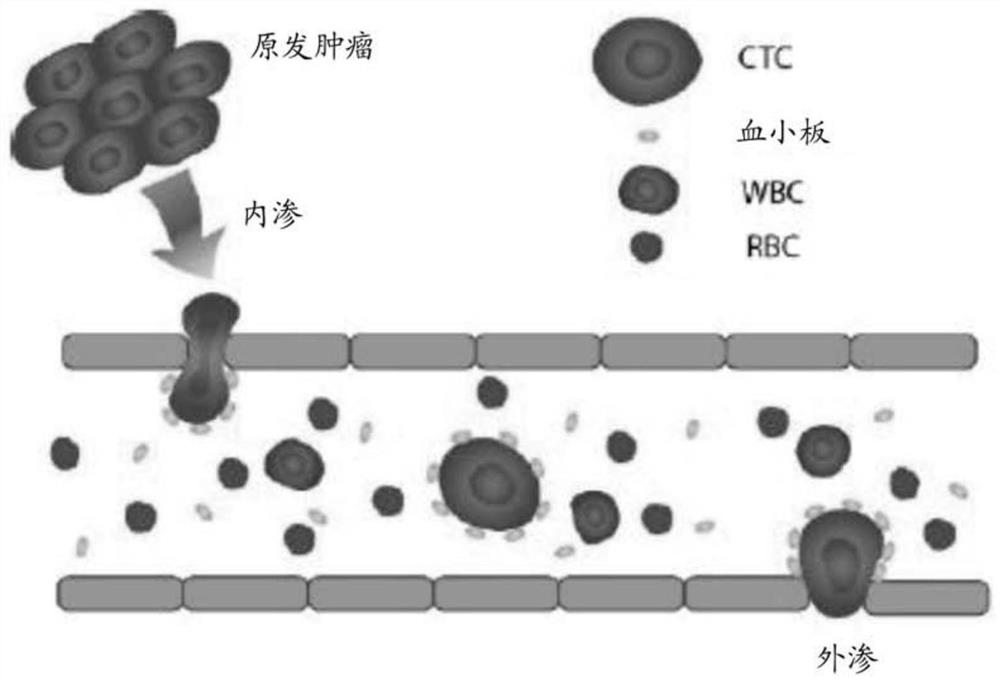
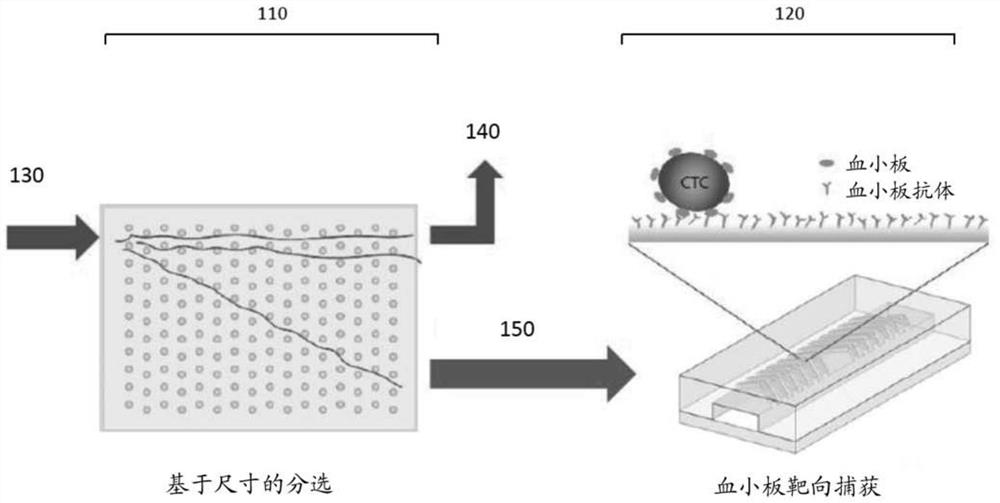
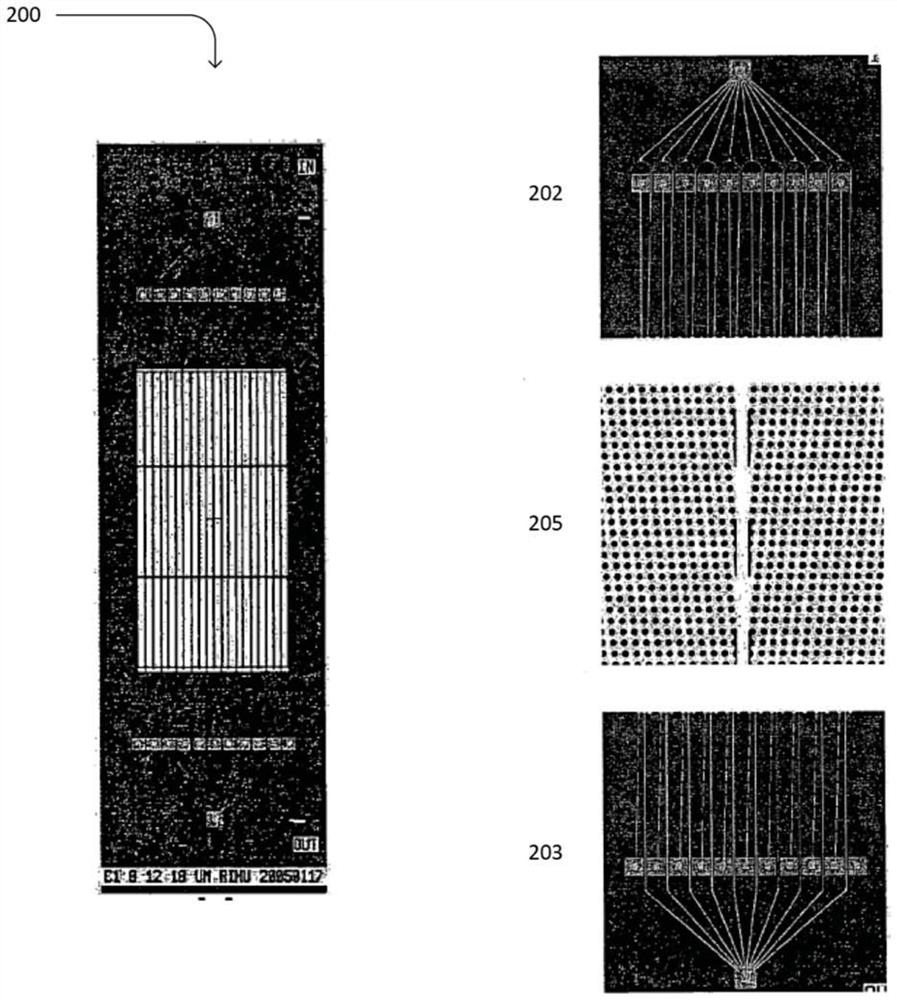
Platelet-targeted microfluidic separation of cells
A technology for fluid separation and platelets, applied in microcarriers, animal cells, fluid controllers, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Example 1—Isolation of CTCs from Clinical Samples
[0100] This method was tested to determine its efficiency in isolating CTCs from different types of cancer.
[0101] Patients with advanced lung cancer, breast cancer, and melanoma were recruited according to an institutional review board (TRB)-approved protocol. All specimens were collected in the anticoagulant EDTA (Becton-Dickinson) tubes and process them using a microfluidic chip within 4 hours of blood draw. Additional platelet inhibitors such as theophylline, adenosine, dipyridamole, argatroban, and prostaglandin I2 were added immediately after blood collection. Collect fixed blood samples directly into BCT tube (Streck).
[0102] Samples were run on the two-stage microfluidic system described above. In particular, first-stage hydrodynamic sorting chips were fabricated on silicon wafers using deep reactive ion etching. Seal the chip using an anodically bonded glass lid to form a microfluidic chamber. A...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Example 2 - Isolation of different types of cancer
[0108] The microfluidic platform was extended to isolate CTCs from different types of cancer patients with epithelial (breast) and non-epithelial (melanoma) tumor origin. Breast CTCs were identified using the same protocol as for samples from lung cancer patients, but melanoma CTCs were