Method for inducing mesenchymal stem cells to be directionally differentiated into Leydig cells and application of method
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and directed differentiation, which is applied in the field of compositions for inducing directed differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into Leydig cells in vitro, and can solve problems such as insufficient source of seed cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
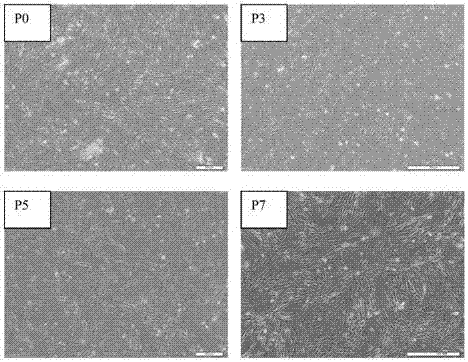
[0037] Example 1 Acquisition of Flk1+ Mesenchymal Stem Cells (Flk1+MSC) and Verification of Differentiation Ability
[0038] In order to evaluate the clinical application value of Flk1+MSCs, we firstly verified their differentiation ability.
[0039] Placental tissue was obtained from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital. Sterile placental tissue blocks were obtained after caesarean section. The collected adipose tissue was washed with D-Hanks to remove blood cells and anesthetics, repeated several times, cut into 1-2mm rice grain size with tweezers, scissors, etc., digested with 0.2% type II collagenase for 1.5-2 hours, and then washed with D-Hanks 2 times to remove collagenase. Cells were collected by centrifugation at 2 × 10 6 / ml density inoculated in 58% DMEM / F12+40% MCDB-201, 5% fetal calf serum (FCS), 10ng / ml EGF, 10ng / ml PDGF, 1 × insulin-transferrin-selenous acid ( Insulin-Transferrin-Selenium, ITS), 1×linoleic acid-bovi...
Embodiment 2
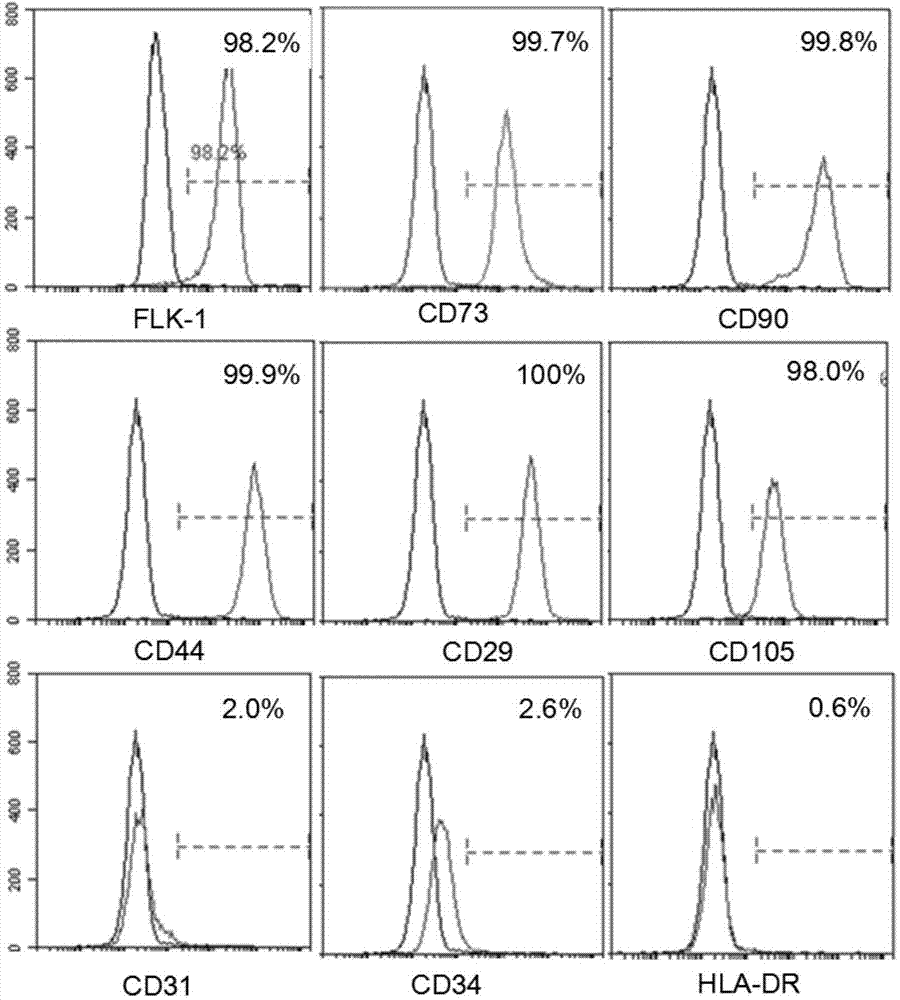
[0042] Example 2: Identification of placenta-derived Flk1+MSC immunophenotype (detection by flow cytometry)
[0043] (1) Indirect immunofluorescence staining was used for staining, and flow cytometry was used for detection. The cells in good condition of the second generation were collected and digested with 0.125% EDTA trypsin (containing 0.01% EDTA) routinely;
[0044] (2) After the cells are evenly dispersed, take a small amount of cell suspension and count, transfer the remaining cells to a centrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 1200rpm for 5 minutes;
[0045] (3) Discard the supernatant, collect the cell pellet, flick the bottom of the tube to disperse the cells, resuspend with D-hank’s, and dispense into flow tubes, about 5×105 cells per tube;
[0046] (4) Add the primary antibody and incubate at 4°C for 30 minutes. The primary antibodies were CD73, CD90, CD29, CD34, CD31, CD44, CD105, HLA-DR and Flk1 (cells were fixed with BD’s Cytofix / CytopermTM Fixation / Permeabilization...
