Method for producing high-yield dye lignin glycosylated derivatives by using cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase
A genistein and glucose-based technology is applied in the field of high-yield genistein glycosylated derivatives, which can solve problems such as instability and easy hydrolysis, and achieve the effects of increasing yield and increasing yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
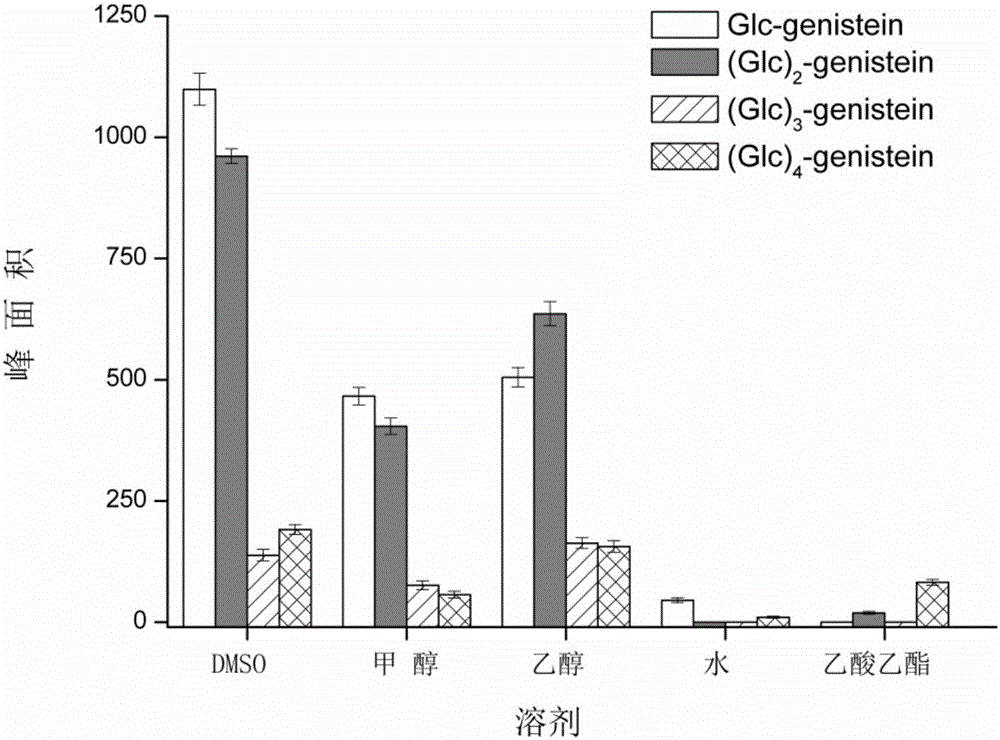
[0021] Example 1: Effects of dissolving genistein in different solvents on the synthesis of glycosylated genistein products.
[0022] 0.1 g of genistein was dissolved in 10 mL of DMSO, methanol, ethanol, water, ethyl acetate and other solvents to prepare different genistein solutions. Then take 300 μL genistein solution, 500 μL concentration is 10g / L α-cyclodextrin solution (solvent is 50mM PBS buffer solution of pH 6.5), 200 μL concentration is 15g / L cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase (solvent is pH 6.5 50mM PBS buffer) in a 2mL capped vial. Shake slowly in a shaker at 30°C for 24h. After the reaction was completed, the product yield was detected by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
[0023] Such as figure 1 It was shown that the yield of glycosylated genistein derivatives was highest when DMSO was used as the genistein solvent. Therefore, DMSO was chosen as the genistein solvent.
Embodiment 2
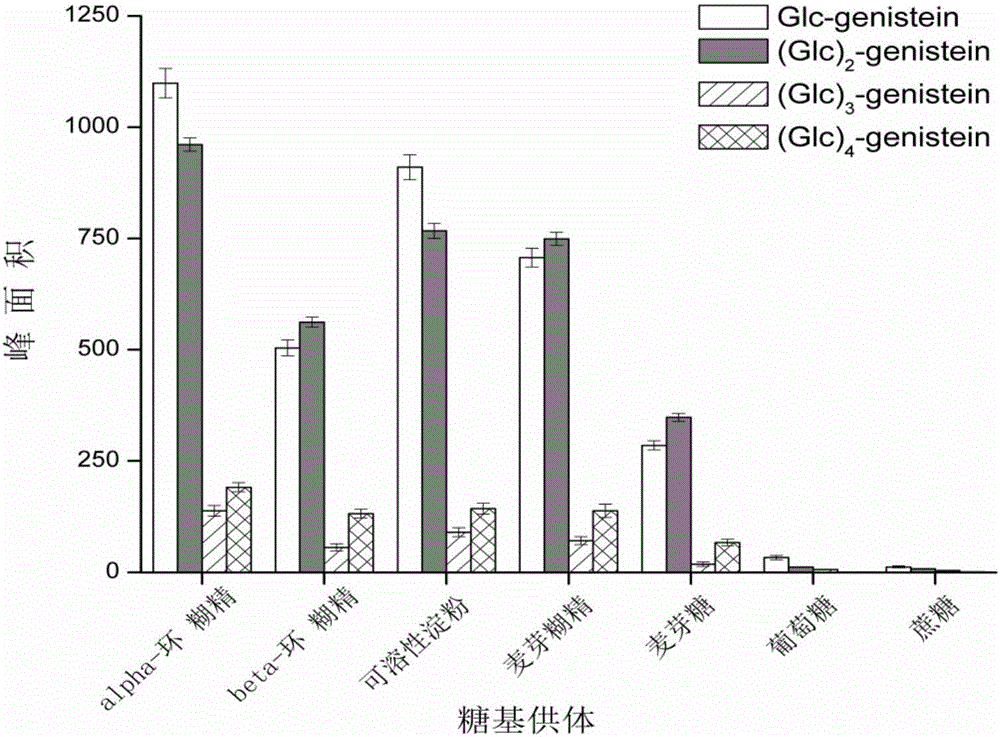
[0024] Example 2: Effect of different glycosyl donors on the synthesis of glycosylated genistein products.
