Tabu search and artificial potential field method combined online digital micro-fluidic chip test method
A technology of artificial potential field method and digital microflow, which is applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of shortening test time, avoiding waste of resources, and shortening planning time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
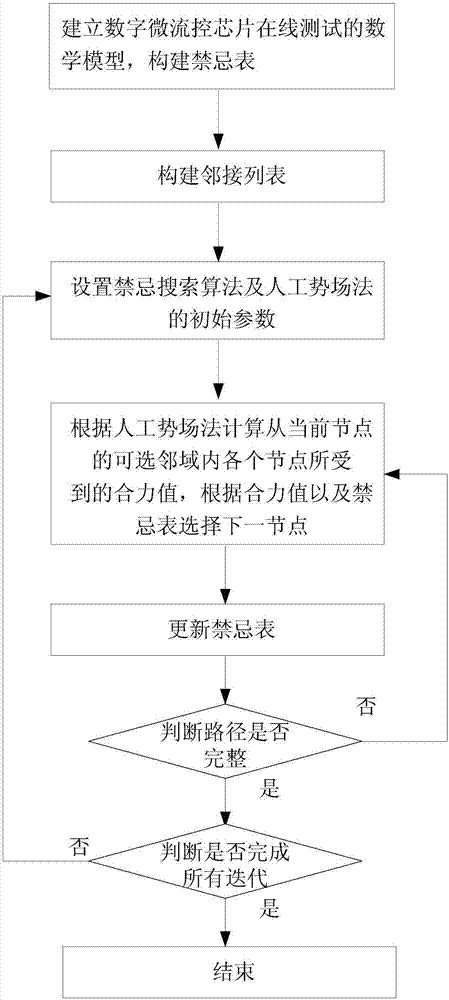
[0052] Specific Embodiment 1: This embodiment provides a digital microfluidic chip online testing method based on the combination of tabu search and artificial potential field method. The method of the present invention is used to generate the moving path of the test droplet on the digital microfluidic chip. The movement path is represented by a sequence of nodes; the nodes are used to represent the electrodes on the digital microfluidic chip;
[0053] The method of the present invention comprises the following steps;
[0054] Step 1: Establish a mathematical model for online testing of digital microfluidic chips, and construct a taboo table.
[0055] Among them, the test task can be described as:
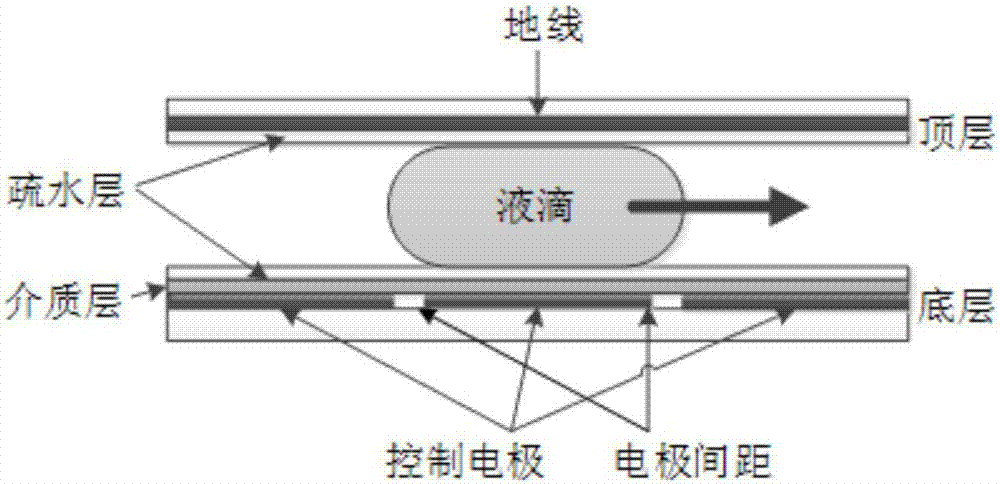
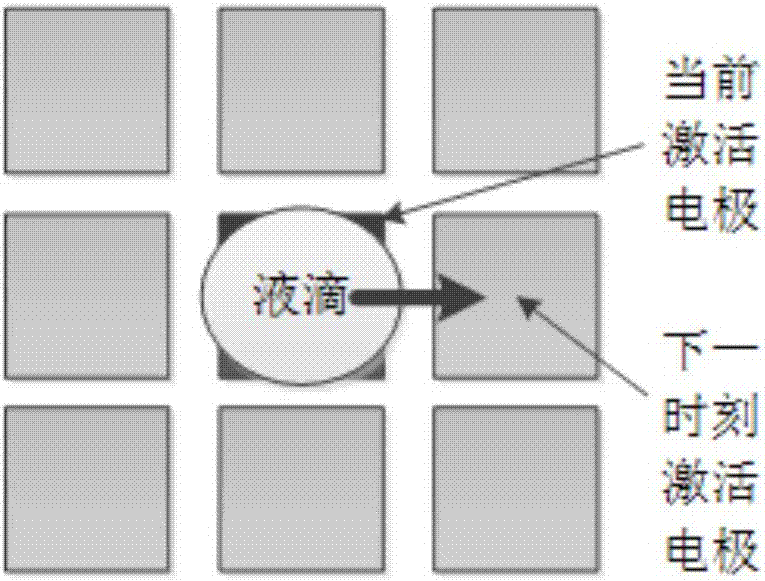
[0056] Starting from the starting point, the test droplet visits each node in the graph in turn according to a certain selection mechanism. In the process of searching the path, it is necessary to avoid the merging and interference areas of the test droplet at the corresponding ti...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0075] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is:
[0076] In step 1, the mathematical model for establishing the online test of the digital microfluidic chip is specifically as follows:
[0077] Establish a model in which the test droplet traverses all vertices and their neighborhoods, the expression is:
[0078]
[0079] Wherein, t is the moment, j is the vertex where the test droplet is located, i is the vertex where the test droplet is located, and N(i) is the neighborhood of vertex i; is the value used to record whether the test droplet moves from position i to position j at time t, if so, then The value of is 1, if not, then value of 0.
[0080] The moving path of the test droplet needs to meet the following fluid constraints:
[0081]
[0082]
[0083] Among them, MR(j, t) indicates the area where the droplets that can fuse with the droplet at position j exist at the same tim...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0088] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is:
[0089] In step 2, the head node of the adjacency list is an electrode in the digital microfluidic chip; the table node of the adjacency list is a matrix with m n rows and 4 columns, which is used to represent the four electrodes adjacent to the electrode corresponding to the head node. where m and n are the number of rows and columns of electrodes on the digital microfluidic chip, respectively.
[0090] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com