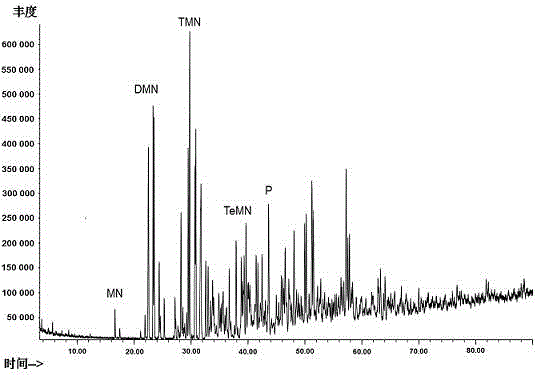
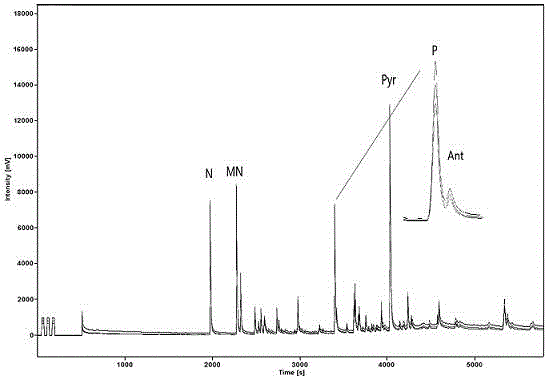
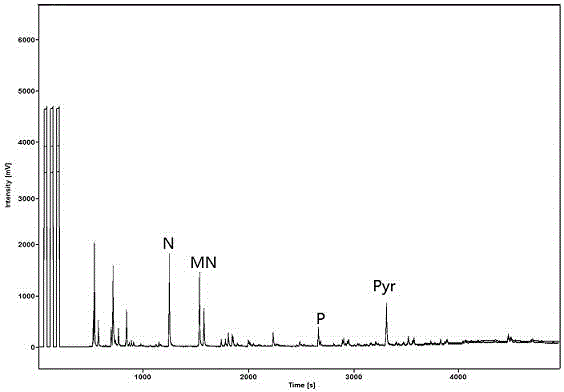
Aromatic hydrocarbon purification method suitable for analyzing specific carbon isotope
A purification method and isotope technology, applied in the field of purification of aromatic hydrocarbons without substituents, can solve problems such as poor controllability and difficulty in distinguishing boundary points between components, and achieve the effects of low cost, easy implementation, and reliable data
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 A method for purifying aromatics suitable for monomer carbon isotope analysis, comprising the following steps:
[0032] (1) Add 0.1g of crude oil into the cleaned glass tube, then replace it with helium three times to remove the air, then vacuumize and seal;
[0033] (2) Place the glass tube containing the crude oil in step (1) in a muffle furnace, and heat at 500°C for 48 hours to obtain a pyrolysis product;
[0034] (3) After the pyrolysis product was cooled to room temperature, it was extracted twice with dichloromethane at 30°C, the frequency was 15 kHz, and the time was 20 min, and combined to obtain the extract;
[0035] (4) The extract was distilled under reduced pressure for 3~5min at a temperature of 30°C and a pressure of 0.04MPa until 1~2mL of solvent remained, and then the asphaltenes were precipitated with n-hexane, and then the aromatic components were analyzed directly (GC-MS) and Monomer carbon isotope test (GC-IRMS) is sufficient.
[0036] A...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 A method for purifying aromatics suitable for monomer carbon isotope analysis, comprising the following steps:
[0039] (1) Add 0.2g of crude oil into the cleaned glass tube, then replace it with helium three times to remove the air, then vacuumize and seal;
[0040] (2) Place the glass tube containing crude oil in step (1) in a muffle furnace, and heat at 550°C for 12 hours to obtain a pyrolysis product;
[0041] (3) After the pyrolysis product was cooled to room temperature, it was ultrasonically extracted 4 times with dichloromethane at 33°C, the frequency was 25 kHz, and the time was 30 min, and the combined extract was obtained;
[0042] (4) The extract was distilled under reduced pressure for 3~5min at a temperature of 33°C and a pressure of 0.06MPa until 1~2mL of solvent remained, and then the asphaltenes were precipitated with n-hexane, and the aromatic components were analyzed directly (GC-MS) and Monomer carbon isotope test (GC-IRMS) is sufficient. ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 A method for purifying aromatics suitable for monomer carbon isotope analysis, comprising the following steps:
[0044] (1) Add 0.15g of crude oil into the cleaned glass tube, then replace it with helium three times to remove the air, then vacuumize and seal;
[0045] (2) Place the glass tube containing the crude oil in step (1) in a muffle furnace and heat at 515°C for 24 hours to obtain a pyrolysis product;
[0046] (3) After the pyrolysis product was cooled to room temperature, it was ultrasonically extracted three times with dichloromethane at 32 °C, the frequency was 20 kHz, and the time was 24 min, and the combined extract was obtained;
[0047] (4) The extract solution was distilled under reduced pressure for 3~5min at a temperature of 32°C and a pressure of 0.05MPa until 1~2mL of the solvent remained. Monomer carbon isotope test (GC-IRMS) is sufficient. Test condition is the same as embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com