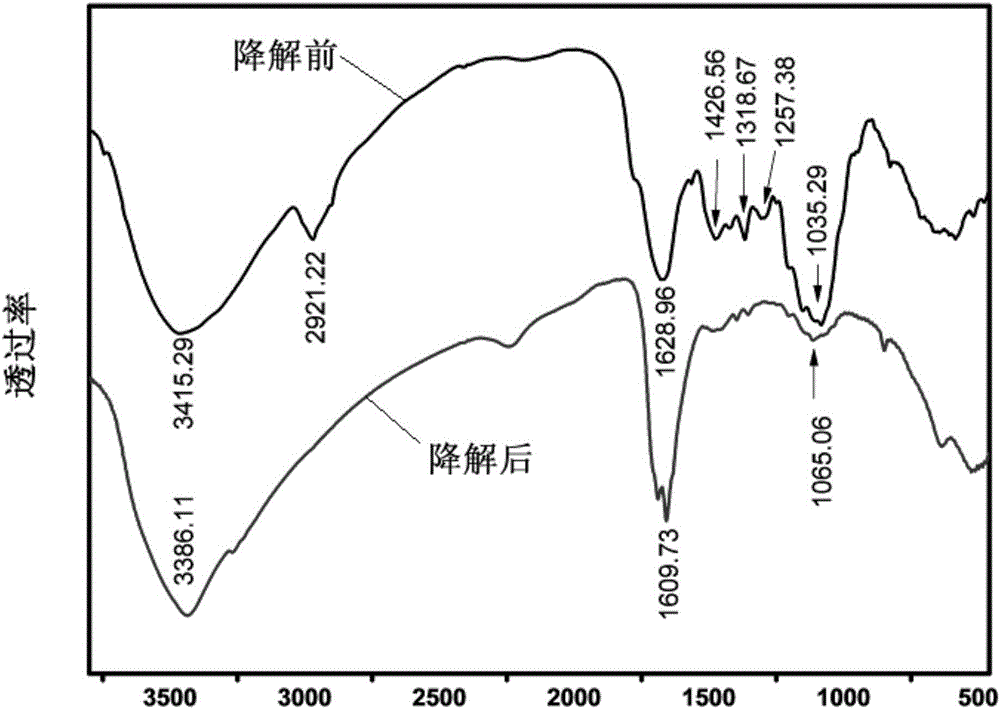
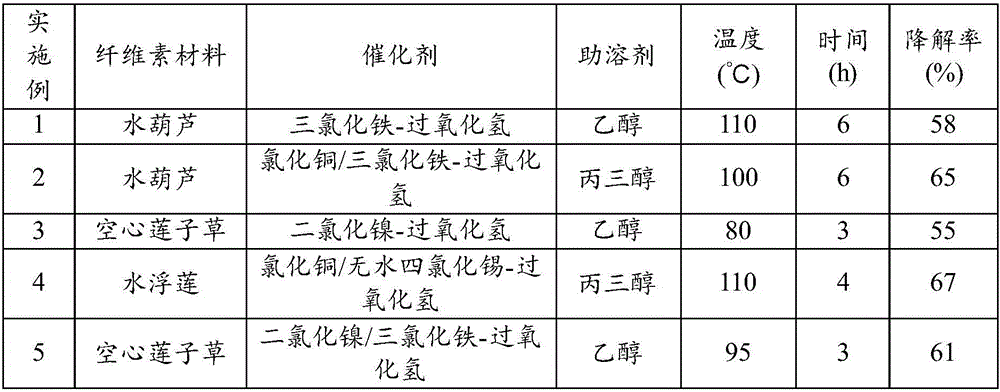
Method for degrading aquatic plants
An aquatic plant and acidic aqueous solution technology, applied in the field of waste treatment, can solve the problems of environmental pollution, waste of resources, large capital and manpower, etc., and achieve the effects of low consumption, high efficiency, low cost, and simple and quick operation steps in the preparation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] a), select fresh water hyacinth to remove impurities, dry and pulverize to make water hyacinth solid particles;
[0042] b), take 0.5mol / L hydrochloric acid aqueous solution as solvent, take 1mL30% hydrogen peroxide and 25gFeCl 3 ·6H 2 O dissolves, stirs, and makes iron trichloride-hydrogen peroxide double catalyst;
[0043] c), take 1.0g of the water hyacinth solid particles of step a) and join in the ethanol solution with a mass concentration of 2%, after mixing evenly, add the double catalyst of step b), after stirring evenly, in an oil bath at a temperature of 110°C Heating in medium temperature and continuously stirring for 6 hours, the liquid was taken and the degradation was completed.
[0044]In order to evaluate the catalytic degradation efficiency of the aquatic plants, the resulting degradation solution was filtered to separate the solid residue, which was washed twice with water and dried at 50 °C to constant weight. After washing and drying, the weight o...
Embodiment 2
[0046] a), select fresh water hyacinth to remove impurities, dry and pulverize to make water hyacinth solid particles;
[0047] b), using 1mol / L hydrochloric acid aqueous solution as solvent, take 1mL hydrogen peroxide, CuCl with a molar ratio of 1:5 2 2H 2 O and FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O dissolves, stirs, and makes cupric chloride / iron trichloride-hydrogen peroxide double catalyst;
[0048] c), take 2.0g of the water hyacinth solid particles of step a) and join in the glycerol solution whose mass concentration is 5%, after mixing evenly, add the double catalyst of step b), after stirring evenly, in a temperature of 100°C Heat in an oil bath, and continue to stir for 6 hours, and the liquid is taken to complete the degradation. The obtained solid residue was separated by filtration, washed, dried, etc., and the weight of the solid residue was weighed, and the degradation rate of the water hyacinth of this embodiment was calculated by the formula. The results are shown in Table 1.
...
Embodiment 3
[0051] a), select the fresh Herba Aculotus to remove impurities, dry and pulverize it to make solid granules of Herba Aerulea;
[0052] b), with 1.5mol / L hydrochloric acid aqueous solution as solvent, take 0.2mL hydrogen peroxide and 25gNiCl 2 ·6H 2 O dissolves, stirs, and makes nickel dichloride-hydrogen peroxide double catalyst;
[0053] c), take 0.5g of step a) and add the water plank lotus solid particles into a 5% ethanol solution, after mixing evenly, add the double catalyst of step b), after stirring evenly, in an oil bath with a temperature of 80°C Heat in the pot, and keep stirring for 3 hours, take its liquid and the degradation is completed. The obtained solid residue was separated by filtration, washed, dried, etc., and the weight of the solid residue was weighed, and the degradation rate of A. japonicus in this embodiment was calculated by the formula. The results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com