Resource allocation method based on equivalent capacity in wireless virtual network
A technology of resource allocation and virtual network, which is applied in the direction of network traffic/resource management, wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory communication requirements, high computational complexity, and slow solution process, and achieve simplified channel complexity, Ease of Solving and Measuring Accurate Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
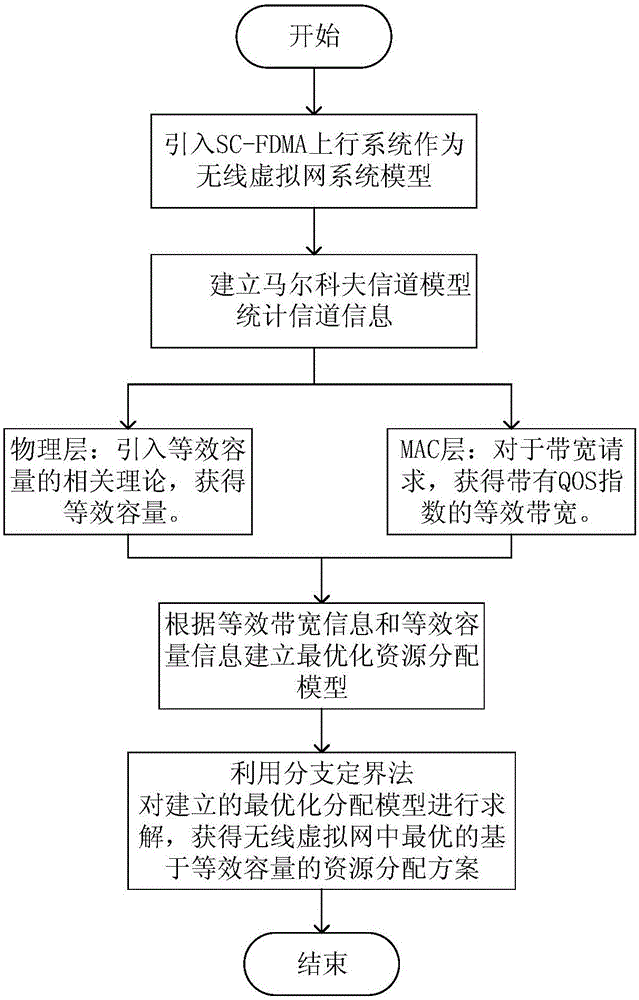
[0024] When the existing wireless virtual network allocates resources, it mainly uses theories such as Shannon capacity and queuing theory, or through iteration, the solution process is slow; or the establishment of a nonlinear large-scale model is complex and the computational complexity is too high. Aiming at this current situation, the present invention conducts research, and proposes a resource allocation method based on equivalent capacity in a wireless virtual network, see figure 1 :
[0025] (1) Introduce the SC-FDMA uplink system as a wireless virtual network system model. The system includes a physical base station and multiple users. The base station and each user are equipped with a transmitting antenna and a receiving antenna respectively. The total physical bandwidth of the base station is The resources are divided into multiple resource blocks, and each resource block is composed of several subcarriers. The subcarriers are the physical resources to be allocated i...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The resource allocation method based on equivalent capacity in the wireless virtual network is the same as in embodiment 1, and the step (2a) is divided into different state spaces according to the threshold, that is, a new wireless fading channel model is generated:
[0037] In a typical propagation channel, the received signal experiences Rayleigh fading and additive Gaussian noise, for an average signal-to-noise ratio SNRγ 0 The received signal, the received instantaneous signal-to-noise ratio SNR is distributed with the following probability density function:
[0038]
[0039] where γ 0 is the average signal-to-noise ratio of the received signal, and γ is the instantaneous signal-to-noise ratio at the sampling moment of the received signal.
[0040] According to the division formula of signal-to-noise ratio SNR gate line in Rayleigh fading channel, obtain the threshold value of each state of signal-to-noise ratio in the channel; Use Γ=[Γ 1 ,Γ 2 ,…,Γ M+1 ] T ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The resource allocation method based on equivalent capacity in the wireless virtual network is the same as in embodiment 1-2, and the statistical information of carrier resources is obtained in step (2b), specifically:
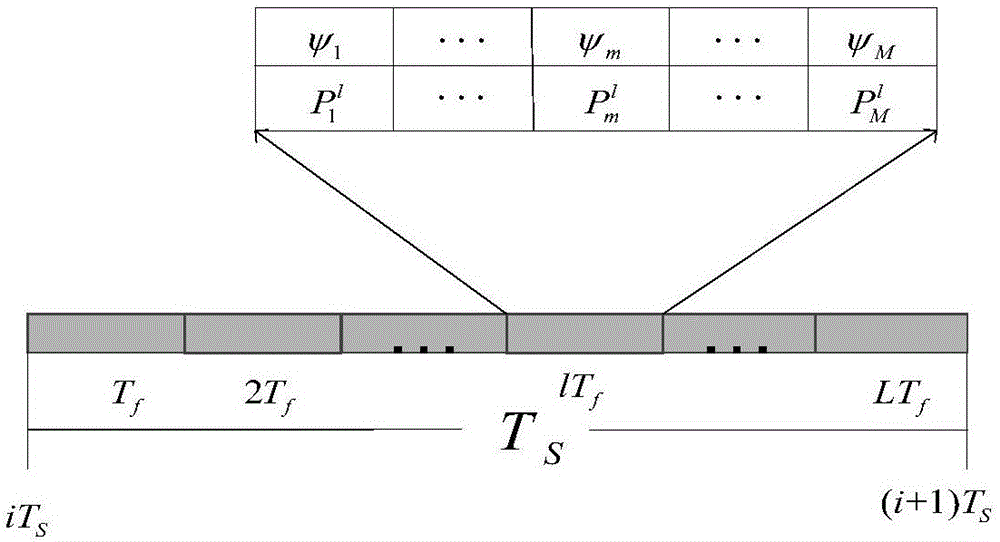
[0048] In the channel model, as shown in Figure (2), a scheduling time slot T s Consists of L frame slots, and the channel state is every time T f a change occurs; r l (i) represent the state information of the lth frame time slot in the i'th scheduling time slot; according to the division of the state space according to the present invention, the values of all data rates are in a limited state space ψ={ψ 1 ,ψ 2 ,…,ψ M}, the value of the data rate ψ m vs. Received SNR Status¶ m There is a one-to-one correspondence between the two, and the value of the data rate is expressed as ψ m =Blog 2 (1 / γ m ). Let P(ψ) represent the space of transition probabilities of all states on the table ψ, the i-th scheduling of the l-th frame P i l The probabili...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com