Embodiment 3
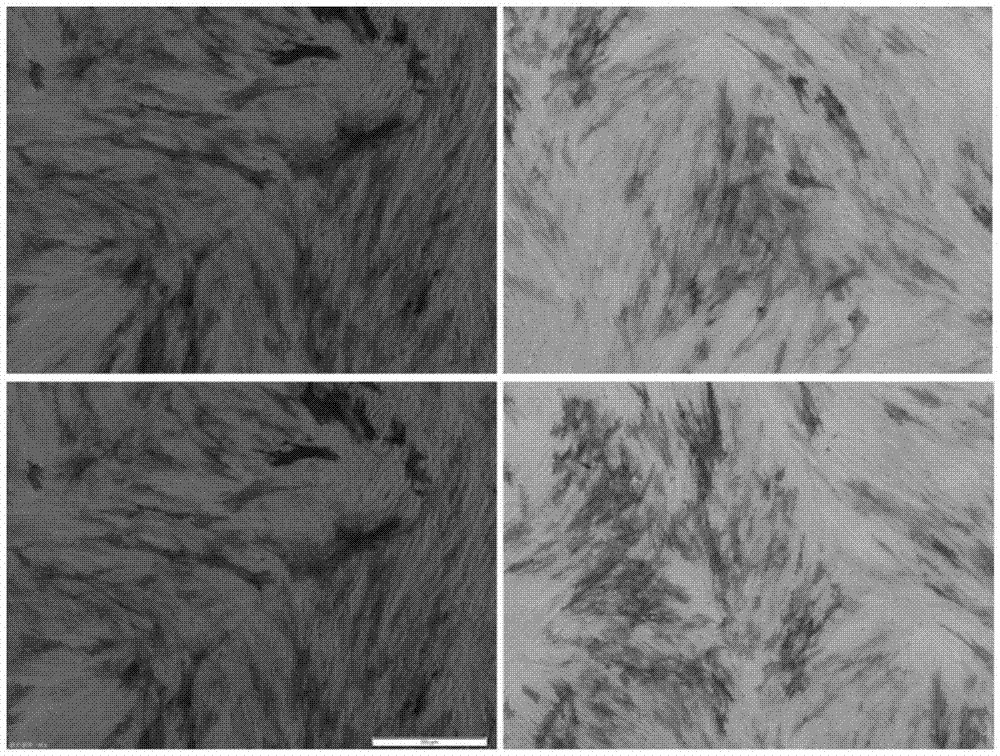
[0052] Example 3: Staining identification of placenta-derived Flk1+MSC adipogenic and osteogenic induction
[0053] Adipogenic Induction Process of Placenta-Derived MSCs
[0054] (1) Take the second-generation human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells, routinely digest and count them, and inoculate them in six-well plates or culture dishes at a density of 2×104 / cm2;
[0055] (2) Observe the growth of the cells, and when the growth reaches 80% confluence, replace the culture medium with an adipogenic induction medium to continue culturing;
[0056] (3) The culture medium was changed every three days, and the changes of cell morphology and the formation of intracellular lipid droplets were observed under an inverted microscope.
[0057] Osteogenic Induction Process of Placenta-Derived MSCs
[0058] (1) Take the second-generation human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells, routinely digest and count them, and inoculate them in six-well plates or culture dishes at a densi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com