[0025] α-cyclodextrin, β-cyclodextrin, soluble starch, maltodextrin, maltose, glucose, and sucrose were selected as sugar donors, and dissolved in 50mM PBS buffer at pH 6.5 to prepare a concentration of 10g / L solution. Then 500 μL of glycosyl donors were mixed with 300 μL of 10 g / L genistein solution (DMSO as the solvent) and 200 μL of 15 g / L cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase (50 mM PBS buffer at pH 6.5) In a 2mL vial with a cap. Shake slowly in a shaker at 30°C for 24h. After the reaction was completed, the product yield was detected by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
[0026] Such as figure 2 It was shown that when α-cyclodextrin was selected as the glycosyl donor, the yield of genistein glycosylation products was the highest. But because α-cyclodextrin is expensive and increases the cost, it is not the most suitable sugar donor. When soluble star...
Embodiment 3
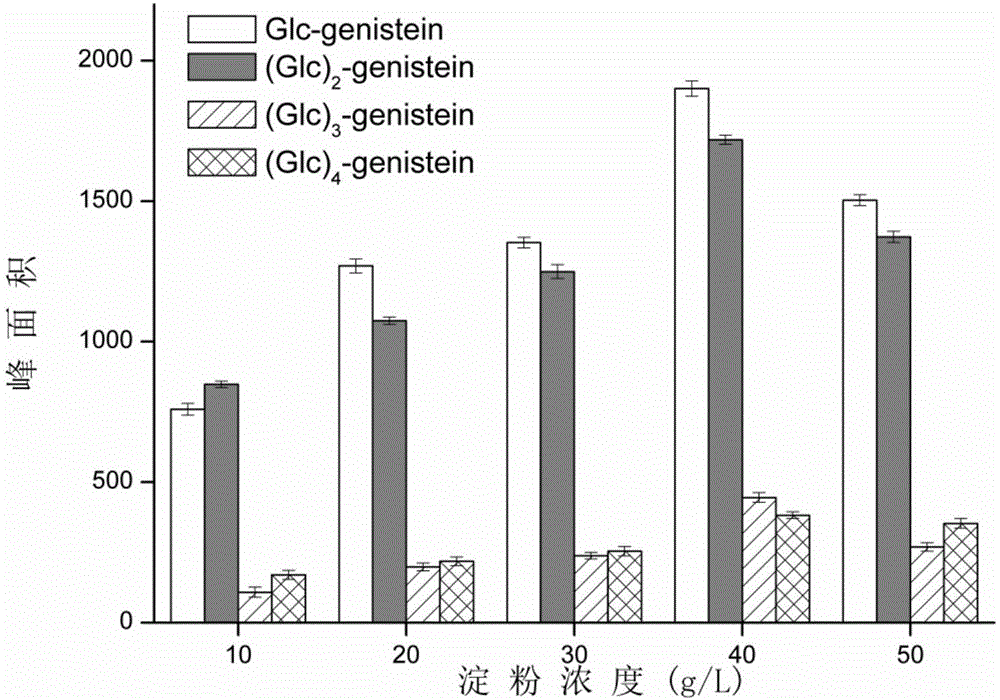
[0027] Example 3: Effects of Different Soluble Starch Concentrations on the Synthesis of Glycosylated Genistein Products
[0028] Soluble starch was dissolved in 50mM PBS buffer solution of pH 6.5 to prepare different concentrations (10, 20, 30, 40, 50g / L), and then 500μL of different concentrations of soluble starch solution and 300μL of 10g / L genistein The solution (solvent is DMSO) and 200 μL cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase (solvent is 50 mM PBS buffer solution, pH 6.5) with a concentration of 15 g / L were mixed in a 2 mL vial with a cap. Shake slowly in a shaker at 30°C for 24h. After the reaction was completed, the product yield was detected by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Such as image 3 As shown, when the concentration of soluble starch was 40g / L, the yield of genistein glycosylated derivatives was the highest. Therefore, the optimum concentration of soluble starch was selected as 40g / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com