stained with a cocktail of antibodies targeting melanoma-specific antigens (CSPG4, MCAM, TYRP1, and α-SMA) as previously reported. Preliminary results demonstrated reliable CTC capture for both cancer types (3 out of 5 breast samples with counts ranging from 0.9 to 2.7 CTC / mL; 5 of 6 melanoma samples with counts ranging from 1.4 to 17CTC / mL). Similar to the results in lung cancer, all CTCs captured using the current method were associated with varying degrees of platelet coverage.
[0109] As discussed above, lung and breast CTCs were identified using EpCAM / cadherin-11 (green) as epithelial and mesenchymal markers, but a cocktail o...
Embodiment 3
[0111] Example 3 - Anticoagulant and CTC Purity
[0112] A key issue potentially limiting the performance of platelet-targeting approaches is the relatively low purity of CTCs compared to other techniques. A large number of contaminating WBCs (>10 5 / mL), which makes downstream analysis very challenging. Staining with a platelet-specific antibody showed that most of the captured WBCs were also coated with platelets. The formation of these so-called platelet-leukocyte aggregates (PLAs) results from spontaneous platelet activation and subsequent expression of p-selectin, which will then bind to the PSGL-1 receptor on the surface of leukocytes. PLA cannot be removed by size-based sorting, and it is captured by anti-platelet antibodies along with platelet-associated CTCs.
[0113] To reduce the contamination of WBCs and improve the purity of CTCs, we tested a variety of platelet inhibitors for blood stabilization, such as theophylline, adenosine, dipyridamole, argatroban, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com