Method for establishing SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) fingerprint spectrum of broad beans
A technology of fingerprints and construction methods, which is applied in the field of identifying broad bean varieties by fingerprints of different varieties of broad beans, and the construction of SSR fingerprints of broad beans. Achieve the effects of preventing counterfeit and inferior varieties from entering the market, protecting crop varieties, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1 is used to identify the screening of SSR and EST-EST primers of broad bean varieties
[0050] In this example, the core genome SSR and EST-SSR primers were synthesized by analyzing the genome sequence and EST sequence of broad bean by using the genomic DNA of 48 varieties of broad bean (see Table 1) popularized in the main producing areas of broad bean in my country as templates. After screening, the molecular marker combinations composed of 15 pairs of genomic SSR and 6 pairs of EST-SSR primers can completely identify the differences of 48 broad bean varieties.
[0051] In the final screening, 15 pairs of genomic SSR molecular markers and 6 pairs of EST-SSR molecular markers were obtained.
[0052] Table 2 21 pairs of SSR core primers
[0053]
[0054]
[0055] The primers in the above Table 1 respectively correspond to SEQ ID NO.1-42 in the sequence listing.
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2 Construction of characteristic fingerprints of broad bean varieties and establishment of identification methods for broad bean varieties
[0057] 1. Total DNA extraction of broad bean varieties
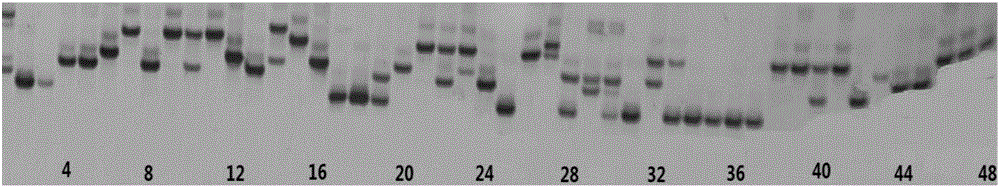
[0058] The improved CTAB method was used to extract the DNA of the tested variety: take about 2g of fresh young leaves, grind them into powder in liquid nitrogen, put them into a 2.0ml centrifuge tube, and store them in a -80°C refrigerator for later use; preheat to 65°C 2×CTAB extract at ℃, add β-mercaptoethanol at a ratio of 1% of the solution volume, and mix thoroughly; take out the ground leaf tissue, add 800 μL of preheated CTAB extract to each sample, and vortex 1-2min, 65°C water bath for 1h (turn it upside down once every 15min, mix well); after the water bath heating, add 800μL chloroform / isoamyl alcohol (24:1) solution to the centrifuge tube, mix for 15-20min, Then centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 15 minutes; absorb about 600 μL of supernatant and transfer it t...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Embodiment 3 Application of the present invention's identification method for broad bean varieties
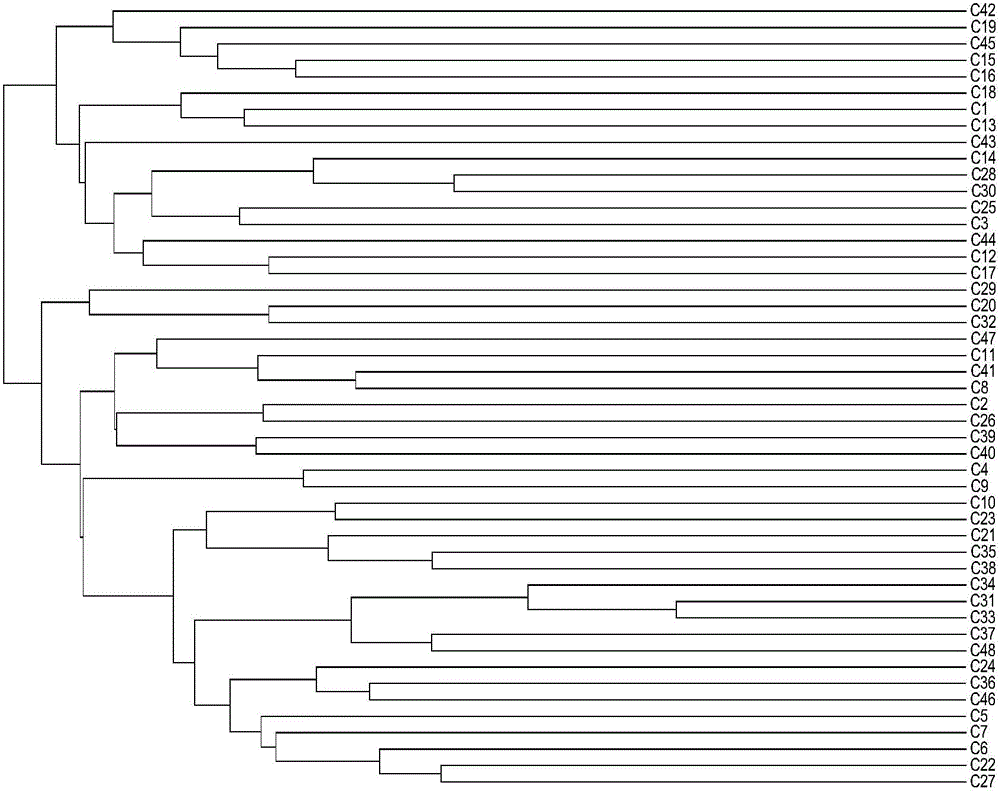
[0108] Extract the leaf DNA of 6 broad bean samples with known variety names, and carry out PCR amplification of the DNA of the broad bean varieties to be checked with 21 pairs of primers in the molecular marker combination screened in Example 1 of the present invention; with reference to Example 2 of the present invention PCR reaction system, PCR reaction program, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and variation site recording method (method 1), and repeated experiments at the same time using fluorescence capillary electrophoresis and variation site recording method (method 2), the fingerprint code obtained and The characteristic fingerprints (Table 5-Table 16) of broad bean varieties obtained in the present invention were compared to verify the accuracy of the identification method established in Example 2 of the present invention.
[0109] As a result, it was found th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com