora ganbajun mycelium polysaccharide
A technology of mycelium polysaccharide and dry bacteria, which can be used in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganism-based methods, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient utilization and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The acquisition of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
[0043]Collect 4 fresh fruiting bodies of D. spp. from different areas in Yunnan Province, disinfect the surface with 75% alcohol, rinse several times with sterile water, use sterilized tweezers to tear off small pieces of the internal tissue of D. spp. and inoculate them with chloramphenicol On the potato dextrose (PDA) medium plate, move it into a 24 ℃ incubator for cultivation. After the mycelium grows, it will be purified repeatedly until the pure culture of D. spp. is obtained. Four strains of S. spp. were screened from 4 S. spp. fruiting bodies and named as TG-1, TG-2, TG-3 and TG-4 respectively.
Embodiment 2
[0044] The liquid fermentation of embodiment 2 dried bacteria
[0045] Carry out fermenter culture experiments, ① Activation of strains. The bacteria strains TG-1, TG-2, TG-3 and TG-4 were respectively inoculated on the activation medium plate (potato 200 g / L, glucose 20 g / L, magnesium sulfate 1 g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.5 g / L), cultured at 24°C for 7 days. Take 0.5 cm 2 The activated strain of D. spp. was inserted into the liquid medium (potato 200 g / L, glucose 20 g / L, peptone 2 g / L, magnesium sulfate 1 g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1.5 g / L, pH natural), The volume of the 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask was 300 mL, and then cultured with shaking on a shaker at 24 °C for 10 days. ② Fermentation tank culture conditions. Loading capacity: 7.5 liters; Inoculation amount: 10%; Fermentation temperature: 24 ℃; Stirring speed: 350 r / min; Foam control: Add two drops of defoamer after inoculation. ③ Determination of pH value and DO value during fermentation. The pH elec...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The extraction of embodiment 3 dried bacteria mycelium polysaccharides
[0051] 1) Separation of the mycelia of D. spp.:
[0052] Centrifuge the dry bacteria culture (10000 r / min, 10 min), collect the mycelium, and wash the mycelium 3 times. The mycelium was dried and pulverized at 55°C to obtain the mycelium powder of D.
[0053] 2) Extraction of polysaccharides from the mycelium of Drosophila:
[0054] Take the mycelium powder of D. spp., mix the mycelium powder with deionized water at a ratio of 1:20, adjust the pH value to 8, and ultrasonically pulverize it with an ultrasonic power of 600 W for 10 min, and then place it at 90 °C In a water bath, extract for 2 h, centrifuge to get the supernatant. The mycelium residue after centrifugation was extracted twice according to the above steps, and the supernatant was combined.
[0055] 3) Purification of polysaccharides from the mycelia of Drosophila:
[0056] Concentrate the polysaccharide extract to 1 / 2 of its origi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com